In the realm of power solutions, the choice between a portable generator and an inverter generator can be pivotal. Understanding the Difference Between a Portable Generator and an Inverter Generator is akin to wielding the keys to uninterrupted power supply.
A portable generator packs a punch, offering robust power output suitable for heavy-duty applications. On the flip side, an inverter generator excels in precision, delivering clean power ideal for sensitive electronics. Navigating this choice hinges on your specific needs and preferences. In this guide, we will delve into the nuances of both, shedding light on their strengths and applications.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 What is a Portable Generator and How Does It Work?
- 3 What is an Inverter Generator and How Does It Work?
- 4 How Does a Portable Generator Produce Power?
- 5 How Does an Inverter Generator Produce Power?
- 6 What is the Difference Between a Portable Generator and an Inverter Generator?
- 7 Pros and Cons of Inverter Generators
- 8 Pros and Cons of Portable Generators
- 9 Applications of Inverter Generators
- 10 Applications of Portable Generators
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 References
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions
- 13.1 Can a Portable Generator Be Used for Sensitive Electronic Devices Like Laptops and Smartphones?
- 13.2 How Does the Noise Level of an Inverter Generator Compare to a Portable Generator?
- 13.3 Can an Inverter Generator Be Connected in Parallel With Another Generator for Increased Power Output?
- 13.4 Are There Any Specific Applications Where a Portable Generator Is More Suitable Than an Inverter Generator?
- 13.5 What Is the Average Runtime of a Portable Generator on a Full Tank of Fuel?
Key Takeaways
- Portable generators have higher power capacities and can run multiple appliances simultaneously.
- Inverter generators are more fuel-efficient due to their advanced technology.
- Inverter generators are designed to be more compact and efficient, leading to quieter operation.
- Inverter generators produce clean and stable power, ideal for sensitive electronic devices.
What is a Portable Generator and How Does It Work?
A portable generator is a versatile and convenient power source that can be easily moved to various locations, providing electricity when and where it’s needed. These generators are commonly used during power outages, outdoor events, or in remote areas where access to the electrical grid is limited.
Portable generators operate on the basic principle of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. The key components of a generator include an engine, an alternator, a fuel system, and a control panel.
The engine is typically fueled by gasoline or propane and is responsible for generating mechanical energy. As the engine runs, it drives a rotor inside the alternator. The rotor consists of a series of magnets surrounded by coils of wire.
As the rotor spins, it creates a changing magnetic field, inducing an electric current in the surrounding coils. This process is known as electromagnetic induction, and it forms the basis of how generators produce electricity. The generated electricity is then passed through the generator’s control panel, where it is regulated to provide a stable and usable power output.
In summary, a portable generator is a mobile power solution that converts mechanical energy from an engine into electrical energy through the process of electromagnetic induction. The simplicity of their design and variety of fuel options make them a practical choice for a range of applications, ensuring a reliable power supply in various situations.
What is an Inverter Generator and How Does It Work?
Unlike traditional generators, an inverter generator doesn’t run at a constant speed. Instead, it employs a sophisticated electronic system to adjust the engine speed based on the power demand.
So, how does an inverter generator work? At its core, it converts DC power to AC power through a multi-step process. First, the engine generates AC power, but this raw electricity is in the form of direct current (DC). The inverter then takes this DC power and transforms it into high-quality, stable AC power.
Why is this conversion process important? Well, the ability to produce high-quality power is a game-changer. Unlike conventional generators that produce electricity with fluctuations, inverter generators provide a consistent and clean power output. This makes them ideal for powering sensitive electronic devices like laptops, smartphones, and even medical equipment.
Moreover, the dynamic nature of inverter generators allows them to operate more efficiently. When the demand for power is low, the engine slows down, conserving fuel and reducing noise. When there’s a surge in demand, the engine revs up to meet it, ensuring a smooth and reliable power supply.
One notable advantage of inverter generators is their compact and lightweight design. Traditional generators tend to be bulkier and heavier, making them less practical for various applications. Inverter generators, on the other hand, are portable and easy to carry, making them a popular choice for camping, outdoor events, and as a backup power source during emergencies.
In summary, an inverter generator’s key features include its ability to produce clean and stable power, operate efficiently at varying loads, and its portability. These qualities make it a valuable and reliable power solution for a range of situations where a stable power supply is crucial.
How Does a Portable Generator Produce Power?
