Ever found yourself in the middle of a power outage, relying on your trusty generator, only to be greeted by silence? Frustrating, isn’t it? We’ve all been there. The heart of the issue: a generator not producing power. But fret not, because understanding the common culprits and their fixes can turn that frustration into empowerment.
In this guide, we’ll walk alongside you, demystifying the complexities and offering practical solutions for how to fix a generator not producing power. From fuel system hiccups to electrical glitches, we’ve got you covered. Say goodbye to powerless moments, as we unravel the secrets of reviving your generator’s vigor. Let’s empower your generator to empower you!
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Main Highlights
- 2 Why Does My Generator Run but Not Produce Power?
- 3 How To Fix A Generator Not Producing Power?
- 3.1 Loss of Residual Magnetism
- 3.2 Fuel Issues
- 3.3 Ignition System Problems
- 3.3.1 1. Identify Faulty Spark Plugs:
- 3.3.2 2. Gather Necessary Tools and Replacement Parts:
- 3.3.3 3. Prepare the Generator:
- 3.3.4 4. Remove Old Spark Plugs:
- 3.3.5 5. Install New Spark Plugs:
- 3.3.6 6. Conduct Regular Ignition System Maintenance:
- 3.3.7 7. Replace Malfunctioning Ignition Coils:
- 3.3.8 8. Test the Generator:
- 3.3.9 9. Regular Maintenance Schedule:
- 3.4 Air Intake Blockages
- 3.5 Engine Mechanical Problems
- 3.6 Generator Head Issues
- 4 Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
- 5 Generator Maintenance Tips
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 References
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
- 8.1 What type of generator do I need for my home?
- 8.2 What should I do if my generator is producing too much power?
- 8.3 How long does it take to repair a generator?
- 8.4 What safety precautions should I take when working with a generator?
- 8.5 What type of maintenance do I need to do on my generator?
- 8.6 Why is my generator running but no power output?
- 8.7 How would you get a generator to work when it has lost its residual magnetism?
- 8.8 Why is my power out generator not working?
Main Highlights
- Malfunctioning voltage regulators and worn/damaged brushes are common causes of generators not producing power.
- Residual magnetism can be restored using methods such as the 12 Volt Generator Battery Method or the Electric Drill Method.
- To fix a generator, replace the faulty voltage regulator or brushes and regularly clean/lubricate brushes for maintenance. A professional electrician may be needed if problems persist.
- To check generator components, inspect fuel level, air filter, spark plug, circuit breaker, and voltage regulator regularly to ensure safe and efficient power output.
Why Does My Generator Run but Not Produce Power?
When your generator runs but fails to produce power, several underlying factors might be at play. It’s crucial to identify these issues promptly to ensure your generator functions optimally. Here are potential causes for this concern:
- Fuel Issues:
- Insufficient or contaminated fuel can hinder power generation.
- Clogged fuel filters may restrict the flow of fuel to the engine.
- Loss of Residual Magnetism:
- The generator may lose its residual magnetism over time, hindering the production of electricity.
- Factors like extended periods of inactivity or certain electrical faults can contribute to the demagnetization of the generator.
- Ignition System Problems:
- Faulty spark plugs may disrupt the combustion process.
- Ignition system malfunctions, such as a defective ignition coil, could lead to power generation issues.
- Air Intake Blockages:
- Restricted air intake due to debris or blockages can impede combustion.
- Dirty air filters may reduce the airflow needed for proper engine function.
- Engine Mechanical Problems:
- Worn-out piston rings or cylinder walls may result in insufficient compression.
- Timing belt issues can affect the synchronization of engine components.
- Generator Head Issues:
- Damaged or worn-out brushes in the generator head can lead to a lack of power generation.
- Faulty voltage regulators may impact the proper distribution of electrical output.
Identifying the specific cause behind your generator running without producing power is the first step towards effective troubleshooting.
How To Fix A Generator Not Producing Power?
