In a world where power is paramount, understanding how does a generator work becomes more than a technical curiosity—it’s an empowerment tool. Picture this: a seamless flow of electricity, not just a buzz of wires and circuits. Generators, the unsung heroes behind the scenes, quietly transform potential into power, offering a lifeline during outages or in remote locations.
Delving into their inner workings reveals a symphony of components working in harmony, translating fuel or other energy sources into the lifeblood of our modern lives. Join us on a journey through the heartbeat of generators, unlocking the mystery that keeps our lights on.
Core Lessons
- Generators use a combination of electric motor and alternator to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- They come in various sizes and types including standby, portable, and solar-powered, and can produce DC electricity and convert it into AC power.
- Generators provide backup power during emergencies, supplement existing electricity generation systems, and can recharge batteries for electric vehicles and electronics.
- Proper safety precautions must be taken when using generators, but they are a reliable source of energy and invaluable for those who want extra peace of mind. Understanding how they work can help make informed decisions about energy needs.
What is a Generator?
A generator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It’s quite efficient, capable of running on almost any fuel source to generate electricity for homes or businesses in the event of a power outage or during times when the demand for electricity is higher than usual. Generators are also used to provide portable power sources for recreational activities like camping and events.
Generators work by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy through the use of an electric motor and alternator combination. The electric motor draws its power from a fuel source, such as gasoline, diesel, natural gas, propane, or even solar, and turns it into rotational motion.
This motion is then transferred to the alternator which uses magnets to create alternating current (AC) electricity. The AC current can be converted into direct current (DC) electricity with the help of rectifiers before being sent to different appliances or electronics in need of power.
Generators come in all shapes and sizes depending on their intended use. Some generators are designed specifically for home use while others may be large enough for commercial applications such as powering entire buildings or providing backup power during emergencies.
All types have become increasingly more efficient over time due to advances in technology resulting in increased energy efficiency and fewer emissions from fuel sources. With this knowledge about how they work, it’s easy to see why generators are so useful! Moving forward we will take a closer look at how these incredible machines actually operate.

How Electricity is Generated?
Electricity is a fundamental aspect of modern life, powering our homes, industries, and technological devices. The process of generating electricity is a fascinating journey that involves converting various forms of energy into the electrical energy we use daily.
At its core, the generation of electricity is often based on the principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday in the 19th century. This principle states that a change in magnetic field within a closed loop of wire induces an electromotive force (EMF), or voltage, in the wire.
One of the primary methods of electricity generation involves using a generator. In a generator, a coil of wire is rotated within a magnetic field, creating a flow of electricity. This mechanical energy can be sourced from various means, such as burning fossil fuels, harnessing the power of flowing water, utilizing wind energy, or capturing sunlight through solar panels.
Power plants are essential players in the large-scale generation of electricity. Fossil fuel power plants burn coal, oil, or natural gas to produce steam that drives turbines connected to generators. Hydroelectric power plants use the kinetic energy of flowing water to turn turbines, converting this mechanical energy into electricity. Similarly, wind turbines transform the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical power.
In the case of solar power, photovoltaic cells in solar panels convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This process involves the release of electrons from atoms in the solar cells, creating an electric current.
In recent years, advancements in technology have also brought about innovative methods of electricity generation, such as geothermal power and tidal energy. Geothermal power plants tap into the Earth’s internal heat, while tidal energy harnesses the gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth’s oceans.
In essence, the generation of electricity is a diverse and intricate process that draws on various sources of energy, each with its unique set of advantages and challenges. As we continue to explore sustainable and efficient methods of electricity generation, the quest for cleaner and more renewable energy sources remains a driving force in shaping the future of our power systems.
