In a world where our dependence on electricity is second nature, understanding the backbone of reliable power becomes paramount. So, what is a power generator? It’s more than a machine; it’s the silent hero in the face of blackouts and emergencies, ensuring that life goes on uninterrupted. Imagine having the ability to summon electricity at the flick of a switch, empowering homes and businesses alike.
A power generator is not just a piece of equipment; it’s a guardian of continuity, a source of resilience. Join us as we unravel the secrets behind this technological marvel and explore the lifeline that keeps the lights on.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Core Lessons
- 2 What is a Power Generator?
- 3 How Does a Power Generator Work?
- 4 What are the Basic Parts of a Power Generator?
- 5 Why Do You Need a Power Generator?
- 6 What are Different Types of Power Generators?
- 7 How to Choose the Right Power Generator for Your House?
- 8 How to Use a Power Generator?
- 9 What are the Applications of Power Generator?
- 10 Troubleshooting Common Power Generator Issues
- 11 Power Generator Maintenance Tips
- 12 Power Generator Safety Tips
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 References
- 15 Frequently Asked Questions
- 15.1 How much does a power generator cost?
- 15.2 Is a power generator easy to maintain?
- 15.3 How much power can a power generator generate?
- 15.4 Are power generators noisy?
- 15.5 How often should a power generator be serviced?
- 15.6 What does a power generator do?
- 15.7 What is the function of a generator in power?
- 15.8 How do I power my house with a generator?
Core Lessons
- Power generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, and there are many types available, such as portable, gas, home, and backup generators.
- Generators can be powered by various sources, including gasoline, diesel, wind turbines, and solar panels, and they come in different sizes and output levels to meet different needs.
- Generators have various applications, including providing a reliable source of electric power during shortages or disruptions to the main grid supply, for industrial and commercial sectors, residential use, construction sites, outdoor events, and emergency backup power.
- When choosing a power generator, factors such as power output and capacity, fuel type and availability, noise level, portability and size, safety features, and maintenance requirements should be taken into consideration to find the best fit for specific usage requirements.
What is a Power Generator?
A Power Generator is a versatile apparatus designed to convert mechanical energy into electrical power. This process involves the utilization of a fuel source, such as gasoline, diesel, or natural gas, to drive a motor or turbine. As the machinery operates, it produces electrical current that can be harnessed for various applications. This capability is particularly crucial in emergency situations, providing a dependable backup power source for homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
One of the key virtues of a Power Generator is its autonomy. By relying on internal combustion engines or other power-producing mechanisms, these devices ensure a degree of self-sufficiency, reducing dependence on external power grids. This autonomy is especially beneficial in regions prone to natural disasters or remote locations where establishing traditional power infrastructure is challenging.
The value of a Power Generator extends beyond mere convenience; it embodies preparedness and resilience. Businesses can avert financial losses during power disruptions, hospitals can maintain life-saving equipment, and households can sustain a semblance of normalcy. As technology advances, generators are becoming more efficient, eco-friendly, and tailored to diverse needs, making them indispensable assets in today’s dynamic energy landscape.
