In the midst of a power outage, the whirr of a generator is a lifeline, promising warmth and illumination. Yet, what happens when that dependable companion is overloaded, teetering on the edge of exhaustion? The answer lies in understanding How to Fix an Overloaded Generator.
Picture this: a chilly evening, your trusted generator protesting under the weight of demand. Fear not, for within these words, we unravel the secrets to revive your faithful ally. It’s not just a machine; it’s the guardian of your comfort. Let’s embark on a journey to nurture it back to strength, ensuring that when darkness falls, your generator stands resilient, ready to illuminate your world.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Main Highlights
- 2 What is Overloading?
- 3 What Makes a Generator Overloaded?
- 4 What are the Signs of an Overloaded Generator?
- 5 How to Fix an Overloaded Generator?
- 6 What Happens when a Generator Gets Overloaded?
- 7 How to Restart an Overloaded Generator?
- 8 How to Prevent a Generator from Overloading?
- 9 Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
- 10 Generator Maintenance Tips
- 11 Generator Safety Tips
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 References
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions
- 14.1 Can an overloaded generator cause damage to my electrical appliances?
- 14.2 How often should I perform regular maintenance on my generator?
- 14.3 Can I use an extension cord to reduce the load on the generator?
- 14.4 What are the common signs of an overloaded generator?
- 14.5 Are there any specific safety precautions I should take while allowing the generator to cool down?
- 14.6 What happens if you put too much load on a generator?
- 14.7 What causes overload on a generator?
- 14.8 Will overloading a generator damage it?
Main Highlights
- Regularly cleaning and replacing air filters is crucial for maintaining generator performance and extending its lifespan.
- Checking the oil level regularly and maintaining it at the recommended mark on the dipstick is essential to prevent engine damage and ensure efficient generator functioning.
- Inspecting and cleaning or replacing the spark plug is important for proper combustion efficiency and diagnosing potential issues with fuel ignition.
- It is important to inspect fuel lines for any damage or obstruction to prevent generator overload issues, and seeking professional help is recommended for complex problems.
What is Overloading?
Overloading transpires when the current flowing through a circuit surpasses its maximum permissible limit. This can happen due to excessive use of devices connected to the circuit or the introduction of power-hungry components. The outcome is an elevated temperature within the circuit, which, if unchecked, can lead to permanent damage.
When a circuit undergoes overloading, the electronic components within it, such as resistors, transistors, and integrated circuits, may experience stress beyond their tolerances. This can result in performance degradation, shortened lifespan, or, in extreme cases, outright failure. Recognizing the signs of overloading is crucial for preventing irreparable damage to electronic systems.
What Makes a Generator Overloaded?
Understanding the various causes of generator overload is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing potential damage. Let’s explore the factors that can contribute to a generator becoming overloaded:
- Exceeding Power Capacity:
- Connecting appliances or equipment that collectively draw more power than the generator’s rated capacity.
- Simultaneous Operation of High-Wattage Devices:
- Running multiple high-wattage appliances at the same time, leading to increased power demand.
- Malfunctioning Voltage Regulators:
- Issues with the voltage regulator can result in the generator producing excess power.
- Incorrect Generator Sizing:
- Choosing a generator with a capacity that is insufficient for the intended power requirements.
- Fuel Supply Problems:
- Inadequate fuel supply or a clogged fuel filter affecting the generator’s efficiency.
- Unstable Electrical Load:
- Fluctuations and spikes in the electrical load can contribute to generator overload.
- Lack of Cooling:
- Inadequate ventilation causing the generator to overheat during operation.
By recognizing these causes, users can take proactive measures to prevent generator overload and ensure the smooth functioning of their power supply systems.
What are the Signs of an Overloaded Generator?
Recognizing the signs of an overloaded generator is essential to prevent potential damage and ensure its longevity.
- Flickering Lights: Lights flickering or dimming inconsistently can indicate an overloaded generator. The generator may struggle to meet the power demand, causing fluctuations in the electrical supply.
- Overheating: Unusual heat emanating from the generator is a clear sign of overloading. Excessive load can lead to overheating, potentially damaging the generator’s internal components.
- Tripped Circuit Breakers: Frequent tripping of circuit breakers is an indication of an overloaded generator. When the generator surpasses its capacity, circuit breakers trip to prevent damage.
- Reduced Power Quality: Appliances and devices not operating at their full capacity suggest an overloaded generator. Overloading may compromise the quality of power supplied, affecting the performance of connected devices.
- Unusual Sounds: Grinding or buzzing noises coming from the generator may signal overloading. The increased stress on the engine and components can lead to abnormal sounds.
- Fuel Efficiency Drop: A sudden decrease in fuel efficiency is a sign of an overloaded generator. Overloaded generators consume more fuel than necessary, affecting efficiency and increasing operational costs.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Unstable voltage levels indicate an overloaded generator. The generator may struggle to maintain consistent voltage, leading to fluctuations that can damage sensitive electronics.
