Curious minds often ponder: Does an inverter generator have a battery? It’s a question that sparks interest for those exploring the realm of portable power. Picture this – you’re camping beneath a starlit sky or working on a remote project site, and the reliability of your generator becomes paramount.
In this quest for power solutions, understanding the dynamics of an inverter generator and its potential reliance on a battery is a common inquiry. Let’s unravel the intricacies, delving into the heart of these ingenious power sources and shedding light on the role a silent powerhouse might play in providing electricity where you need it most.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 What is an Inverter Generator and How Does It Work?
- 3 What are the Basic Parts of an Inverter Generator?
- 4 Does an Inverter Generator Have a Battery?
- 5 Why Do Inverter Generators Need Battery?
- 6 How Inverter Generators Produce Energy?
- 7 Inverter Generator Vs Conventional Generator
- 8 Troubleshooting Common Inverter Generator Issues
- 9 How to Properly Store Your Inverter Generator?
- 10 Maintenance Tips for Inverter Generator’s Battery
- 11 Inverter Generator Maintenance Tips
- 12 Inverter Generator Safety Tips
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 References
- 15 Frequently Asked Questions
- 15.1 Can I Use an Inverter Generator Without a Battery?
- 15.2 How Does the Presence or Absence of a Battery Affect the Starting Mechanism of an Inverter Generator?
- 15.3 Are There Any Limitations or Drawbacks to Using an Inverter Generator With a Battery?
- 15.4 Do Inverter Generators With Batteries Require a Specific Type of Battery or Can Any Battery Be Used?
- 15.5 Can I Add a Battery to an Inverter Generator That Does Not Come With One Originally?
- 15.6 Do inverter generators have batteries?
- 15.7 How is an inverter generator powered?
- 15.8 Does an inverter come with a battery?
Key Takeaways
- Inverter generators can have a battery or be battery-free, depending on specific needs and preferences.
- Including a battery in an inverter generator offers advantages such as reliable power during startup and backup power during outages.
- Battery-free generators are more portable and potentially more affordable, while battery-equipped generators offer versatility and adaptability in various situations.
- Batteries in inverter generators enhance portability, provide backup power supply, serve as portable energy storage, and contribute to enhanced energy efficiency and quiet operation.
What is an Inverter Generator and How Does It Work?
An inverter generator is a cutting-edge power solution that stands apart from traditional generators. Unlike its counterparts, an inverter generator employs advanced electronic circuitry to convert AC power to DC and then back to a stable AC output. This process ensures a consistent and clean flow of electricity, making it especially suitable for powering sensitive electronic devices.
Here’s how an inverter generator works:
- Voltage Control Mechanism:
- Inverter generators employ advanced electronic components to control voltage fluctuations during the power generation process.
- The generator initially produces AC (Alternating Current) power.
- Transformation to DC Power:
- The AC power generated is then directed through an inverter module, where it undergoes a transformation into DC (Direct Current) power.
- Inversion Back to AC:
- The crucial step involves inverting the DC power back to AC, but with a significant difference.
- Unlike conventional generators, the inverter generator maintains a finely controlled voltage during this inversion process.
- Precision in Voltage Control:
- The inverter technology allows for precise adjustments to the voltage output, ensuring a stable and consistent flow of electricity.
- This level of precision is a stark contrast to traditional generators that may exhibit voltage fluctuations.
- Elimination of Voltage Fluctuations:
- The finely controlled voltage eliminates the fluctuations typically associated with conventional generators.
- This characteristic makes inverter generators particularly suitable for powering sensitive electronic devices, as it minimizes the risk of voltage spikes or drops.
- Reliability and Safety:
- The elimination of voltage fluctuations contributes to the overall reliability of inverter generators.
- The finely tuned voltage control enhances the safety of connected devices, reducing the likelihood of damage due to irregular power supply.
In summary, the inverter generator’s operation involves a sophisticated process of controlling voltage fluctuations, transforming AC to DC, and then finely tuning the inverted power back to AC. This precision ensures a reliable and safe power source with minimal voltage variations, making it an ideal choice for various applications.
What are the Basic Parts of an Inverter Generator?
Inverter generators play a crucial role in providing reliable and stable power, especially in remote locations or during power outages. Understanding the basic components of an inverter generator is essential for users seeking efficient and portable power solutions.