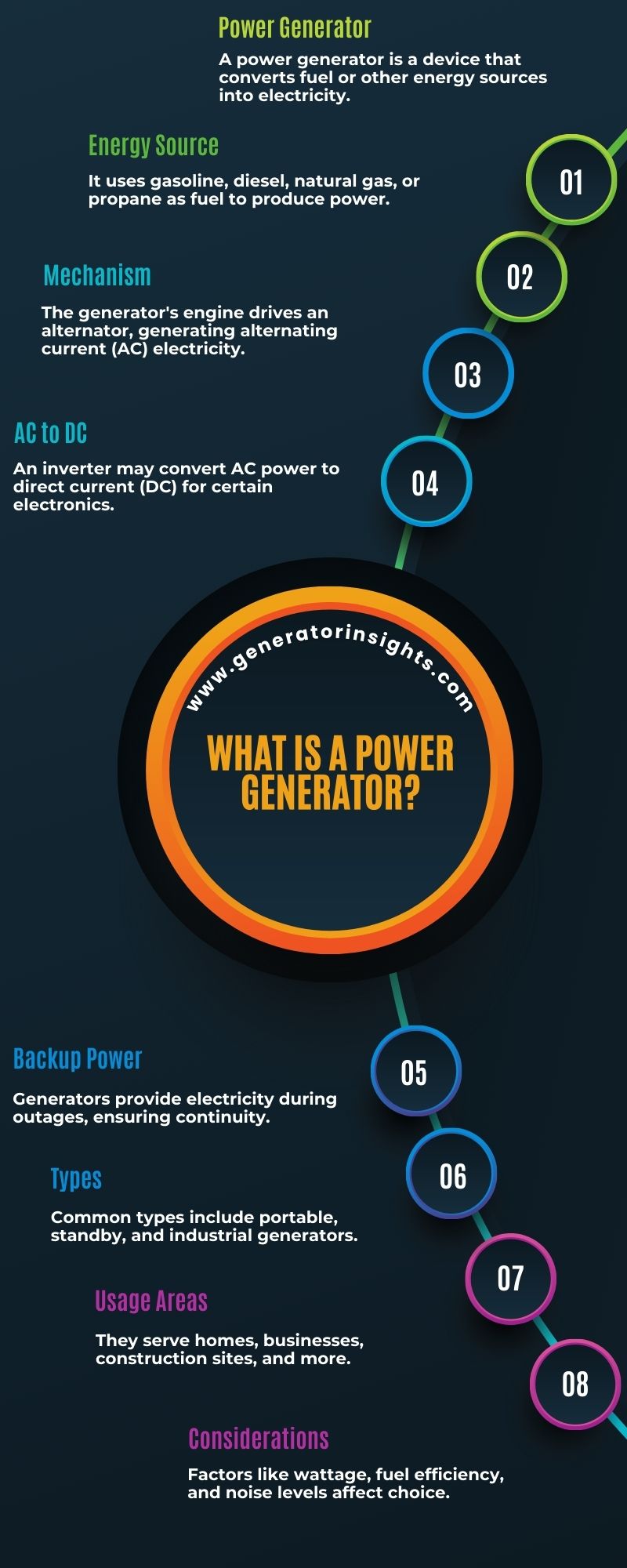
How Does a Power Generator Work?
Power generators play a pivotal role in ensuring a steady and reliable supply of electricity. These devices, often essential during power outages or in off-grid locations, function on the principle of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Generators typically consist of an engine, commonly fueled by diesel or gasoline, and an alternator. The engine powers the alternator, which, in turn, produces alternating current (AC) electricity. This process involves a fascinating interplay of components. The engine’s combustion generates mechanical energy, propelling the alternator’s rotor.
As the rotor spins within a magnetic field, it induces an electric current in the generator’s coils. The result is a flow of electrical power that can be harnessed for various applications. Understanding the intricacies of power generators is crucial for both emergency preparedness and sustainable energy solutions.

What are the Basic Parts of a Power Generator?
Understanding the basic parts of a power generator is essential for both maintenance and troubleshooting. Let’s delve into the key components that make these machines function effectively.
1. Engine
The engine serves as the powerhouse of a generator, converting fuel (usually diesel, gasoline, or natural gas) into mechanical energy. It’s the initial stage where the generator begins its power generation process.
2. Alternator
Also known as a generator head, the alternator is responsible for converting the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. Coils within the alternator produce an alternating current (AC), a crucial step in the electricity generation process.
3. Fuel System
The fuel system ensures a steady and controlled supply of fuel to the engine. Components like fuel tanks, filters, and pumps play a vital role in maintaining the engine’s efficiency and longevity.
4. Voltage Regulator
To ensure a stable power output, the voltage regulator monitors and controls the electrical output. It adjusts the voltage levels to meet the required specifications, preventing damage to connected devices.
5. Cooling System
Generators produce a significant amount of heat during operation. The cooling system, often using radiators and fans, regulates the temperature to prevent overheating, ensuring continuous and reliable performance.
6. Battery Charger
A battery charger maintains the charge of the generator’s starting battery. This ensures that the generator can start quickly when needed, especially during unexpected power interruptions.
7. Control Panel
The control panel houses the necessary instruments and controls to manage the generator. It includes elements like the start/stop button, gauges, and indicator lights, allowing users to monitor and operate the generator efficiently.