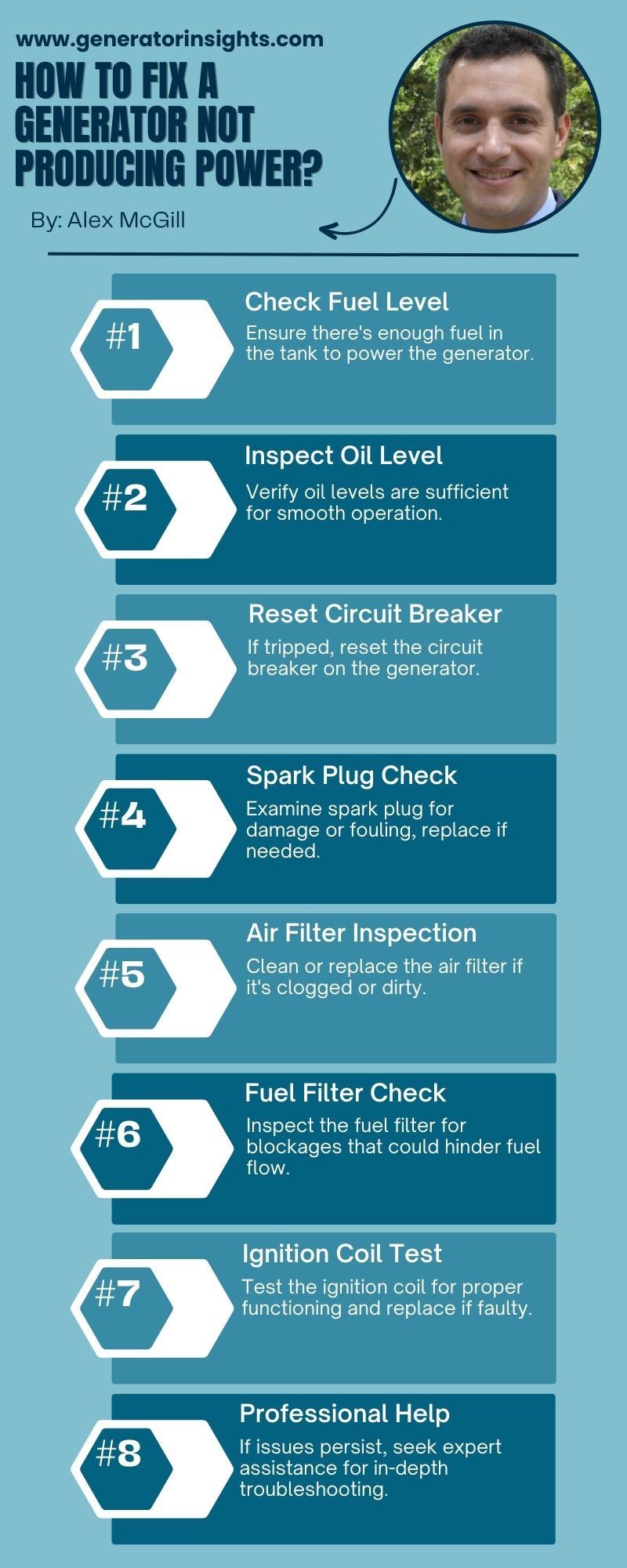
Now that we’ve pinpointed potential causes for your generator running without producing power, let’s explore possible fixes to rectify these issues:
- Fuel Issues:
- Ensure the fuel supply is clean and of the correct type.
- Regularly replace fuel filters to maintain an unobstructed fuel flow.
- Loss of Residual Magnetism:
- Re-establish residual magnetism by using a process called “flashing.” This involves momentarily applying a low voltage to the generator’s field winding to restore magnetic strength.
- Ignition System Problems:
- Replace faulty spark plugs with the appropriate ones for your generator.
- Conduct regular maintenance on the ignition system, addressing issues like a malfunctioning ignition coil.
- Air Intake Blockages:
- Clear any debris obstructing the air intake system.
- Replace or clean air filters to ensure proper airflow to the engine.
- Engine Mechanical Problems:
- Address worn-out piston rings or cylinder walls through engine repair or replacement.
- If the timing belt is damaged, promptly replace it to restore proper engine timing.
- Generator Head Issues:
- Replace damaged brushes in the generator head.
- Address voltage regulator malfunctions by replacing the faulty component.