- Engine:
- The engine is the heart of an inverter generator, converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- A smaller, more fuel-efficient engine is a hallmark of inverter generators, ensuring optimal performance.
- Alternator:
- The alternator transforms mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy.
- In inverter generators, advanced alternators produce clean and stable power, vital for sensitive electronics.
- Inverter Module:
- The inverter module is a key component responsible for converting raw electrical power into a stable AC output.
- This technology allows for a consistent power supply, crucial for electronic devices and appliances.
- Voltage Regulator:
- A built-in voltage regulator maintains a steady voltage output, preventing fluctuations that can damage devices.
- This feature enhances the reliability and safety of the power supply.
- Fuel Tank:
- The fuel tank stores the necessary fuel, typically gasoline or propane, to power the generator.
- Inverter generators are known for their fuel efficiency, providing extended run times on a single tank.
- Control Panel:
- The control panel offers user-friendly access to various functions such as starting, stopping, and monitoring.
- It may include features like fuel gauge, output indicators, and power outlets.
- Muffler:
- The muffler reduces noise produced by the generator, making inverter generators quieter compared to traditional models.
- This feature is valuable for both user comfort and environmental considerations.
- Casing and Frame:
- The generator’s casing and frame provide durability and protection for internal components.
- Sturdy construction ensures the generator can withstand the rigors of transportation and outdoor use.

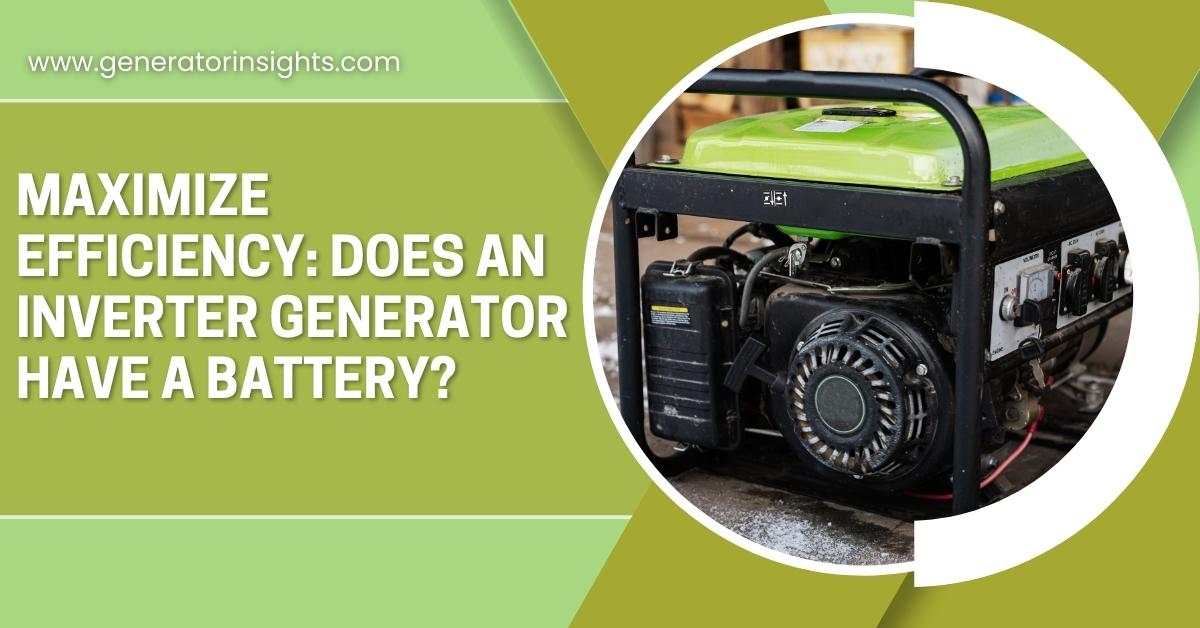
Does an Inverter Generator Have a Battery?
Inverter generators, known for their efficiency and ability to produce clean and stable power, operate on a different principle than traditional generators. Unlike conventional generators that rely on a mechanical alternator to generate AC power, inverter generators use advanced electronics to convert DC power to AC. One common question is whether an inverter generator has a battery. The answer, in most cases, is yes.