Why Do You Need a Power Generator?
Whether you’re a homeowner, a business owner, or an outdoor enthusiast, investing in a quality power generator brings a multitude of benefits. First and foremost, a generator acts as a safeguard against power outages, ensuring uninterrupted electricity during emergencies. This is especially critical for essential appliances, medical equipment, and business operations that rely on a consistent power source.
Moreover, a power generator provides an added layer of security and peace of mind, allowing you to navigate through unexpected blackouts without compromising your daily activities. The versatility of a generator is another compelling reason to consider one; it can be used for camping trips, outdoor events, or as a backup power source for construction sites.
Ultimately, having a power generator is an investment in resilience, providing you with the assurance that you can weather unforeseen power challenges with ease.
What are Different Types of Power Generators?
Understanding the different types of generators is crucial for selecting the most suitable option for specific needs. Here, we delve into the details of various power generators, highlighting their key features and applications.
| Generator Type | Description | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Diesel Generators | Diesel generators use combustion engines for electricity generation, renowned for efficiency and reliable power output. | – Efficient fuel consumption. | – Emergency power backup. |
| – Quick start-up time. | – Remote locations. | ||
| – Long lifespan. | – Industrial settings. | ||
| 2. Gas Generators | Gas generators utilize natural gas or propane for power generation, offering a cleaner alternative to diesel. | – Environmentally friendly. | – Residential power backup. |
| – Lower emissions. | – Small businesses. | ||
| – Cost-effective fuel. | – Peak shaving in utilities. | ||
| 3. Solar Generators | Solar generators harness energy from the sun through photovoltaic cells, providing sustainable and renewable power. | – Environmentally sustainable. | – Off-grid living. |
| – Low operating costs. | – Remote installations. | ||
| – Minimal maintenance. | – Camping and outdoor events. | ||
| 4. Wind Generators | Wind generators convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity through turbine blades, ideal for windy regions. | – Clean and renewable energy. | – Wind farms for grid power. |
| – Low operating costs. | – Rural electrification. | ||
| – Scalable for large projects. | – Offshore power generation. | ||
| 5. Hydro Generators | Hydro generators utilize the flowing water’s kinetic energy for electricity, offering a reliable source of renewable energy. | – High energy efficiency. | – Hydropower plants. |
| – Low greenhouse gas emissions. | – Remote communities. | ||
| – Long lifespan with proper maintenance. | – Irrigation and water supply. | ||
| 6. Synchronous Generators | Synchronous generators produce electricity with a fixed speed and synchronized output, making them suitable for grid-connected applications. | – Stable and synchronized power output. | – Power plants for grid stability. |
| – Efficient for constant load. | – Industrial and commercial applications. | ||
| – Effective for large-scale power generation. | – Utility power generation. | ||
| 7. Induction Generators | Induction generators operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, providing a simple and robust design. | – Simple and rugged construction. | – Wind power generation. |
| – Self-starting capability. | – Remote and off-grid areas. | ||
| – Low maintenance requirements. | – Small-scale power plants. | ||
| 8. Inductor Alternators | Inductor alternators use inductive devices to generate alternating current, offering versatility in various applications. | – Versatile in AC power generation. | – Emergency backup systems. |
| – Simple design and operation. | – Mobile and portable power. | ||
| – Reliable for intermittent loads. | – Construction sites. | ||
| 9. Direct-Current Generators | Direct-current generators produce a unidirectional flow of electric charge, suitable for specific applications requiring DC power. | – Simple and efficient DC power generation. | – Battery charging systems. |
| – Precise control over voltage. | – Telecommunication systems. | ||
| – Common in off-grid solar systems. | – Railway and marine applications. |
This comprehensive overview aids in understanding the diverse landscape of power generators, facilitating informed choices aligned with specific operational requirements.
How to Choose the Right Power Generator for Your House?
When it comes to ensuring uninterrupted power supply during outages, selecting the right power generator for your house is crucial. Consider the following factors to make an informed decision:
- Assess Your Power Needs:
- Calculate your average electricity consumption to determine the generator capacity required.