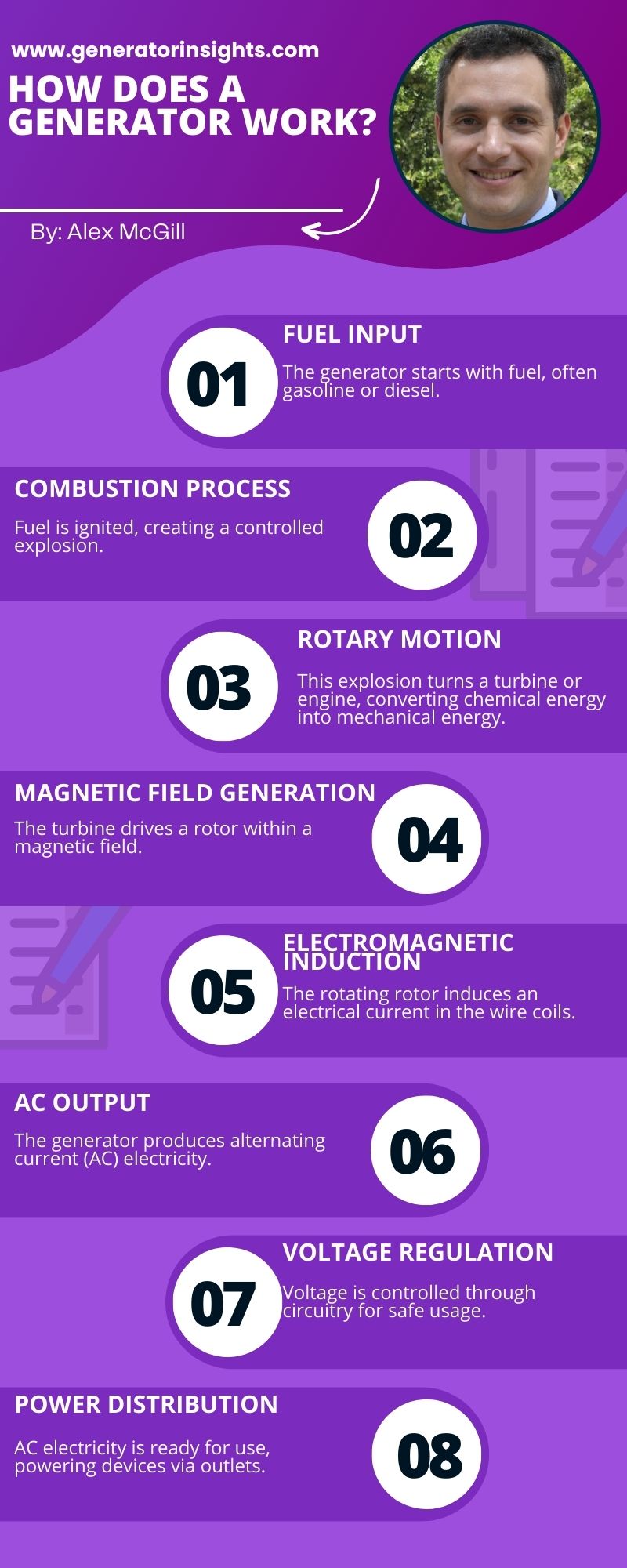
How Does a Generator Work?
Generators are intricate machines designed to provide electrical power in times of need. The step-by-step process of how a generator operates involves various components working in harmony to convert mechanical energy into electrical power.
1. Fuel Combustion:
The process begins with the combustion of fuel in the generator’s engine. Whether it’s gasoline, diesel, natural gas, or propane, the fuel undergoes controlled combustion within the engine.
2. Mechanical Energy Generation:
The combustion of fuel produces a high-pressure and high-temperature gas. This expanding gas is harnessed to turn the generator’s engine, converting chemical energy from the fuel into mechanical energy.
3. Alternator Action:
Connected to the engine is an alternator, a key component in the process. As the engine turns the alternator, it induces a flow of electricity within the generator’s windings through the principle of electromagnetic induction.
4. Voltage Generation:
The electromagnetic induction creates an alternating current (AC) in the generator’s windings. This alternating current is then converted into a usable electrical voltage, typically at 120 or 240 volts, depending on the application.