- Warning Lights or Alarms: Activation of warning lights or alarms on the generator is a clear indication of overloading. Modern generators are equipped with safety features that alert users to overloads, ensuring timely intervention.
Recognizing these signs of an overloaded generator is crucial for prompt action, preventing potential damage and ensuring the reliable functioning of your power supply system.

How to Fix an Overloaded Generator?
Addressing the causes of generator overload is essential for maintaining optimal functionality and preventing potential damage. Let’s explore how to fix an overloaded generator effectively:
- Exceeding Power Capacity:
- Calculate the total power demand before connecting devices, ensuring it does not surpass the generator’s rated capacity.
- Simultaneous Operation of High-Wattage Devices:
- Prioritize and stagger the use of high-wattage appliances, preventing simultaneous operation to avoid overloading.
- Malfunctioning Voltage Regulators:
- Regularly inspect and maintain the voltage regulator, ensuring it operates correctly to prevent overloading.
- Incorrect Generator Sizing:
- Choose a generator that matches your power needs, considering both continuous and surge power requirements.
- Fuel Supply Problems:
- Regularly check and maintain fuel levels and filters, ensuring a consistent fuel supply to prevent overloading.
- Unstable Electrical Load:
- Stabilize the electrical load by using surge protectors and avoiding sudden power surges.
- Lack of Cooling:
- Ensure adequate airflow around the generator, preventing overheating and potential overload.
Implementing these solutions mitigates the risk of generator overload, ensuring the reliable operation of power supply systems.
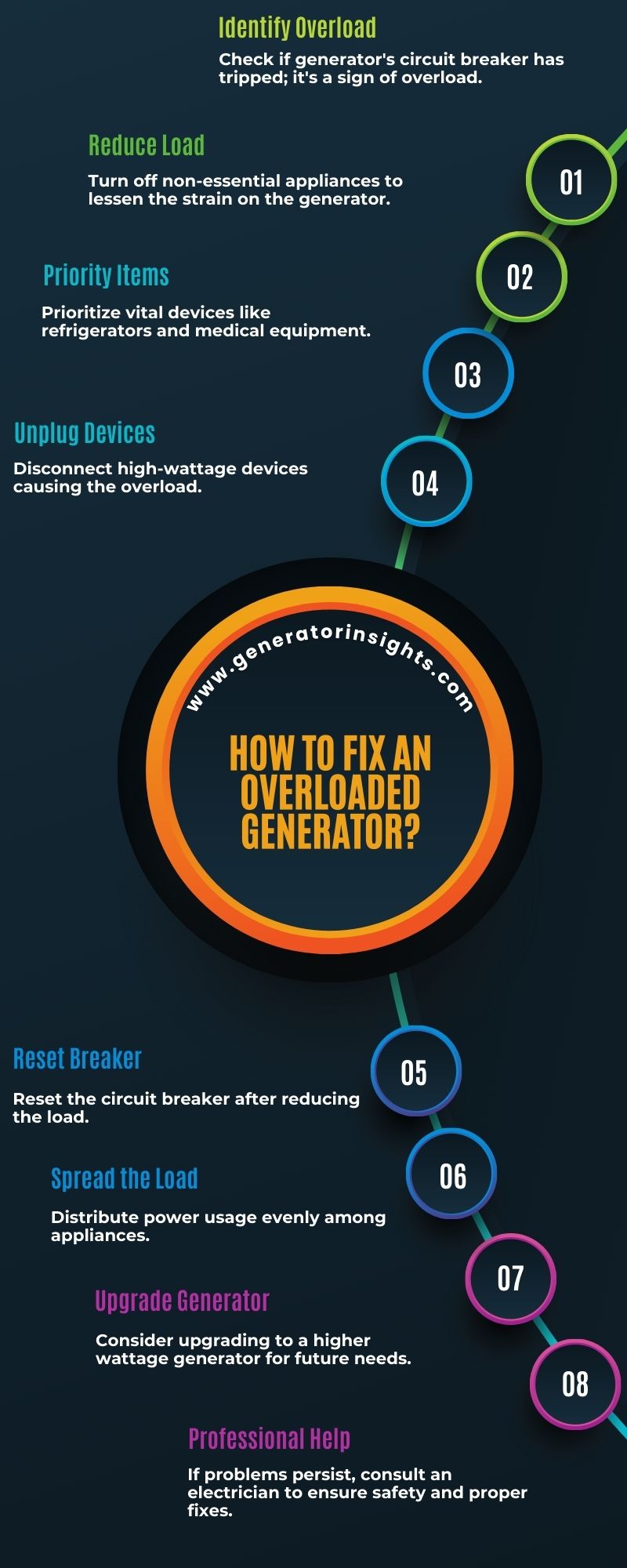
Now let’s discuss a step-by-step systematic approach of how to fix an overloaded generator.
Identify the Cause of Overload
The cause of an overloaded generator can be determined by analyzing the specific electrical load requirements and comparing them to the generator’s capacity. To troubleshoot an overloaded generator, it is important to understand the signs of overload.