An inverter generator typically features a battery, which plays a crucial role in the startup process. The battery is responsible for initiating the initial electrical spark needed to kickstart the engine. Once the engine is running, the generator’s alternator takes over to produce electricity, and simultaneously, it charges the battery for the next startup.
This design is especially beneficial in situations where a constant power supply is essential. Having a battery allows for a quick and smooth startup, and it ensures a reliable power source even in challenging conditions. The battery in an inverter generator is usually a small, maintenance-free unit, designed to provide the necessary power for the ignition system.
For example, imagine camping in a remote location where power outlets are scarce. An inverter generator with a battery ensures that you can start the generator effortlessly, providing a reliable power source for your essential devices and appliances. The presence of a battery enhances the convenience and usability of inverter generators, making them a popular choice for various applications.
In conclusion, the inclusion of a battery in an inverter generator is a practical design choice that enhances the generator’s performance and ensures a reliable power supply in diverse situations. Whether for outdoor activities or as a backup power source at home, understanding the role of the battery in an inverter generator sheds light on their efficient and user-friendly operation.

Why Do Inverter Generators Need Battery?
Inverter generators, known for their efficiency and quiet operation, may leave some wondering why they require a battery. The answer lies in the mechanics of these modern power sources. Unlike traditional generators, inverter generators produce electricity in a two-step process. Initially, they generate AC (alternating current), which is then converted into DC (direct current). This DC power is then inverted back into AC power, but with a cleaner and more stable waveform.
The battery in an inverter generator plays a crucial role in this conversion process. It acts as a buffer, storing the generated DC power and ensuring a consistent flow of electricity, especially during fluctuations in demand. This feature allows for a more reliable and stable power output, making inverter generators suitable for sensitive electronics like laptops and smartphones.
The battery serves as a vital component, smoothing out the electrical flow and providing a reliable source of power for your various needs. So, when evaluating inverter generators, recognizing the role of the battery in ensuring a consistent and clean power output is key to understanding their overall functionality.
How Inverter Generators Produce Energy?
Let’s delve into the step-by-step process of how inverter generators generate energy:
- Variable Speed Engine:
- Inverter generators are equipped with a variable speed engine, which adjusts its speed based on the power demand. Unlike conventional generators that run at a constant speed, this feature improves fuel efficiency.
- Generation of AC Power:
- The generator starts by producing alternating current (AC) power through the initial generator mechanism. This is similar to the process in conventional generators, creating a raw AC power output.
- Conversion to DC Power:
- The raw AC power is then converted into direct current (DC) power by the inverter module. This is a crucial step that allows for precise control and stability in the generated electricity.
- Inversion to AC Power:
- The inverter takes the DC power and, as the name suggests, inverts it back to AC power. However, this AC power is not a simple replication of the initial AC power; it is a high-quality, stable form of electricity.
- Voltage Regulation:
- Inverter generators excel in voltage regulation. The inverted AC power undergoes thorough voltage regulation to ensure a consistent and clean power output. This is crucial for sensitive electronic devices.
- Pure Sine Wave Output:
- Unlike traditional generators that may produce a rough or irregular power waveform, inverter generators generate a pure sine wave output. This is a smooth, high-quality waveform that closely mimics the electricity from the grid.
- Final Power Output:
- The end result is a reliable and stable AC power output with the characteristics of a pure sine wave. This clean power is ideal for powering sensitive electronics like laptops, smartphones, and other electronic devices.
Understanding how inverter generators produce energy showcases their efficiency and suitability for a wide range of applications, from camping to powering electronic appliances during power outages.
Inverter Generator Vs Conventional Generator
When it comes to selecting a power generator, the choice often boils down to inverter generators and conventional generators. Understanding the differences between these two types can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
1. Power Generation
- Conventional Generator: Traditional generators produce AC power directly, typically at a constant speed, making them reliable for heavy-duty applications.
- Inverter Generator: Inverter generators, on the other hand, utilize advanced technology to convert AC power to DC power before inverting it back to clean, stable AC power. This results in more consistent and reliable electricity.
2. Power Output
- Conventional Generator: These generators are known for their raw power output, making them suitable for high-demand tasks. However, the electricity they produce may not be as consistent, leading to potential voltage fluctuations.