5. Voltage Regulation:
To ensure a consistent and stable electrical output, generators are equipped with voltage regulators. These regulators adjust the electrical output to meet the required voltage levels, preventing fluctuations that could damage connected devices.
6. Control Panel Operation:
The generator’s control panel plays a crucial role in the operation. It allows users to start or stop the generator and often includes features for monitoring and controlling output parameters.
7. Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS):
In standby generators, an automatic transfer switch (ATS) monitors the electrical supply. If a power outage is detected, the ATS activates the generator, ensuring a seamless transition from the main power source to the backup generator.
What are Different Parts of a Generator?
Understanding the various components of a generator is crucial for both maintenance and troubleshooting. A generator is a complex machine composed of several parts working together to produce electrical power. Let’s explore the different components that make up a typical generator.
- Engine: The heart of the generator, the engine is responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Alternator: Also known as the generator head, it transforms the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy.
- Fuel System: Includes the fuel tank, fuel pump, and fuel lines, ensuring a steady supply of fuel to the engine.
- Voltage Regulator: Maintains a consistent voltage output for stable electrical power.
- Battery Charger: Charges the generator’s battery, ensuring it’s ready to start when needed.
- Control Panel: Houses the various controls, switches, and meters for monitoring and operating the generator.
- Cooling System: Prevents the generator from overheating during prolonged use, typically using a radiator and cooling fan.
- Exhaust System: Guides and expels the exhaust gases produced during the combustion process.
- Base Frame and Enclosure: Provides structural support and protection, minimizing noise and shielding the generator from environmental elements.
Understanding these key components empowers users to maintain their generators effectively and troubleshoot issues when they arise.
What are Different Types of Generators?
Generators are essential devices that provide backup power in various situations. They come in different types, each designed for specific applications and fuel sources. Understanding the different types of generators is crucial for selecting the right one to meet your power needs. Below is a table outlining the key characteristics of various generator types:
| Generator Type | Description | Fuel Type | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portable Generators | Compact and mobile, suitable for temporary power needs. | Gasoline, Propane | Camping, Construction Sites, Home Backup |
| Standby Generators | Permanent fixtures designed for automatic backup power. | Natural Gas, Propane, Diesel | Homes, Businesses, Hospitals |
| Inverter Generators | Produce clean and stable power, ideal for sensitive electronics. | Gasoline | Camping, RVs, Tailgating |
| Diesel Generators | Known for fuel efficiency and durability. | Diesel | Industrial Settings, Construction Sites |
| Solar Generators | Harness solar energy for eco-friendly power generation. | Solar Panels | Camping, Outdoor Events, Emergency Power |
Understanding the distinctions between these generator types allows you to make an informed decision based on your specific needs and circumstances.
How to Use a Generator?
In times of power outages or outdoor activities, a generator can be your reliable source of electricity. Knowing how to use a generator properly ensures a seamless and efficient power supply. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process.
1. Read the Manual: Before diving into generator operation, familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s instructions outlined in the manual. Each generator model may have specific features and requirements, and understanding these details is crucial for safe and effective use.
2. Choose a Suitable Location: Place the generator on a flat, stable surface in a well-ventilated area. Keep it away from enclosed spaces to prevent carbon monoxide buildup. Ensure there’s ample space around the generator for proper ventilation and maintenance.
3. Fueling the Generator: Depending on the fuel type (such as gasoline, propane, or diesel), follow the recommended fueling procedures. Take precautions to avoid spills and use appropriate containers for fuel storage.
4. Start-Up Procedure: Turn the generator’s fuel valve on, set the choke (if applicable), and turn the engine switch to the “on” position. Pull the starter cord or use the electric starter, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Once started, allow the generator to run for a few minutes to stabilize.
5. Connect Appliances: Using extension cords, connect your essential appliances directly to the generator’s outlets. Prioritize power needs and avoid overloading the generator beyond its rated capacity, as this can lead to damage or malfunction.