Remember, these fixes should be implemented based on a thorough diagnosis of the specific issue affecting your generator. Consulting a professional for a comprehensive assessment is advisable for complex problems.
Now let’s discuss these fixes in detail.
Loss of Residual Magnetism
Fortunately, there are two methods of restoring residual magnetism to the generator and getting it back up and running – the 12 Volt Generator Battery Method or the Electric Drill Method. In this article, we’ll look at these methods in detail so you can quickly get your generator back to functioning properly.
12 Volt Generator Battery Method
To fix a generator not producing power, you’ll need to use the volt generator battery method: unplug the two wires connecting to the generator brushes, connect one of those to the ground battery terminal, and plug in a light. Here’s what this step-by-step process looks like:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Unplug two wires | Unplug the two wires that connect to the generator brushes. One is red and the other is black or white. |
| Connect one wire to ground terminal | Connect the black or white wire to your generator ground battery terminal. |
| Plug in a light & turn on switch/breaker | Plug in a light and turn on your generator breaker or switch and start the motor. |
| Connect battery +12 volts (red cable) for 3 secs | Connect your battery +12 volts (red cable) to the red wire on removed terminals for three seconds. |
| Replace plug & finish up | Remove your wires and replace the plug; your generator should now be producing power again! |
Once you’ve completed these steps using the volt generator battery method, you’re ready to move onto fixing it with an electric drill.
Electric Drill Method
Plugging in an electric drill to the generator receptacle and switching the direction to forward can help excite the field, allowing the generator to produce electricity. To do this, depress the trigger on the drill while spinning it in reverse.
This process will kick start a generator that is not producing power. Once finished, releasing the trigger and turning off the generator will ensure everything is running properly. With this method, you can easily fix a generator not producing power without having to replace any parts or hire a professional.
Fuel Issues
Ensure the Fuel Supply is Clean:
- Inspect Fuel Quality:
- Begin by visually inspecting the fuel in the generator’s tank.
- Ensure the fuel is clean, free from debris, and matches the recommended type specified in the generator’s manual.
- Drain Old Fuel if Necessary:
- If the fuel is old or contaminated, drain the tank completely.
- Dispose of the old fuel properly according to environmental regulations.
- Refill with Clean, Recommended Fuel:
- Fill the tank with fresh, clean fuel of the correct type.
- Use a clean and approved container to avoid introducing impurities into the fuel system.
- Check Fuel Lines:
- Inspect fuel lines for any signs of damage, leaks, or blockages.
- Replace damaged or leaking fuel lines promptly.
Regularly Replace Fuel Filters:
- Locate the Fuel Filter:
- Consult the generator’s manual to locate the fuel filter. It is typically situated in the fuel line between the tank and the engine.
- Turn Off the Generator:
- Before attempting to replace the fuel filter, turn off the generator and allow it to cool.
- Release Pressure:
- If your generator has a pressure release valve, activate it to release any pressure in the fuel system.
- Remove the Old Fuel Filter:
- Disconnect the fuel lines connected to the filter.
- Carefully remove the old fuel filter, taking note of the direction of fuel flow.
- Install the New Fuel Filter:
- Install a new, compatible fuel filter in the correct orientation.
- Reconnect the fuel lines, ensuring a secure fit.
- Prime the Fuel System:
- If your generator requires priming after filter replacement, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to prime the fuel system.
- Restart the Generator:
- Turn the generator back on and monitor for any signs of improved performance.
Regular maintenance, including monitoring fuel quality and replacing fuel filters, is essential for the longevity and optimal performance of your generator. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific details related to your generator model. If issues persist, consult a professional for further diagnosis and repair.
Ignition System Problems
1. Identify Faulty Spark Plugs:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the spark plugs for signs of wear, damage, or carbon buildup.
- Check Spark Plug Gap: Ensure the spark plug gap is within the manufacturer’s specifications.
2. Gather Necessary Tools and Replacement Parts:
- Tools: You may need a socket wrench, spark plug socket, and a gap gauge.
- Replacement Spark Plugs: Obtain the correct spark plugs compatible with your generator model.
3. Prepare the Generator:
- Turn Off the Generator: Ensure the generator is powered off to guarantee safety during the replacement process.