- Inverter Generator: Inverters deliver a more stable and precise power output, making them ideal for sensitive electronics like laptops and smartphones. The clean power ensures a steady flow without risking damage to your devices.
3. Fuel Efficiency
- Conventional Generator: Typically, conventional generators operate at a constant speed, irrespective of the power demand, leading to higher fuel consumption.
- Inverter Generator: Inverters adjust their speed based on the required load, resulting in greater fuel efficiency. This feature is particularly advantageous during periods of low power demand.
4. Noise Level
- Conventional Generator: Traditional generators are notorious for their noise levels, which can be a significant concern, especially in residential areas.
- Inverter Generator: Inverters are designed to be quieter, thanks to their ability to adjust the engine speed based on the power demand. This makes them more suitable for environments where noise is a consideration.
5. Portability
- Conventional Generator: Due to their larger size and weight, conventional generators are often bulkier and less portable.
- Inverter Generator: Inverters are generally more compact and lightweight, making them easy to transport. This feature is particularly valuable for outdoor activities or camping.
Thus, selecting between an inverter and a conventional generator depends on your specific needs. If you prioritize clean power for sensitive devices, fuel efficiency, and portability, an inverter generator might be the optimal choice. However, for heavy-duty power requirements where noise and portability are less critical, a conventional generator could be the more suitable option.
Troubleshooting Common Inverter Generator Issues
Inverter generators are essential for reliable power in various settings. However, users may encounter issues that hinder their performance. Understanding and troubleshooting these common problems is crucial for maintaining optimal generator functionality.
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Low Oil Level | Generator shutting down unexpectedly, abnormal engine noise. | Ensure that the oil level is within the recommended range. If low, add the appropriate oil type. Regularly check and change the oil according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. |
| 2. Spark Plug Issues | Difficulty starting, irregular engine operation. | Examine the spark plug for fouling or damage. Clean or replace it if necessary. Ensure the spark plug gap adheres to the manufacturer’s specifications. Regularly inspect and replace spark plugs based on usage and maintenance guidelines. |
| 3. Fuel System Problems | Poor engine performance, starting issues. | Confirm the fuel level and quality. Clean or replace the fuel filter regularly. Inspect the fuel lines for blockages. Ensure the fuel shut-off valve is open. Use fresh, stabilized fuel. Periodically clean the carburetor to prevent varnish buildup. |
| 4. Overloading | Generator shutting down during use, possible damage to appliances. | Check the generator’s wattage capacity and the combined wattage of connected devices. Avoid overloading by redistributing the load or disconnecting non-essential devices. Refer to the generator’s manual for the recommended load limits. |
| 5. Air Filter Clogs | Reduced power output, engine stalling. | Inspect and clean or replace the air filter regularly. A clogged filter can restrict airflow, affecting engine performance. Ensure proper seating of the air filter, and use the recommended filter type. |
| 6. Battery Issues | Electric start not working, insufficient power. | Check the battery voltage using a multimeter. Charge or replace the battery if voltage is low. Inspect and clean battery terminals. Ensure proper storage practices, such as charging the battery before extended periods of inactivity. |
| 7. Inverter Failure | Fluctuating power output, electrical anomalies. | Consult the manufacturer’s guide for inverter troubleshooting. Perform diagnostics using a multimeter. In case of malfunctions, seek professional repair services. Regularly inspect and maintain the inverter components as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. |
| 8. Engine Overheating | Generator shutting down due to overheating. | Check for obstructions around the engine and cooling system. Ensure proper ventilation. Monitor the ambient temperature and avoid running the generator in excessively hot conditions. Regularly clean the cooling fins and maintain proper oil levels. |
By addressing these common issues methodically, users can enhance the longevity and performance of their inverter generators. Regular maintenance and adherence to manufacturer guidelines play a crucial role in ensuring consistent power generation.
How to Properly Store Your Inverter Generator?
Properly storing your inverter generator is crucial for maintaining its longevity and ensuring it’s ready to power up when you need it. A well-maintained generator is more reliable and efficient, so let’s delve into the key steps to store your inverter generator effectively.
- Clean the Generator:
- Remove debris and dust from the generator’s exterior using a soft brush.
- Wipe the surface with a damp cloth to prevent any dirt from settling during storage.
- Check and Change Oil:
- Verify the oil level and change it if needed.
