In the dance of modern living, where electricity reigns supreme, the humble portable generator emerges as a silent hero, ready to cast away the shadows of blackouts. Ever wondered, amidst flickering lights, How do portable generators work for a house?
Picture this: a seamless transition from darkness to illumination, a heartbeat that keeps essential appliances alive during power outages. These trusty companions aren’t just machines; they’re the guardians of convenience, whispering assurance to families in the face of electrical uncertainty. Join us on a journey to unravel the magic behind these power-packed companions, as we demystify the synergy between homes and portable generators.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Key Points
- 2 How Do Portable Generators Work for a House?
- 3 Different Types of Portable Generators
- 4 Key Components and Parts of a Portable Generator
- 5 How Does a Portable Home Generator Work?
- 6 How to Properly Set Up and Install a Portable Generator?
- 7 How Long Does it Take for a Generator to Start Working?
- 8 Can You use a Portable Generator to Power a Whole House?
- 9 Safety Tips for Using a Portable Generator at Home
- 10 Maintenance and Care for Portable Generators
- 11 Troubleshooting Common Issues With Portable Generators
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 References
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions
- 14.1 Can a Portable Generator Be Used Indoors?
- 14.2 How Much Noise Does a Portable Generator Make?
- 14.3 Can a Portable Generator Power the Entire House?
- 14.4 Is It Safe to Connect a Portable Generator Directly to the Electrical Panel?
- 14.5 Can a Portable Generator Be Used During Extreme Weather Conditions?
- 14.6 How do I hook up a portable generator to my house?
- 14.7 Can a portable generator power a whole house?
- 14.8 What are the disadvantages of a portable generator?
Key Points
- There are different types of portable generators for home use, including gasoline-powered, propane-powered, and diesel-powered generators, with different brands available for comparison.
- Power output and wattage are important factors to consider when selecting a portable generator, as it determines the rate of electrical energy generation or consumption and helps in calculating power requirements for appliances.
- The key components and parts of a portable generator include the engine, alternator, fuel tank, control panel, and exhaust system.
- Portable generators can run on different fuel options, such as gasoline and propane, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of energy density, availability, combustion cleanliness, shelf life, and carbon emissions.
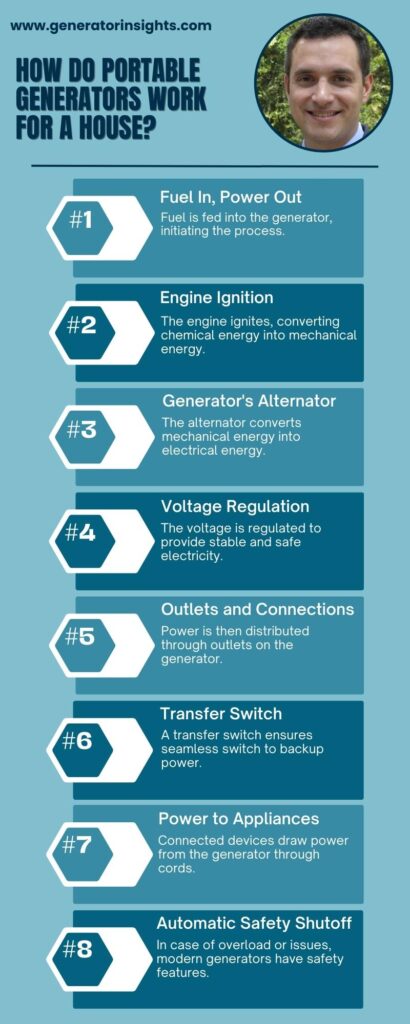
How Do Portable Generators Work for a House?
Portable generators play a crucial role in providing backup power to households during outages. Understanding how these generators work ensures effective utilization when needed.
- Internal Combustion Engine: Portable generators typically operate on an internal combustion engine, fueled by sources like gasoline, propane, or diesel.