- Identify essential appliances and devices that must remain powered during outages.
- Fuel Type:
- Choose between gasoline, propane, or diesel generators based on availability and cost-effectiveness.
- Consider the shelf life and stability of the chosen fuel type.
- Portability vs. Stationary:
- Assess whether you need a portable generator for occasional use or a stationary generator for continuous power needs.
- Portability is ideal for camping or occasional power outages, while stationary generators offer consistent backup power.
- Noise Level:
- Consider the decibel rating to ensure the generator operates within permissible noise levels.
- Quieter generators are preferable for residential areas to minimize disturbances.
- Automatic vs. Manual Start:
- Opt for an automatic start generator if you want seamless power restoration without manual intervention.
- Manual start generators may require more attention but could be cost-effective.
- Brand Reputation:
- Research and choose generators from reputable brands with a track record of reliability.
- Check online reviews and customer feedback for insights into performance and durability.
- Maintenance Requirements:
- Evaluate the maintenance needs of the generator, including oil changes and component checks.
- Choose a generator with manageable maintenance requirements to ensure longevity.
- Budget Considerations:
- Set a realistic budget for the generator purchase and installation.
- Compare prices, taking into account long-term costs such as fuel and maintenance.
How to Use a Power Generator?
Power generators are essential tools for ensuring a reliable power supply during emergencies or in off-grid locations. Understanding how to use a power generator correctly is crucial to maximize its efficiency and ensure safety. Let’s delve into the detailed steps of effectively utilizing a power generator.
- Read the Manual:
- Begin by thoroughly reading the manufacturer’s manual for your specific power generator model.
- Manuals provide crucial information on safety guidelines, operational procedures, and maintenance requirements.
- Choose a Suitable Location:
- Place the generator in a well-ventilated area, preferably outdoors, to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes.
- Keep it on a stable, flat surface to ensure proper operation and ease of maintenance.
- Fueling the Generator:
- Check the fuel type recommended by the manufacturer and use only high-quality fuel.
- Fill the tank with the recommended fuel, avoiding overfilling to prevent spills and potential hazards.
- Start-Up Procedure:
- Turn the generator switch to the “off” position before starting.
- Follow the specific start-up procedure outlined in the manual to prevent damage to the generator and ensure a smooth start.
- Power Distribution:
- Prioritize essential appliances and devices when connecting to the generator.
- Use a heavy-duty extension cord to connect appliances directly to the generator’s outlets.
- Load Management:
- Be mindful of the generator’s wattage capacity to avoid overloading it.
- Start and connect appliances one at a time, ensuring the generator can handle the cumulative load.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Schedule routine maintenance checks as advised in the manual to keep the generator in optimal condition.
- This includes oil changes, air filter replacements, and general inspections.
- Shutdown Procedure:
- Allow the generator to run without a load for a few minutes before turning it off.
- Turn the generator switch to the “off” position and disconnect all appliances before shutting down.
What are the Applications of Power Generator?
Understanding the diverse applications of power generators is crucial for optimizing their usage across different scenarios.
Emergency Power Supply
In critical situations, power generators act as lifelines by ensuring an uninterrupted power supply during emergencies. Hospitals, data centers, and essential services rely on generators to maintain operations, safeguarding lives and preserving vital information.
Construction Sites
Construction projects often operate in locations without immediate access to the power grid. Generators become indispensable on construction sites, powering tools, machinery, and lighting to facilitate seamless project progress.
Remote Areas and Off-Grid Locations
In remote or off-grid areas, where traditional power infrastructure is absent, generators step in to bridge the gap. Whether it’s powering remote research stations, telecommunications equipment, or temporary events, generators enable functionality in areas without established power networks.
Backup Power for Businesses
Business continuity is crucial, and power outages can result in significant financial losses. Many businesses invest in backup power generators to ensure continuous operations, preventing disruptions due to unforeseen power failures.
Events and Entertainment
Large-scale events, concerts, and outdoor festivals demand substantial power. Generators play a vital role in providing the necessary electricity for stage lighting, sound systems, and various amenities, ensuring the success of these events.
Agriculture and Farming
In rural settings, farms often require a reliable power source for irrigation systems, barns, and machinery. Generators offer a dependable solution, supporting agricultural activities and contributing to increased efficiency in farming practices.