6. Monitor the Generator: Keep an eye on the generator’s status, including fuel levels, oil levels, and any warning lights or indicators. Regularly check for signs of wear and tear, and perform maintenance tasks as recommended in the manual.
7. Shut Down Safely: When you’re finished using the generator, turn off and unplug all connected appliances. Allow the generator to run without a load for a few minutes to cool down, then turn the engine switch to the “off” position. Close the fuel valve to prevent fuel leaks during storage.
By following these guidelines, you can use your generator efficiently, ensuring a stable power supply when needed. Always prioritize safety and adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal performance and longevity.
Common Applications of a Generator
Generators play a pivotal role in various settings, providing reliable power when conventional sources fail. Below are common applications of generators:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Residential Backup Power | Ensures uninterrupted power supply during outages, safeguarding essential appliances and maintaining comfort. |
| Commercial and Industrial Use | Powers critical equipment, machinery, and lighting in businesses, factories, and construction sites. |
| Emergency Services and Healthcare | Vital for hospitals, emergency shelters, and first responders, ensuring continuous power for life-saving operations. |
| Outdoor Events and Entertainment | Provides electricity for concerts, festivals, and outdoor events, supporting lighting, sound systems, and vendors. |
| Construction and Remote Sites | Essential for powering tools and equipment at construction sites and remote locations without access to the grid. |
| Recreational Vehicles (RVs) | Enables independent power supply for RVs, allowing for a comfortable living experience while on the road. |
Generators offer versatile solutions across various sectors, contributing to safety, productivity, and convenience in diverse scenarios.
Safety Tips When Using a Generator
Generators are indispensable during power outages, but ensuring safety is paramount when operating them. Here are essential safety tips to keep in mind:
- Location and Ventilation:
- Place the generator outdoors: Always operate the generator in a well-ventilated area, away from doors, windows, and vents to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
- Maintain clear spaces: Ensure there’s ample space around the generator for proper airflow and cooling.
- Fuel Handling:
- Use the correct fuel: Only use the type of fuel recommended by the manufacturer for your generator.
- Store fuel safely: Keep fuel in approved containers, away from living spaces, and never store it near the generator while it’s running.
- Electrical Precautions:
- Avoid backfeeding: Never plug a generator directly into a wall outlet (backfeeding), as it poses a severe risk to utility workers.
- Use a transfer switch: Install a transfer switch to safely connect the generator to your home’s electrical system.
- Generator Operation:
- Read the manual: Familiarize yourself with the generator’s manual, understanding its features, maintenance requirements, and safety instructions.
- Regular maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule to ensure the generator operates smoothly.
- Cord and Connection Safety:
- Use heavy-duty extension cords: Connect appliances directly to the generator using heavy-duty extension cords designed for outdoor use.
- Inspect cords regularly: Check for frays, cuts, or damage in cords to prevent electrical hazards.
- Grounding:
- Follow grounding instructions: Ensure the generator is properly grounded according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to prevent electrical shock.
- Turn Off Before Refueling:
- Allow cooling time: Turn off the generator and let it cool down before refueling to prevent accidents.
Remember, prioritizing safety is crucial when using a generator. Following these tips will help ensure a secure and reliable power source during outages.
Conclusion
You now know how does a generator work and the different types that are available. Generators can be used in a variety of ways and it’s important to take the necessary safety precautions when using one. Whether you’re powering up your home or running a construction site, generators provide dependable power when you need it most.
Be sure to choose the right size for your application and always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use. With these tips, you can make sure your generator is working safely and efficiently every time!
References
- Study of the impact of operation distance of outdoor portable generators under different weather conditions
- Noise control of engine driven portable generator set
- Experiment assessment of hydrogen production from activated aluminum alloys in portable generator for fuel cell applications
- Optimal design of an enclosure for a portable generator