- Generator Alternator: The engine drives a generator alternator, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Voltage Regulation: The generator alternator produces an alternating current (AC), which is then regulated to ensure a consistent and safe voltage level for household appliances.
- Power Outlets: Portable generators are equipped with power outlets, allowing users to plug in appliances directly. Some models may also have USB ports for charging smaller devices.
- Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR): Higher-end portable generators often feature an Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR) to maintain a stable voltage output, crucial for sensitive electronics.
- Fuel Supply: The generator’s runtime depends on the available fuel supply. Gasoline-powered generators have a limited runtime based on the fuel tank’s capacity, while propane and diesel generators may provide longer operation with larger fuel tanks.
- Example: Consider a scenario where a household experiences a power outage. A portable generator with a gasoline engine is started, activating the internal combustion engine. As the engine runs, it turns the generator alternator, producing electrical energy that is then regulated and made accessible through power outlets. The generator continues to operate until the fuel supply is depleted.
Understanding the intricacies of how portable generators work empowers homeowners to make informed decisions, ensuring a reliable source of backup power when needed.
Different Types of Portable Generators
One aspect to consider when discussing portable generators for home use is the different types available on the market. These types vary in terms of fuel source, power output, and portability.
Portable generators come in various types, each catering to specific needs and preferences. Understanding the distinctions between different types of generators can help you make an informed decision.
| Generator Type | Description | Key Features | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Inverter Generators | Inverter generators produce clean and stable power by converting AC to DC and then back to AC. They are compact, lightweight, and fuel-efficient, making them ideal for sensitive electronics. | – Quiet operation – Fuel efficiency – Parallel capability | Honda EU2200i |
| 2. Conventional Generators | Conventional or standard generators produce power directly without the need for inversion. They are affordable and reliable but may have fluctuations in power output. | – Cost-effective – Durable – Suitable for heavy-duty applications | DuroMax XP12000EH |
| 3. Portable Dual-Fuel Generators | These generators offer the flexibility of running on either gasoline or propane. They are versatile and suitable for various fuel availability scenarios. | – Dual fuel options – Fuel efficiency – Long runtime | Champion Power Equipment 76533 |
| 4. Solar Generators | Solar generators harness energy from the sun using solar panels. They are silent, environmentally friendly, and require minimal maintenance. | – Clean energy source – Quiet operation – Low maintenance | Goal Zero Yeti 500X |
| 5. Emergency Backup Generators | Designed for standby power during outages, these generators are installed permanently and connected to the electrical system. They automatically start when power is lost. | – Automatic operation – Seamless transition – Permanent installation | Generac Guardian Series |
| 6. RV Generators | Specifically designed for recreational vehicles, these generators are compact and built for mobile use. They are ideal for powering appliances and electronics in RVs. | – Compact design – RV-ready features – Quiet operation | Champion 3400-Watt Dual Fuel RV Ready Portable Inverter Generator |
| 7. Gasoline Generators | Gasoline generators are common and widely available. They are easy to refuel, portable, and suitable for various applications. | – Widely available fuel – Portable – Cost-effective | WEN 56203i |
| 8. Diesel Generators | Diesel generators are known for their fuel efficiency and durability. They are often used in industrial settings and for heavy-duty power needs. | – Fuel efficiency – Long lifespan – Well-suited for high-demand applications | DuroStar DS7000Q |
| 9. Propane Generators | Propane generators are clean-burning and provide a stable fuel source. They are suitable for situations where propane is readily available. | – Clean-burning fuel – Efficient combustion – Long shelf life of propane | Westinghouse WGen3600DF |
| 10. Natural Gas Generators | Natural gas generators are connected directly to a natural gas line. They provide a continuous power supply as long as the gas line remains active. | – Continuous fuel supply – Low emissions – Suitable for long-duration use | Kohler 20RESCL-200SELS |
Selecting the right portable generator, considering the fuel type, depends on your specific requirements, fuel availability, and the intended application. Whether you prioritize fuel efficiency, environmental impact, or ease of use, there’s a portable generator tailored to meet your needs.