Portable generators are handy devices that provide a source of electricity when regular power sources are unavailable. Understanding the process by which these generators produce power is essential for their effective and safe use.
- Fuel Source:
- Portable generators typically run on gasoline, propane, or diesel.
- The fuel is stored in a designated tank attached to the generator.
- Engine Operation:
- The generator’s engine, similar to a car engine, is responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- The engine’s crankshaft starts rotating when fuel is ignited in the combustion chamber.
- Alternator Function:
- Connected to the engine, there is an alternator or generator head.
- As the crankshaft rotates, it turns the alternator, producing an alternating current (AC).
- Conversion to Electrical Power:
- The generated AC is then transformed into direct current (DC) by the alternator’s rectifier.
- DC is the form of electricity commonly used to power electronic devices.
- Voltage Regulation:
- The voltage produced can fluctuate, so there is a voltage regulator to ensure a steady and safe voltage output.
- This helps prevent damage to sensitive electronics connected to the generator.
- Power Outlets:
- The generator has outlets where users can plug in their devices.
- These outlets provide a convenient way to access the electricity generated by the generator.
How Does an Inverter Generator Produce Power?
Inverter generators have become popular for their efficient and stable power output. Unlike traditional generators, inverter generators utilize advanced technology to produce a consistent and reliable source of electricity. Let’s delve into the step-by-step process of how an inverter generator generates power.
- Generator Setup:
- Inverter generators start with a standard generator setup, including a fuel source (usually gasoline), an engine, and an alternator.
- AC Power Generation:
- The engine powers the alternator, producing alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the initial form of electrical output.
- Rectification:
- The generated AC power then undergoes a process called rectification. This involves converting AC power into direct current (DC).
- Inversion Process:
- The crucial step in inverter technology is the inversion process. The DC power is inverted back to AC power using sophisticated electronics.
- Voltage Regulation:
- Inverter generators excel in voltage regulation. The produced AC power is finely controlled to maintain a stable voltage, usually within a narrow range like 120V.
- Pure Sine Wave Output:
- Unlike conventional generators that produce a less stable power output, inverter generators produce a pure sine wave. This high-quality waveform is vital for powering sensitive electronics.
- Final Output:
- The result is a clean and stable AC power output with a consistent frequency and voltage, making it ideal for powering a wide range of devices, from laptops to refrigerators.

What is the Difference Between a Portable Generator and an Inverter Generator?
Here are the key differences between a portable generator and an inverter generator:
| Aspect | Portable Generator | Inverter Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Output | AC only, less stable, may have voltage spikes | AC converted to DC then back to stable AC |
| Size and Weight | Larger and heavier | Compact and lightweight |
| Fuel Efficiency | Less efficient, runs at constant speed | Highly efficient, adjusts to demand |
| Noise Level | Louder due to constant engine speed | Quieter due to variable engine speed |
| Total Harmonic Distortion | Higher THD, not suitable for sensitive electronics | Lower THD, safe for sensitive devices |
| Parallel Operation | Available, can connect with other generators | Available, allows for increased capacity |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Higher initial cost, but cost-effective in long run |
| Fuel Types | Can run on various fuels (gasoline, diesel, propane) | Typically run on gasoline or propane |
| Applications | Backup power for larger appliances and tools | Suitable for sensitive electronics, camping, and RVs |
| Portability | Slightly less portable due to size and weight | Highly portable, easy to transport |
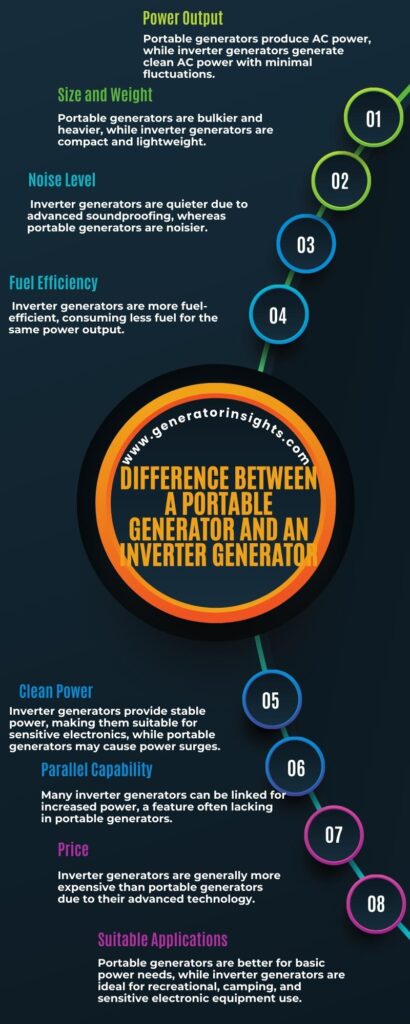
Now let’s discuss these differences in more detail.