Telecommunications
Telecommunication infrastructure relies heavily on a constant power supply. Backup generators are essential to ensure the uninterrupted functioning of cell towers, data centers, and communication networks, especially during power outages.
Thus, the applications of power generators are diverse and extend across numerous industries and scenarios. From providing emergency power during crises to supporting essential services and enhancing productivity in various sectors, power generators prove to be versatile tools essential for modern-day operations.
Troubleshooting Common Power Generator Issues
Power generators are vital for ensuring uninterrupted electricity supply. However, issues may arise, causing disruptions. Let’s explore common problems and effective troubleshooting steps.
| Issue | Possible Causes | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. No Power Output | Insufficient fuel, faulty alternator, or a malfunctioning engine. | – Ensure an adequate fuel supply. – Check the alternator for any damages. – Inspect the engine for signs of malfunction. |
| 2. Engine Fails to Start | Dead battery, fuel problems, or a malfunctioning starter motor. | – Check the battery voltage. – Verify the fuel supply and quality. – Examine the starter motor for issues. |
| 3. Low Power Output | Dirty air filters, worn-out spark plugs, or a clogged fuel filter. | – Clean or replace air filters regularly. – Check and replace spark plugs when necessary. – Inspect the fuel filter for any clogs. |
| 4. Overheating | Low coolant levels, a malfunctioning thermostat, or a faulty radiator. | – Ensure there is enough coolant in the system. – Check the thermostat for proper functioning. – Inspect the radiator for any damages. |
| 5. Unusual Noises | Loose components, worn-out bearings, or damaged belts. | – Tighten any loose components. – Inspect and replace worn-out bearings. – Check the condition of belts and replace if necessary. |
| 6. Generator Won’t Start | Empty fuel tank, faulty ignition switch, or a flooded engine. | – Confirm an adequate fuel level. – Check the ignition switch for proper functionality. – If flooded, wait for some time before attempting to start again. |
| 7. Generator Won’t Keep Running | Clogged fuel line, air in the fuel system, or a malfunctioning carburetor. | – Inspect and clear any clogs in the fuel line. – Bleed air from the fuel system. – Examine the carburetor for any issues and clean or repair as needed. |
By addressing these common generator issues systematically, you can enhance the reliability and performance of your power generator, ensuring it operates smoothly when needed the most.
Power Generator Maintenance Tips
Ensuring the optimal performance of your power generator is crucial for uninterrupted power supply. Regular maintenance is key to preventing breakdowns and extending the lifespan of your equipment. Here are some power generator maintenance tips to keep your system running smoothly:
- Scheduled Inspections:
- Conduct routine inspections to identify potential issues.
- Inspect for loose wires, leaks, and signs of wear.
- Fluid Checks:
- Regularly check and change the oil and fuel filters.
- Ensure proper coolant levels to prevent overheating.
- Battery Health:
- Monitor the battery condition and connections.
- Clean terminals to prevent corrosion, ensuring a reliable start.
- Load Testing:
- Periodically test the generator under different loads.
- This helps identify potential problems and ensures it can handle peak demands.
- Exhaust System Inspection:
- Inspect the exhaust system for leaks and corrosion.
- Addressing these issues promptly prevents damage to the generator and ensures safety.
- Control Panel Checks:
- Verify the accuracy of the control panel settings.
- Calibration ensures the generator operates according to required specifications.
- Tighten Loose Components:
- Check and tighten any loose bolts or connections.
- Vibration during operation can cause components to loosen over time.
- Fuel Stability:
- Use fuel stabilizers for stored fuel.
- This prevents fuel degradation and maintains the generator’s efficiency.
- Professional Maintenance:
- Schedule regular professional generator servicing.
- Trained technicians can address complex issues and provide comprehensive maintenance.
- Record Keeping:
- Maintain a detailed maintenance log.
- Documenting repairs and servicing helps track the generator’s performance and informs future maintenance needs.
By incorporating these power generator maintenance tips, you ensure the reliability of your system, preventing unexpected failures and optimizing its overall performance.