Key Components and Parts of a Portable Generator
Portable generators are versatile power sources, ideal for various applications from camping trips to emergency backup at home. Understanding the key components and parts of a portable generator is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Engine: The heart of the generator, responsible for converting fuel (gasoline, propane, or diesel) into mechanical energy to drive the generator’s alternator.
- Alternator (Generator Head): Converts the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy, producing the power output for your devices.
- Fuel Tank: Stores the generator’s fuel supply, and the size determines the generator’s runtime. Common fuels include gasoline, propane, and diesel.
- Control Panel: Houses the generator’s controls and outlets. It includes features like the start/stop switch, circuit breakers, and power outlets for connecting devices.
- Voltage Regulator: Maintains a stable output voltage, ensuring the connected devices receive consistent power to prevent damage.
- Spark Arrestor: A safety feature in the exhaust system that prevents sparks from exiting the exhaust and reduces the risk of fire, particularly important in outdoor settings.
- Air Filter: Filters the air entering the engine, preventing dust and debris from causing damage. Regular cleaning or replacement is crucial for optimal performance.
- Oil Fill and Dipstick: Portable generators require oil to lubricate the engine. The oil fill allows you to replenish oil, and the dipstick indicates the oil level.
- Muffler: Reduces noise produced by the exhaust gases, making the generator operation quieter.
- Wheels and Handles: Found on larger portable generators, these components enhance mobility, making it easier to transport the generator to different locations.
- Hour Meter: Tracks the number of hours the generator has been in operation. Useful for scheduling maintenance tasks and understanding overall usage.
Example: For instance, a popular portable generator like the Honda EU2200i features a fuel-efficient engine, inverter technology in the alternator for clean power output, a user-friendly control panel, and an eco-throttle system for fuel efficiency and reduced noise. Understanding these components ensures efficient and safe use of the generator.
How Does a Portable Home Generator Work?
Portable home generators are essential backup power solutions, ensuring uninterrupted electricity during outages. These versatile devices operate on the principle of converting stored fuel into electrical energy.
Typically powered by gasoline, propane, or diesel, portable generators utilize an internal combustion engine to drive an alternator, which produces electrical power. The process begins by starting the generator, which activates the engine. As the engine runs, it spins the alternator, generating an alternating current (AC).
This raw electricity then passes through a series of components, including a voltage regulator to maintain a steady output. The AC is then converted into direct current (DC) and back into AC through an inverter if the generator is equipped with one. The final output is a stable AC power supply that can be used to run various appliances and devices.
How to Properly Set Up and Install a Portable Generator?
Setting up and installing a portable generator requires careful consideration to ensure a safe and efficient power source during emergencies or outdoor activities. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you through the process.
1. Choose the Right Location:
- Select a well-ventilated area away from doors and windows to prevent exhaust fumes from entering your home.
- Ensure the generator is on a stable, level surface to avoid any accidents or fuel leakage.
2. Read the User Manual:
- Thoroughly review the user manual provided by the manufacturer for specific instructions and safety guidelines.
- Pay close attention to the recommended maintenance schedule and troubleshooting tips.
3. Assemble the Generator:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to assemble the portable generator properly.
- This may include attaching wheels, handles, or other components for ease of transportation.
4. Fuel Considerations:
- Use the recommended fuel type specified in the user manual.
- Store fuel in approved containers away from the generator and other heat sources.
5. Connect the Load:
- Prioritize essential appliances and connect them to the generator using appropriate extension cords.
- Avoid overloading the generator by calculating the total wattage of connected devices.
6. Grounding the Generator:
- Properly ground the generator to minimize the risk of electrical shock.
- Use a grounding rod and follow the instructions in the user manual for safe grounding practices.
7. Start-Up Procedure:
- Follow the recommended start-up procedure outlined in the user manual.