Power Output
The power output of a generator is a critical factor to consider when choosing between a portable generator and an inverter generator. Power output refers to the amount of electrical power that a generator can produce. Both portable generators and inverter generators have different power capacities, which can greatly influence their performance in various applications.
Portable generators are known for their higher power capacities, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They are commonly used in construction sites, outdoor events, and as backup power sources for homes during emergencies. Portable generators are designed to provide a larger amount of power, enabling them to run multiple appliances and devices simultaneously. However, their high power capacity also means higher fuel consumption, making them less fuel-efficient compared to inverter generators.
On the other hand, inverter generators are designed to provide a more stable and reliable power output. They use advanced electronics to convert the raw power produced by the generator into a clean and consistent electrical supply. Inverter generators are more fuel-efficient due to their ability to adjust the engine speed based on the required power load. This feature not only reduces fuel consumption but also extends the generator’s runtime.
When considering the power output, it is essential to assess your specific power needs. If you require a higher power capacity and are willing to trade off fuel efficiency, a portable generator may be the better option. However, if you prioritize fuel economy and a stable power supply, an inverter generator would be more suitable.
Fuel Efficiency
When considering power output, it is important to also evaluate the fuel efficiency of both portable generators and inverter generators. Fuel efficiency refers to the amount of power generated per unit of fuel consumed.
Here are three important factors to consider when comparing the fuel efficiency of these generators:
- Inverter Technology: Inverter generators are known for their fuel efficiency due to their advanced technology. They have the ability to adjust the engine speed to match the power demand, resulting in optimal fuel consumption. This technology allows inverter generators to achieve higher fuel efficiency compared to traditional portable generators.
- Noise Reduction: Inverter generators are designed to operate at lower noise levels compared to portable generators. The noise reduction not only provides a more pleasant user experience but also indicates better fuel efficiency. Lower noise levels indicate that the generator is running more efficiently, consuming less fuel to produce the same amount of power.
- Environmental Impact: Inverter generators are known for their lower environmental impact due to their fuel efficiency. With reduced fuel consumption, they emit fewer greenhouse gases and pollutants. This makes them a more environmentally friendly option compared to portable generators.
In the next section, we will explore another important factor to consider when comparing portable generators and inverter generators – their noise level.
Noise Level
When comparing a portable generator and an inverter generator, one of the key factors to consider is the noise level. This is an important consideration as generators can produce significant noise, which can have an impact on the surrounding environment.
The noise levels of portable generators and inverter generators can be compared to assess the difference in their sound emissions. With advancements in technology, both types of generators have made significant progress in noise reduction. However, there are still notable differences in the noise levels between the two:
- Size and Design: Portable generators tend to be larger and bulkier, which can result in louder noise levels. Inverter generators, on the other hand, are designed to be more compact and efficient, leading to quieter operation.
- Engine Technology: Inverter generators use advanced engine technology, such as variable speed engines, which helps reduce noise levels by automatically adjusting the engine speed based on the required load. Portable generators typically have a fixed engine speed, resulting in a constant noise level.
- Noise Dampening Materials: Inverter generators often incorporate noise dampening materials in their construction, further reducing noise emissions. Portable generators may not have the same level of noise insulation.
Cost
Cost is a significant factor when comparing a portable generator to an inverter generator. While both types of generators serve the purpose of providing power in remote locations or during power outages, their cost profiles differ due to variations in technology and features.
Portable generators are generally more affordable upfront compared to inverter generators. They are designed to deliver raw power and are suitable for powering large appliances and tools. However, portable generators may not offer the same level of fuel efficiency and clean power output as inverter generators.
Inverter generators, on the other hand, are equipped with advanced technology that allows them to produce clean and stable power, making them ideal for sensitive electronic devices. Their ability to adjust engine speed based on the required load also contributes to their fuel efficiency, resulting in lower long-term operating costs.
While inverter generators may have a higher initial cost, their long-term cost benefits, such as reduced fuel consumption and maintenance requirements, can outweigh the upfront investment. Additionally, inverter generators are often quieter and more compact, making them a popular choice for recreational activities or situations where noise levels need to be minimized.