- Locate the Spark Plugs: Identify the location of the spark plugs on your generator.
4. Remove Old Spark Plugs:
- Use a Socket Wrench: Loosen and remove the old spark plugs carefully.
- Inspect Threads: Check the threads for any signs of damage.
5. Install New Spark Plugs:
- Check Gap: Confirm the gap of the new spark plugs matches the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Hand Tighten: Carefully thread the new spark plugs into place by hand to avoid cross-threading.
- Use Socket Wrench: Use the socket wrench to tighten the spark plugs snugly.
6. Conduct Regular Ignition System Maintenance:
- Inspect Ignition Coils: Check for visible signs of damage, such as cracks or corrosion.
- Measure Resistance: Use a multimeter to measure the resistance of the ignition coils, comparing the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
7. Replace Malfunctioning Ignition Coils:
- Acquire Replacement Coils: Obtain replacement ignition coils if the existing ones are malfunctioning.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper installation.
- Securely Attach Coils: Ensure the new ignition coils are securely attached, and all electrical connections are properly made.
8. Test the Generator:
- Power On: Start the generator and observe its performance.
- Check for Sparks: Verify that sparks are present at the spark plug electrodes during startup.
9. Regular Maintenance Schedule:
- Establish Routine Checks: Implement a regular maintenance schedule, including spark plug inspection and replacement as needed.
- Address Issues Promptly: If issues arise, address them promptly to prevent further damage to the ignition system.
By following these steps, you can effectively address ignition system problems in your generator, ensuring proper spark plug function and maintaining the overall reliability of the system.
Air Intake Blockages
Step 1: Inspection
Start by turning off the generator and allowing it to cool down. Then, visually inspect the air intake system for any visible debris or blockages. This includes checking the air intake grills, ducts, and the area surrounding the air filter.
Step 2: Remove External Debris
Use a soft brush or compressed air to gently remove any loose debris, leaves, or dirt that may be obstructing the air intake. Be cautious not to push debris further into the system.
Step 3: Air Filter Examination
Access the air filter housing and inspect the air filter. If the filter is visibly dirty or clogged, it’s essential to clean or replace it.
Step 4: Cleaning the Air Filter
If the air filter is reusable, carefully remove it and clean it according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This often involves tapping it to remove loose dirt or washing it with mild soap and water. Ensure the filter is completely dry before reinstalling.
Step 5: Replacement
If the air filter is not reusable or is damaged, replace it with a new one. Make sure to use the recommended type of air filter specified in your generator’s manual.
Step 6: Reassembly
Once the air intake system is free from debris and the air filter is either cleaned or replaced, reassemble the components carefully. Ensure that all parts are securely in place.
Step 7: Test Run
Start the generator and observe its performance. Check for any unusual sounds or signs of obstruction. If the generator now produces power as expected, the air intake blockage issue has likely been resolved.
Engine Mechanical Problems
1. Worn-out Piston Rings or Cylinder Walls:
- Step 1: Diagnosis
- Perform a compression test to identify low compression levels, indicating potential issues with piston rings or cylinder walls.
- Step 2: Remove Cylinder Head
- Disconnect the battery to ensure safety.
- Remove the cylinder head to access the pistons and cylinders.
- Step 3: Inspection
- Examine the piston rings and cylinder walls for wear, scoring, or damage.
- Measure cylinder bore diameter to determine if it’s within acceptable tolerances.
- Step 4: Repair or Replace
- If wear is minimal, honing the cylinders may suffice.
- Extensive damage may require cylinder re-sleeving or engine replacement.
- Step 5: Reassembly
- Reassemble the engine, ensuring proper torque settings for bolts.
- Install a new head gasket during reassembly.
2. Damaged Timing Belt:
- Step 1: Visual Inspection
- Locate the timing belt and inspect it for visible signs of wear, fraying, or damage.
- Step 2: Disconnect Components
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove components blocking access to the timing belt, such as the drive belts and covers.
- Step 3: Remove the Old Belt
- Align timing marks to ensure proper engine timing.
- Remove the old timing belt, taking note of the orientation and positioning of components.
- Step 4: Install the New Belt
- Carefully install the new timing belt, following the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Ensure proper tension and alignment as specified in the vehicle manual.