- Allow the generator to run for a few minutes before connecting any loads.
8. Ongoing Maintenance:
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule, including checking oil levels and changing oil as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Clean or replace the air filter and spark plug according to the specified intervals.
9. Use a Transfer Switch:
- For seamless power transfer, consider installing a transfer switch.
- This device ensures a safe and quick transition from the main power source to the generator during an outage.
10. Safety Measures:
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home to monitor gas levels.
- Educate yourself and others in your household on generator safety, including the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Remember, safety is paramount when setting up and installing a portable generator. Always adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines and prioritize proper ventilation and fuel handling to ensure a reliable and secure power source.
How Long Does it Take for a Generator to Start Working?
When facing a power outage, the urgency of having a generator kick in promptly cannot be overstated. The time it takes for a generator to start working is influenced by various factors, ranging from its type to the maintenance it receives.
In essence, the starting time of a generator is contingent upon its design, fuel type, and whether it is an automatic standby generator or a manual one. Automatic standby generators are designed to kick in seamlessly when a power outage is detected, offering a swift response to electrical disruptions. On the other hand, manual generators require human intervention, which may introduce a delay.
Factors Influencing Generator Starting Time
- Automatic vs. Manual Start:
- Automatic generators equipped with advanced sensors and controls can start within seconds of detecting a power outage. This instantaneous response ensures a continuous power supply without any manual intervention.
- Manual generators, while reliable, depend on the user’s prompt action. The starting time can vary based on how quickly the generator is manually activated.
- Type of Fuel:
- The type of fuel the generator utilizes also plays a role in its starting time. For instance, natural gas generators connected to a reliable gas supply can start almost instantly. In contrast, diesel generators may require a slightly longer ignition time.
- Maintenance and Readiness:
- Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring a generator’s swift response. Well-maintained generators with clean fuel systems, charged batteries, and properly functioning components are more likely to start quickly.
- Periodic testing and readiness checks can significantly reduce the starting time. This proactive approach ensures that the generator is always in optimal condition to spring into action when needed.
Can You use a Portable Generator to Power a Whole House?
Portable generators are a convenient solution for providing temporary power in various situations, from camping trips to emergency outages. However, using a portable generator to power an entire house requires careful consideration of several factors.
Portable generators come in different sizes, typically measured in watts. The wattage determines the amount of electrical power the generator can produce. While smaller generators may be sufficient for running a few essential appliances, powering an entire house requires a larger unit.
When considering whether a portable generator can meet the power needs of your entire house, it’s essential to assess your household’s total power consumption. Make a list of the appliances and devices you consider essential during an outage, and add up their wattage requirements.
In most cases, portable generators are best suited for providing power to selected circuits or appliances through the use of extension cords or a transfer switch. A transfer switch allows you to connect the generator directly to your home’s electrical panel, providing a more seamless and safer power distribution.
Attempting to power an entire house with a portable generator without a transfer switch can overload the generator and potentially damage both the generator and your appliances. It’s crucial to prioritize and distribute power based on your needs and the generator’s capacity.
Investing in a generator that matches your power requirements and using it strategically ensures a more efficient and safer power supply during outages. Additionally, always follow proper safety protocols, including using the generator outdoors to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
In summary, while portable generators offer a flexible and portable power solution, powering an entire house with one requires careful planning, consideration of wattage needs, and the use of a transfer switch for safe and efficient power distribution.
Safety Tips for Using a Portable Generator at Home
When utilizing a portable generator at home, it’s crucial to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and ensure efficient operation.
- Location Matters:
- Place the generator outdoors, away from windows, doors, and vents to avoid carbon monoxide buildup.
- Ventilation is Key:
- Ensure proper ventilation to dissipate exhaust fumes. Never operate the generator in enclosed spaces.
- Follow Fueling Guidelines:
- Refuel the generator only when it’s cool to prevent fires. Store fuel in approved containers and away from the generator.