When considering the cost of a generator, it is essential to evaluate not only the upfront price but also the long-term cost implications, including fuel consumption, maintenance, and potential damage to sensitive equipment. This analysis will help determine the most cost-effective option based on individual needs and budget constraints.
Size and Portability
Size and portability are important factors to consider when comparing a portable generator and an inverter generator. When it comes to size, portable generators come in various sizes and weights depending on the power output they provide. Smaller portable generators are typically lighter and more compact, making them easier to transport and store. However, larger portable generators may offer higher power capacities but are bulkier and require more effort to move around.
On the other hand, inverter generators are designed with portability in mind. They are generally smaller and lighter than traditional portable generators. Inverter generators often come equipped with built-in handles or wheels, allowing for easy transportation. Some models even have telescopic handles and collapsible wheels for added convenience.
The portability features of inverter generators make them suitable for a variety of applications, such as camping, tailgating, or powering small appliances during power outages. Their compact design and ease of transportation make them an ideal choice for those who value mobility and versatility.
Battery Life and Capacity
With regards to battery life and capacity (runtime), inverter generators utilize advanced technology to maximize their performance and efficiency. Inverter generators typically have longer battery life compared to portable generators, thanks to their ability to adjust the engine speed based on the power demand. This feature not only saves fuel but also extends the battery life.
Additionally, inverter generators have a higher charging capacity, allowing them to recharge their batteries faster than portable generators. This means less downtime and more productivity. The battery life comparison between inverter generators and portable generators clearly favors the former, as they offer longer runtime and quicker recharging capabilities.
This makes inverter generators a preferred choice for those who require a reliable and efficient power source for extended periods of time.
Voltage Stability
When it comes to voltage stability, a key distinction between a portable generator and an inverter generator lies in their ability to maintain a consistent power output. Voltage regulation and power quality are essential factors to consider when choosing a generator, as they directly impact the performance and reliability of electrical appliances and equipment.
Portable generators typically use an alternator with a fixed speed engine, resulting in less precise voltage regulation. This can lead to fluctuations in power output, affecting the performance and lifespan of sensitive electronics. On the other hand, inverter generators utilize advanced electronic circuitry to produce clean and stable power. These generators use a variable speed engine that adjusts its RPM based on the load demand, resulting in a consistent voltage output.
To better understand the difference in voltage stability between portable generators and inverter generators, let’s compare them in the table below:
| Aspect | Portable Generator | Inverter Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Regulation | Less precise | Highly precise |
| Power Quality | Inconsistent | Clean and stable |
| Fluctuations | Common | Minimal |
As the table demonstrates, inverter generators offer superior voltage stability compared to portable generators. This makes them ideal for powering sensitive electronics such as laptops, smartphones, and medical equipment that require a consistent and clean power supply.
Parallel Capability
Parallel capability refers to the ability of generators to be connected together to increase power output. This feature offers increased versatility for larger loads, allowing users to meet their power requirements more efficiently.
Portable generators can achieve an amplified power output through the capability of being connected in parallel. This feature allows multiple portable generators to be linked together, increasing the overall power output to meet increased power demand or higher power output requirements.
Moreover when it comes to inverter generators, their parallel capability allows two units to be connected, working in tandem to effectively double the power capacity.
This feature is particularly advantageous in situations where a single generator may fall short in meeting the power demands. By connecting two inverter generators with parallel capability, users can achieve a combined power output without sacrificing the quality of the electrical supply. This is especially beneficial for outdoor activities, camping trips, or during power outages where the need for additional power can arise unexpectedly.
The process of connecting generators in parallel is straightforward. Most inverter generators equipped with this capability come with parallel kits that include the necessary cables and connectors. Connecting the generators involves linking the outlets of each unit with the parallel kit, ensuring synchronization in power delivery. This user-friendly setup allows individuals with limited technical knowledge to harness the benefits of increased power without complications.
Here are three benefits of increased power output through parallel capability:
- Scalability: By connecting multiple generators in parallel, users can easily scale up their power output as needed. This is particularly useful in situations where power demand fluctuates or when additional power is required for larger loads.
- Redundancy: Parallel capability provides a backup power solution. If one generator fails, the remaining parallel generators can continue to supply power, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Flexibility: Users can choose to connect or disconnect generators as needed, allowing them to customize their power output based on specific requirements.