Power Generator Safety Tips
When operating a power generator, safety is paramount to avoid accidents and ensure the smooth functioning of the equipment. Follow these essential tips to ensure the safe use of power generators:
- Proper Ventilation:
- Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of toxic gases like carbon monoxide.
- Place the generator outdoors or in a well-ventilated area to dissipate exhaust fumes.
- Fuel Storage:
- Store fuel in approved containers away from living spaces and potential ignition sources.
- Keep fuel containers tightly sealed to prevent leaks and spills that could lead to fire hazards.
- Regular Inspections:
- Conduct routine inspections of the generator for fuel leaks, loose connections, or any signs of wear.
- Address any issues promptly to prevent them from escalating into safety hazards.
- Electrical Connection:
- Use grounded extension cords to connect appliances to the generator.
- Avoid overloading the generator to prevent overheating and potential electrical fires.
- Grounding:
- Ensure proper grounding of the generator to prevent electric shock.
- Use grounding rods as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Distance Matters:
- Place the generator at a safe distance from buildings, windows, and vents to prevent exhaust infiltration.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding the recommended clearance.
- Fire Prevention:
- Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and ensure it is in working condition.
- Clear debris and flammable materials around the generator to minimize fire risks.
- Exhaust System Check:
- Regularly inspect and clean the exhaust system to prevent carbon buildup.
- Replace faulty mufflers promptly to maintain proper ventilation.
- Safe Shutdown:
- Turn off appliances before shutting down the generator to prevent sudden power surges.
- Follow the manufacturer’s shutdown procedure for a safe and efficient turn off.
- Educate Users:
- Provide clear instructions on generator operation and safety to all users.
- Highlight emergency procedures to ensure a quick and effective response in case of any issues.
Adhering to these power generator safety tips is crucial for a secure and efficient power supply, minimizing risks and ensuring a reliable energy source.
Conclusion
We hope that by the end of what is a power generator, you would have learned that a power generator is an essential device used to create electricity. Its basic principles involve converting mechanical energy into electrical energy, and there are several types of generators on the market to suit various applications.
When selecting a generator, consider factors like noise level, fuel efficiency, and cost. Fascinatingly, one large generator can produce enough electricity to power up to 30 average-sized homes! So the next time you’re in need of some extra juice for your home or business, make sure you invest in a reliable power generator.
References
- Development of 500 W PEM fuel cell stack for portable power generators
- Modeling low-bandgap thermophotovoltaic diodes for high-efficiency portable power generators
- Biomechanical energy‐driven hybridized generator as a universal portable power source for smart/wearable electronics
- Portable fuel cell power generator
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does a power generator cost?
The cost of a power generator can vary greatly, from as little as $100 to thousands of dollars. On average, you can expect to pay around $500 for a quality generator that will meet your energy needs.
Is a power generator easy to maintain?
Yes, a power generator is relatively easy to maintain. Regular maintenance checks and replacing any worn-out parts can help keep it running smoothly. You’ll also want to ensure fuel levels stay topped up for optimum performance.
How much power can a power generator generate?
It depends on the size and type of generator you have. Generally, a typical small to medium-sized generator can produce up to 10 kilowatts of power. Large generators can produce up to several hundred kilowatts or even megawatts of electricity.
Are power generators noisy?
Yes, power generators can be noisy. They often have a roaring sound that is like a thunderstorm in your backyard!
How often should a power generator be serviced?
You should service your power generator every few months to ensure it runs smoothly. Doing regular maintenance can help prevent any potential issues and keep it running efficiently.
What does a power generator do?
A power generator doesn’t generate electricity; instead, it transforms mechanical or chemical energy into electrical energy. By harnessing the power of motion, it compels electrons from an external source through an electrical circuit.
What is the function of a generator in power?
The generator serves as a device that converts mechanical energy from an external source into electrical energy. It’s crucial to note that a generator doesn’t generate electrical power; rather, it propels the movement of existing electrical charges in the wire of its windings using external mechanical power.
How do I power my house with a generator?
Estimate the home’s power needs first by listing items for portable generator use. Place the portable generator in a suitable location, plug it in, start the generator, and then connect devices and appliances. Lastly, ensure to refuel the portable generator for continuous power supply.