- Use Heavy-Duty Cords:
- Employ heavy-duty extension cords to connect appliances, and ensure they are rated for outdoor use.
- Grounding is Essential:
- Properly ground the generator to prevent electrical shocks. Follow manufacturer instructions for grounding procedures.
- Prioritize Dry Conditions:
- Keep the generator and all electrical components dry. Shelter it under a canopy if necessary to protect from rain or snow.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Conduct routine maintenance checks, including oil changes and filter replacements, as specified in the user manual.
- Respect the Load Capacity:
- Avoid overloading the generator by matching the load capacity with the appliances you connect to it.
- Emergency Shut-off Knowledge:
- Familiarize yourself with the emergency shut-off procedures in case of any malfunctions or unsafe conditions.
- Carbon Monoxide Alarms:
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home to provide early warnings in case of a buildup.
- Secure Against Theft:
- Prevent theft by securing the generator with chains or locks, especially during prolonged power outages.
Maintenance and Care for Portable Generators
Portable generators are invaluable tools, providing a reliable source of power in various situations, from camping trips to emergency power outages. To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of your portable generator, regular maintenance and care are essential.
1. Regular Inspections:
Routine inspections are the first line of defense against potential issues. Before each use, visually inspect the generator for any visible damage or loose components. Pay attention to the fuel lines, connections, and the general condition of the unit.
2. Oil Level Checks:
Proper lubrication is crucial for the generator’s engine. Check the oil level regularly, following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Running a generator with insufficient oil can lead to engine damage and reduced performance.
3. Fuel System Maintenance:
The fuel system requires attention to ensure a smooth operation. If your generator uses gasoline, be mindful of stale fuel issues. Consider using fuel stabilizers and, if possible, run the generator periodically to prevent fuel from sitting in the system for too long.
4. Air Filter Inspection and Replacement:
The air filter plays a key role in the generator’s performance. Inspect it regularly and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer. A clogged air filter can hinder airflow, affecting combustion and overall efficiency.
5. Spark Plug Maintenance:
Spark plugs are critical components for ignition. Regularly check and clean them, and replace them as needed. Properly functioning spark plugs ensure efficient fuel combustion and reliable generator operation.
6. Battery Care:
If your portable generator has a battery, keep it charged. A well-maintained battery is essential for electric start models. Check the battery terminals for corrosion and clean them if necessary.
7. Storage Considerations:
If your generator will be stored for an extended period, follow proper storage procedures. This may include draining the fuel system, protecting the generator from the elements, and storing it in a cool, dry place.
8. Professional Servicing:
While basic maintenance can be done by the user, consider professional servicing at regular intervals. A trained technician can perform in-depth inspections, identify potential issues, and conduct more complex maintenance tasks.
Troubleshooting Common Issues With Portable Generators
Portable generators are invaluable during power outages, providing a reliable source of electricity. However, like any machinery, they may encounter issues. The following table outlines common problems, possible causes, and solutions to keep your generator running smoothly.