Pros and Cons of Inverter Generators
Inverter generators have become popular for their versatility and efficiency. Let’s explore the pros and cons of these generators:
Pros and Cons of Portable Generators
Portable generators are a popular choice for various applications. Let’s delve into their pros and cons:
Applications of Inverter Generators
- Camping and RVing: Ideal for providing quiet and clean power for electronic devices without disturbing the outdoor experience.
- Tailgating Events: Portable and efficient for powering small appliances, grills, and entertainment equipment during tailgating parties.
- Backup Power at Home: Perfect for powering essential electronics during power outages, ensuring a continuous and stable energy supply.
- Outdoor Events: Suited for providing electricity to outdoor parties, weddings, or any event where a reliable power source is needed.
- Charging Electronics: Safely charges sensitive electronics like smartphones, laptops, and cameras due to their stable power output.
- Construction Sites: Can be used to run power tools and equipment on construction sites, providing a reliable and fuel-efficient power source.
- Boating and Fishing Trips: Compact and portable, making them convenient for providing power on boats or during fishing trips.
- Emergency Preparedness: Valuable for emergency situations, as inverter generators offer a reliable source of power for medical equipment and essential appliances.
Applications of Portable Generators
- Emergency Backup Power: Essential during power outages, portable generators can keep refrigerators, lights, and other vital appliances running.
- Construction Sites: Well-suited for powering tools and equipment at construction sites where a temporary and mobile power source is necessary.
- Outdoor Events and Parties: Perfect for providing electricity for outdoor gatherings, parties, and events, running lights, sound systems, and other equipment.
- Camping and Outdoor Activities: Portable generators are handy for camping trips, providing power for cooking appliances, lights, and charging devices.
- RV and Boating: Ideal for powering appliances and electronics in RVs and boats, enhancing the comfort and convenience of recreational vehicles.
- Remote Work: Valuable for powering electronic devices and equipment when working in remote locations without access to traditional power sources.
- Farming and Agriculture: Useful on farms for various applications, such as running electric fences, water pumps, and other agricultural equipment.
- DIY Projects at Home: A portable generator can be beneficial for DIY enthusiasts, providing power for electric tools and equipment in locations without easy access to outlets.
- Tailgating and Sporting Events: Convenient for tailgating parties and sporting events, powering grills, TVs, and other entertainment equipment.
Conclusion
Ultimately, grasping the Difference Between a Portable Generator and an Inverter Generator empowers you to make an informed decision tailored to your unique power requirements. Whether it’s the brawny might of a portable generator or the refined finesse of an inverter generator, both hold their place in the arsenal of power solutions. By weighing the pros and cons against your needs, you can ensure a seamless power supply in any situation.
So, whether you’re embarking on outdoor adventures or safeguarding your home during outages, understanding these distinctions paves the way for a reliable and tailored power solution.
References
- Electrical generators for large wind turbine: Trends and challenges
- Bio-inspired water-driven electricity generators: From fundamental mechanisms to practical applications
- Power electronic drives, controls, and electric generators for large wind turbines–an overview
- Stabilization of two electricity generators
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Portable Generator Be Used for Sensitive Electronic Devices Like Laptops and Smartphones?
Portable generators have limitations when it comes to powering sensitive electronic devices like laptops and smartphones. Inverter generators, on the other hand, offer advantages such as stable and clean power output, making them more suitable for such devices.
How Does the Noise Level of an Inverter Generator Compare to a Portable Generator?
The noise level of an inverter generator is significantly lower compared to a portable generator. This is one of the key benefits of using an inverter generator, as it allows for quieter operation in various settings.
Can an Inverter Generator Be Connected in Parallel With Another Generator for Increased Power Output?
Yes, an inverter generator can be connected in parallel with another generator to increase power output. This is advantageous for camping or outdoor activities where a higher power capacity is required.
Are There Any Specific Applications Where a Portable Generator Is More Suitable Than an Inverter Generator?
In specific use cases where noise level is not a concern and a higher power output is needed, a portable generator may be more suitable than an inverter generator due to its advantages in terms of cost, fuel efficiency, and versatility. However, it is important to consider the disadvantages such as heavier weight and potential voltage fluctuations.
What Is the Average Runtime of a Portable Generator on a Full Tank of Fuel?
The average runtime of a portable generator on a full tank of fuel depends on its fuel consumption rate, which varies based on the generator’s power output. Portable generators offer benefits such as portability and versatility in powering various appliances and equipment.