- Fresh oil prevents corrosion and ensures smooth operation upon startup.
- Fuel System Considerations:
- Add a fuel stabilizer to the tank to prevent the formation of varnish and gum.
- Run the generator for a few minutes to allow the stabilizer to circulate through the fuel system.
- Battery Maintenance:
- For generators with electric starters, ensure the battery is fully charged.
- Consider removing the battery for long-term storage and keep it in a cool, dry place.
- Store in a Dry Location:
- Choose a cool, dry location for storage to prevent moisture-related issues.
- Use a breathable cover to protect the generator from dust while allowing proper ventilation.
- Ventilation:
- Ensure the storage area has proper ventilation to prevent the buildup of fumes.
- Avoid storing the generator in enclosed spaces to reduce the risk of carbon monoxide accumulation.
- Regular Maintenance Schedule:
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule even during periods of inactivity.
- Periodically start the generator and let it run for a short duration to keep internal components lubricated.
- Protect from Pests:
- Place mothballs or rodent repellent around the generator to deter pests.
- Inspect the generator periodically for any signs of pest activity.
- Secure from Theft:
- Consider securing the generator with a chain or lock to prevent theft.
- Store it in a location that is not easily accessible to unauthorized individuals.
- Documentation:
- Keep all user manuals and documentation in a safe place for reference.
- Note down the last maintenance date and any specific storage instructions provided by the manufacturer.
By following these steps, you’ll ensure that your inverter generator remains in optimal condition, ready to provide reliable power whenever you need it.
Maintenance Tips for Inverter Generator’s Battery
Ensuring the longevity of your inverter generator’s battery is crucial for uninterrupted power supply. Follow these maintenance tips to keep your generator running smoothly:
- Regular Charging:
- Charge the battery regularly, especially during periods of inactivity.
- This prevents deep discharge, which can lead to a shorter battery lifespan.
- Clean Connections:
- Regularly clean the battery terminals and connections to prevent corrosion.
- Corrosion can impede the flow of electricity, affecting the generator’s performance.
- Proper Storage:
- Store the generator in a cool, dry place, away from extreme temperatures.
- Avoid exposing the battery to prolonged heat, as high temperatures can accelerate battery degradation.
- Use the Right Charger:
- Select a charger designed for your battery type to avoid overcharging or undercharging.
- Improper charging can lead to damage and a decrease in battery efficiency.
- Check Fluid Levels:
- For lead-acid batteries, ensure the electrolyte levels are within the recommended range.
- Maintaining proper fluid levels is crucial for optimal battery performance.
- Avoid Overloading:
- Do not overload the generator beyond its capacity, as this can strain the battery.
- Overloading contributes to excessive wear and can lead to premature battery failure.
- Routine Inspections:
- Inspect the battery regularly for signs of damage or wear.
- Addressing issues promptly can prevent further damage and extend the battery’s life.
Remember, following these maintenance tips not only prolongs the life of your inverter generator’s battery but also ensures reliable power when you need it most.
Inverter Generator Maintenance Tips
Ensure optimal performance and longevity of your inverter generator with these essential maintenance tips.
- Scheduled Oil Changes:
- Regularly change the oil as recommended by the manufacturer to maintain proper lubrication and extend the generator’s lifespan.
- Air Filter Inspection:
- Check the air filter routinely, cleaning or replacing it when needed, to prevent engine damage caused by dirt and debris.
- Spark Plug Care:
- Inspect and clean or replace the spark plug regularly to ensure efficient fuel combustion and prevent starting issues.
- Fuel System Maintenance:
- Stabilize the fuel when storing the generator for prolonged periods to prevent varnish buildup in the carburetor and fuel system.
- Battery Check:
- If your generator has a battery, check it for corrosion and maintain a full charge to ensure reliable starts during operation.
- Exhaust System Examination:
- Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks or blockages to maintain optimal engine performance and ensure safe operation.
- Cooling System Inspection:
- Check the cooling system, ensuring the radiator and cooling fins are clean to prevent overheating issues during prolonged use.
- Tighten Loose Parts:
- Regularly inspect and tighten loose nuts, bolts, and screws to prevent vibration-related damage and ensure overall stability.
- Run the Generator Regularly:
- Even if not in use, run the generator periodically to prevent fuel system issues and keep internal components lubricated.