- Step 5: Reassemble Components
- Reinstall components previously removed, such as drive belts and covers.
- Reconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Step 6: Test Run
- Start the engine and monitor for any unusual noises or vibrations.
- Verify that the engine operates smoothly and maintains proper timing.
These steps should be executed with precision and attention to detail. If you are not familiar with engine mechanics, it is advisable to seek professional assistance to ensure the correct diagnosis and implementation of the necessary repairs.
Generator Head Issues
1. Replacing Damaged Brushes in the Generator Head:
- Step 1: Safety First Ensure the generator is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Safety should always be the priority when working on any electrical equipment.
- Step 2: Access the Generator Head Locate the generator head, typically positioned at the end of the generator opposite the control panel. Remove any covers or panels obstructing access.
- Step 3: Identify and Remove Brushes Locate the brushes, which are typically rectangular components with conductive material. Carefully remove them from their holders, taking note of their orientation.
- Step 4: Inspect for Damage Thoroughly examine each brush for signs of wear, damage, or excessive wear. If a brush is worn down or damaged, it needs replacement.
- Step 5: Install New Brushes Install replacement brushes in the same orientation as the removed ones. Ensure a secure fit, and double-check that they make proper contact with the slip rings.
- Step 6: Reassemble and Test Reassemble any parts you removed to access the brushes. Turn on the generator and check if the power output is restored. If the issue persists, further investigation may be necessary.
2. Addressing Voltage Regulator Malfunctions:
- Step 1: Turn Off the Generator Ensure the generator is turned off and disconnected from the power source before attempting any repairs.
- Step 2: Locate the Voltage Regulator The voltage regulator is often located near the generator head or within the control panel. Identify and access the regulator.
- Step 3: Disconnect Power Disconnect any power sources to the voltage regulator to prevent electrical shocks during the replacement process.
- Step 4: Remove the Faulty Regulator Carefully detach the faulty voltage regulator from its mounting. Take note of the wiring connections to ensure correct reassembly.
- Step 5: Install the New Voltage Regulator Connect the new voltage regulator following the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure all wires are correctly attached and secure.
- Step 6: Test the Generator Turn on the generator and monitor the power output. Check for stable voltage levels and ensure the generator is now producing power consistently.
Always refer to the generator’s manual for specific instructions related to your model, and if you are uncertain about any steps, seek professional assistance.
Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
Generators are indispensable during power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply. However, users may encounter issues that hinder their optimal performance. Below is a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot common generator issues and restore seamless operation.
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Engine Fails to Start | – Silent operation | – Check fuel levels and ensure there’s an adequate supply. |
| – Starter motor cranks but fails to ignite | – Inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or wear. Replace if necessary. | |
| – Strong smell of gasoline | – Examine the carburetor for blockages and clean or replace if needed. | |
| 2. Low Power Output | – Dimming lights and fluctuating power output | – Verify the load capacity and ensure it doesn’t exceed the generator’s limit. |
| – Appliances not running at full capacity | – Inspect the voltage regulator for malfunctions and replace if necessary. | |
| 3. Generator Overheating | – Unusual heat emanating from the generator | – Check the cooling system, including the radiator and coolant levels. Clean or replace components as required. |
| – Frequent shutdowns due to overheating | – Ensure proper ventilation around the generator and clean any debris obstructing airflow. | |
| 4. Excessive Noise Levels | – Unusual or loud sounds during operation | – Inspect the muffler for damage and replace if needed. Adjust engine RPM to recommended levels. |
| – Vibrations and rattling noises | – Tighten any loose bolts and secure all components properly. | |
| 5. Electric Shock from Generator | – Users experiencing electric shocks | – Immediately disconnect the generator from the power source. Inspect and repair any damaged wiring or outlets. |
| – Tingling sensation when touching the generator | – Check for grounding issues and ensure the generator is properly grounded. | |
| 6. Smoke Emission | – Visible smoke during operation | – Examine the oil level and quality. Change oil if it appears dirty or insufficient. |
| – Unpleasant burning smell | – Inspect the air filter for clogs and replace if necessary. |
Addressing these common generator issues promptly will help maintain the reliability of your power source. If problems persist, consider seeking professional assistance for more complex diagnostics and repairs.