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Won’t Start | Fuel tank is empty | Refill the fuel tank with the appropriate fuel type. |
| Stale fuel | Drain old fuel and replace it with fresh, high-quality fuel. | |
| Spark plug is fouled | Clean or replace the spark plug. | |
| Choke is closed or open improperly | Adjust the choke to the correct position. | |
| Low Power Output | Overloading | Reduce the load on the generator by disconnecting non-essential devices. |
| Dirty air filter | Clean or replace the air filter. | |
| Engine speed is incorrect | Adjust the engine speed according to the manufacturer’s specifications. | |
| Generator Shuts Down | Low oil level | Check and refill the oil to the recommended level. |
| Faulty spark arrestor | Clean or replace the spark arrestor. | |
| Overheating | Ensure proper ventilation and check for any debris blocking the cooling system. | |
| Noisy Operation | Loose or damaged parts | Tighten or replace any loose or damaged components. |
| Uneven surface or improper placement | Place the generator on a stable, level surface away from structures to minimize vibrations. | |
| Exhaust system issues | Inspect and repair any issues with the exhaust system to reduce noise. | |
| Electric Shock Risk | Damaged power cords or outlets | Replace or repair damaged cords and outlets immediately. |
| Wet conditions | Operate the generator in a dry environment and keep electrical components protected from moisture. | |
| Improper grounding | Ensure the generator is properly grounded according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. | |
| Pull Cord Jammed | Snagged or tangled pull cord | Carefully untangle or replace the pull cord if it is damaged. |
| Engine compression issues | Consult the user manual to diagnose and address any compression-related problems. | |
| Worn-out recoil starter | Replace the recoil starter assembly if it shows signs of wear. | |
| Fuel Leaks | Loose or damaged fuel lines | Tighten connections or replace damaged fuel lines. |
| Faulty fuel tank cap | Inspect and replace a faulty fuel tank cap to prevent leaks. | |
| Cracked fuel tank | Repair or replace a cracked fuel tank immediately. |
Addressing these common issues promptly ensures that your portable generator remains a reliable source of power when you need it most. Regular maintenance and understanding the troubleshooting steps can prolong the life of your generator and enhance its performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, How Do Portable Generators Work for a House illuminates the ingenious technology behind these versatile power solutions. Understanding the interplay of fuel, combustion, and electrical generation equips you to harness the full potential of portable generators. Whether for emergencies or outdoor adventures, these machines offer a lifeline of power independence.
Let this guide serve as your beacon, guiding you through the intricacies of portable generators and empowering you to make informed decisions for your household. Embrace the convenience and peace of mind that comes with a reliable portable generator, ensuring your home stays powered, no matter the circumstance.
References
- An electromagnetic, vibration-powered generator for intelligent sensor systems
- Electric generators and motors: An overview
- Analysis of a micro-electric generator for microsystems
- Linear electric actuators and generators
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Portable Generator Be Used Indoors?
Portable generators should not be used indoors due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. However, they can provide benefits such as backup power during outages and portability for various applications. Safety precautions must be taken when operating portable generators outdoors.
How Much Noise Does a Portable Generator Make?
The noise level produced by a portable generator varies depending on the model and its specifications. However, there are soundproofing options available to reduce the noise emitted during operation, ensuring quiet operation for those who desire it.
Can a Portable Generator Power the Entire House?
Portable generators have limitations when it comes to powering an entire house. They typically provide enough energy for essentials like lights and small appliances, but may not support high-energy-consuming devices. Alternative power sources like solar panels or wind turbines can be considered for a more sustainable and reliable solution.
Is It Safe to Connect a Portable Generator Directly to the Electrical Panel?
Connecting a portable generator directly to the electrical panel raises concerns about electrical safety. It is crucial to follow proper installation procedures and use appropriate transfer switches or interlocks to ensure safe operation and prevent backfeeding of electricity into the grid.
Can a Portable Generator Be Used During Extreme Weather Conditions?
Extreme weather conditions can pose challenges for the use of portable generators. Adequate maintenance, such as regular inspection and cleaning, is necessary to ensure safe operation. Choosing the right size generator is crucial to meet power demands during adverse weather events.
How do I hook up a portable generator to my house?
To connect the portable generator to the house, use a gen cord to link it with the transfer switch. Start the generator outdoors, then switch the main breakers in the transfer switch from “Line” to “Generator” power. Gradually turn on the desired circuits one at a time.
Can a portable generator power a whole house?
The ability of a portable generator to power an entire house depends on individual power needs. For general guidance, a generator providing 5,000 to 7,500 watts is usually sufficient to cover household power requirements during an outage.
What are the disadvantages of a portable generator?
While portable generators serve well for temporary power needs, they come with potential hazards. Risks include carbon monoxide poisoning from the exhaust, electric shock, fire, and burns. It’s crucial to operate them with caution to avoid these dangers.