- Store Properly:
- When storing the generator, keep it in a cool, dry place to prevent rust and corrosion, and use a cover to shield it from the elements.
Remember, a well-maintained inverter generator not only ensures reliable power but also extends its lifespan, saving you from costly repairs.
Inverter Generator Safety Tips
When it comes to operating inverter generators, prioritizing safety is paramount. Follow these essential tips to ensure a secure environment while harnessing the power of your generator:
- Positioning Matters:
- Optimal Placement: Place the inverter generator at least 20 feet away from your living or work area to prevent carbon monoxide exposure.
- Ventilation Awareness: Keep the generator in an open space with ample ventilation to dissipate exhaust gases effectively.
- Fueling Caution:
- No-Spill Rule: Refuel the generator only when it’s turned off to minimize the risk of spills.
- Use Fresh Fuel: Utilize fresh, stabilized fuel to maintain the generator’s efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Electrical Connection Safety:
- Proper Grounding: Ensure the generator is grounded correctly to avoid electrical hazards.
- Responsible Use of Extension Cords: Use heavy-duty, grounded extension cords designed for outdoor use to connect appliances.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Scheduled Checks: Perform regular checks on oil levels, air filters, and spark plugs to keep the generator in top condition.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Adhere to the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines for optimal performance.
- Emergency Shutdown Protocol:
- Immediate Response: Familiarize yourself with the emergency shutdown procedure to swiftly turn off the generator in case of any issues.
- Safety First: Prioritize your safety and that of others in case of emergencies.
By adhering to these inverter generator safety tips, you not only safeguard yourself and others but also extend the lifespan of your valuable equipment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of a battery in an inverter generator is indeed a linchpin for its functionality. As we’ve delved into the intricacies of Does an inverter generator have a battery, it’s evident that this integral component acts as a stabilizing force, guaranteeing a consistent power supply even in fluctuating conditions.
So, whether you’re planning outdoor adventures or safeguarding your home against unforeseen outages, recognizing the symbiotic relationship between an inverter generator and its battery proves pivotal for a reliable power source.
References
- Biomechanical energy‐driven hybridized generator as a universal portable power source for smart/wearable electronics
- Portable fuel cell power generator
- A thermophotovoltaic micro-generator for portable power applications
- Fuel cells-the clean and efficient power generators
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Use an Inverter Generator Without a Battery?
Using an inverter generator without a battery is possible, but not recommended. Incorporating a battery offers several advantages, including increased portability, uninterrupted power supply, and improved efficiency in managing power fluctuations.
How Does the Presence or Absence of a Battery Affect the Starting Mechanism of an Inverter Generator?
The presence or absence of a battery in an inverter generator can have a significant impact on the starting mechanism and overall performance. A battery-powered starting mechanism provides convenience and reliability, while the absence of a battery may require alternative methods for starting the generator.
Are There Any Limitations or Drawbacks to Using an Inverter Generator With a Battery?
Using a battery with an inverter generator can provide certain advantages, such as backup power during outages. However, there are limitations and drawbacks to consider, including the added cost, maintenance requirements, and potential limitations on the generator’s power output.
Do Inverter Generators With Batteries Require a Specific Type of Battery or Can Any Battery Be Used?
Battery compatibility is essential for optimal performance in inverter generators. While some models may be compatible with various battery types, using a specific battery type recommended by the manufacturer can offer advantages such as longer run times and improved efficiency.
Can I Add a Battery to an Inverter Generator That Does Not Come With One Originally?
Adding a battery to an inverter generator that does not come with one originally can provide several benefits. It allows for portable power storage, smoother power output, and increased fuel efficiency.
Do inverter generators have batteries?
An inverter generator operates by converting DC power into AC, providing a stable electric signal. Unlike traditional generators, it doesn’t have an internal combustion system. Instead, it draws power from a separate battery that charges through electricity.
How is an inverter generator powered?
It converts AC current to DC, then inverts it back to AC, resulting in a cleaner electricity waveform. For those unfamiliar with AC and DC power distinctions, additional information can be found in an article about electrical phases.
Does an inverter come with a battery?
No, an inverter itself is a conversion unit and does not include a battery. Users need to purchase a battery separately and connect it to the inverter for proper functionality.