Generator Maintenance Tips
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, making a well-maintained generator crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply. Regular maintenance not only enhances longevity but also guarantees optimal performance. Here are some key tips to keep your generator in top shape:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct routine checks on your generator to identify any signs of wear, loose connections, or potential issues before they escalate.
- Fluid Levels: Regularly check and replenish the oil and fuel levels to guarantee efficient operation. Proper lubrication is essential for preventing friction-related damage.
- Battery Health: Ensure the generator’s battery is charged and in good condition. A healthy battery is vital for a swift start when power is needed.
- Air Filter Checks: Keep the generator’s air filter clean and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer. A clogged filter can compromise performance and fuel efficiency.
- Coolant System Inspection: Verify the coolant levels and inspect the system for leaks. Overheating can lead to severe damage, so maintaining the right coolant levels is crucial.
- Capacitor Maintenance: Check and test the generator’s capacitors regularly. Faulty capacitors can lead to electrical issues, affecting the generator’s ability to produce a consistent power output.
- Run the Generator Regularly: Regularly starting the generator, even if it’s not in use, helps keep the engine components lubricated and prevents fuel system issues.
- Storage Considerations: If the generator is stored for an extended period, use a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel deterioration. Empty the fuel tank or run the generator dry before storage to avoid gumming.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, including capacitor checks, you’ll ensure that your generator is ready to provide reliable power when you need it the most.
Conclusion
In conclusion of how to fix a generator not producing power, we discussed that by following our step-by-step guide, you would have identified the problem and have taken the necessary steps to fix it. Now you can relax knowing that your generator will produce power when you need it most. With regular maintenance, your generator will be reliable for years to come.
You can now enjoy the convenience of having a backup power supply and peace of mind in knowing that you’re prepared for any unexpected outages. You’ve done a great job troubleshooting and fixing your generator so it runs smoothly again!
References
- Control of electric generators: a review
- Significant power enhancement of magneto-mechano-electric generators by magnetic flux concentration
- Performance and power management of droplets-based electricity generators
- Towards modelling and design of magnetostrictive electric generators
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of generator do I need for my home?
You’ll need to determine what size generator is best for your home. Consider the amount of power you need, as well as other factors like noise level and fuel type. You can use this information to help you decide which type of generator will work best for you.
What should I do if my generator is producing too much power?
If your generator is producing too much power, turn it off and disconnect from the grid. If that doesn’t work, check your connections and adjust the voltage regulator accordingly.
How long does it take to repair a generator?
It depends on the complexity of the repair. Generally, it can take anywhere from a few hours to several days. Check with your local repair shop for an estimate.
What safety precautions should I take when working with a generator?
When working with a generator, take appropriate safety precautions. Wear protective gear, ensure the area is well-ventilated and avoid contact with live wires. Be sure to disconnect the power before servicing or making repairs.
What type of maintenance do I need to do on my generator?
You need to perform regular maintenance on your generator to keep it running properly. Check the fuel levels, air filter, and spark plugs regularly and replace them if needed. Make sure all connections are tight and inspect for signs of damage or wear.
Why is my generator running but no power output?
The generator may not produce power due to the loss of residual magnetism. This can happen if the generator has been unused for a while, had a connected load when turned off, ran without a load for an extended period, or experienced vibration during long-distance transportation. To restore magnetism, it’s recommended to “flash” the excitation coil by applying an appropriate DC voltage across the field terminals.
How would you get a generator to work when it has lost its residual magnetism?
To restore a generator’s lost residual magnetism, the recommended method is to “flash” the excitation coil. This involves applying an appropriate DC voltage across the field terminals to pass a DC current through the field coils in the correct polarity. This process helps the core retain enough residual magnetism to start generating power independently.
Why is my power out generator not working?
If the generator is not producing power during an outage, it’s essential to check the main line breaker. Ensure it is in the ON position, as a turned-off breaker prevents power transfer from the generator to the home. Additionally, verify the functionality of the generator’s control board. If the control board is not working, it could be due to battery failure or loose/defective cables.