One common sign is when the circuit breaker trips frequently or when fuses blow repeatedly. This indicates that the generator is unable to handle the electrical load being placed on it. Another sign is when appliances or equipment connected to the generator are not operating at their full capacity or are running slower than usual.
To identify the cause of overload, it is necessary to calculate the total power demand of all connected devices and compare it to the rated power output of the generator. Ensure that no single device exceeds its rated wattage and consider using a power meter for accuracy. Additionally, check if any devices have short circuits, as they can cause excessive current draw.
To reduce the load on the generator and prevent overloading, prioritize essential appliances and disconnect non-essential ones. Consider redistributing some loads by connecting certain devices to different circuits or using multiple generators if available.
By understanding troubleshooting tips and recognizing signs of overload, one can effectively address an overloaded generator situation without compromising safety or performance.
Reduce the Load on the Generator
To alleviate the strain on the power source, it is crucial to implement measures that minimize the burden placed upon it. To reduce the load on an overloaded generator, increasing efficiency and ensuring proper usage are key.
One way to increase efficiency is by optimizing the power consumption of connected devices. This can be achieved by using energy-efficient appliances and turning off unnecessary electrical equipment. Additionally, redistributing the load across multiple generators can help balance the power demand more effectively.
Proper usage of a generator is also essential in reducing its load. This involves avoiding overloading by not connecting devices that surpass the generator’s capacity. It is important to consult the generator’s user manual or consult a professional to determine its maximum load capacity. Furthermore, regular maintenance and servicing of the generator can improve its performance and prevent overload situations.
By implementing these measures, users can mitigate excessive strain on their generators and ensure they operate within safe parameters. Checking fuel levels and filters is another crucial step to maintain optimal performance of a generator without compromising its longevity or causing damage due to overload situations.
Check the Fuel Levels and Filters
One effective strategy for maintaining optimal performance and preventing damage to a power source is regularly checking the fuel levels and filters. By ensuring that the generator has an adequate supply of clean fuel, it can operate efficiently and avoid potential issues caused by contaminated or insufficient fuel.
Additionally, regularly inspecting and cleaning the filters helps to prevent clogs and blockages that could hinder the proper flow of fuel.
To effectively check the fuel levels and filters, it is important to follow a systematic approach. Firstly, ensure that there is enough fuel in the tank by visually inspecting the gauge or dipstick. If needed, refuel with clean, high-quality gasoline or diesel. Secondly, locate the fuel filter(s) in your generator system and examine them for any signs of dirt or debris accumulation. Clean or replace as necessary according to manufacturer guidelines.
By carefully following these steps, you can help ensure that your generator operates optimally without any hindrances caused by inadequate fuel supply or dirty filters. Once these checks have been completed successfully, it is essential to proceed with allowing the generator sufficient time to cool down before performing additional maintenance tasks.
Allow the Generator to Cool Down
After completing the necessary maintenance checks on your generator, it is crucial to allow sufficient time for the equipment to cool down before proceeding with any further tasks. This step is vital in ensuring that the generator operates optimally and efficiently.
To begin, check the wiring connections of the generator to ensure they are secure and free from any loose or damaged wires. Loose connections can lead to overheating and potential damage to both the generator and connected devices.
Next, monitor the generator’s temperature closely during operation. Excessive heat can cause malfunctions and decrease its lifespan. It is recommended to use a digital thermometer specifically designed for measuring generator temperature. Keep an eye on any sudden spikes or fluctuations in temperature as they may indicate underlying issues that need immediate attention.
Once you have allowed ample time for the generator to cool down, you can proceed with resetting the circuit breaker if necessary. This will help restore power flow in case of an overload or short circuit.
By following these steps diligently, you can ensure proper functioning of your overloaded generator and avoid potential hazards or damage caused by excessive heat or faulty wiring connections.
Reset the Circuit Breaker
Resetting the circuit breaker is akin to pressing a reset button on an electrical system, allowing for the restoration of power flow and addressing any potential overload or short circuit. When a generator becomes overloaded, it can trip the circuit breaker to protect itself from damage.
To reset the circuit breaker and resolve the issue, follow these steps:
- Locate the circuit breaker panel: The panel contains individual breakers that control different circuits in your electrical system.
- Turn off all appliances: Before resetting the circuit breaker, it is important to turn off all connected appliances to prevent further overload.
- Find the tripped breaker: Identify which breaker has been tripped by looking for one that is in between its ‘on’ and ‘off’ position.
- Reset the breaker: Push the tripped breaker firmly into its ‘off’ position and then back to its ‘on’ position until you feel it click.
By successfully resetting the circuit breaker, you have addressed any potential overload or short-circuit issues.
However, it is important to note that constantly resetting breakers may indicate an underlying problem with your generator’s load capacity. To avoid future overloads, consider adjusting your load capacity or limiting simultaneous use of high-power appliances.
Seek Professional Help if Needed
If the issue persists despite attempting basic troubleshooting methods, it may be prudent to seek assistance from a qualified professional in order to rectify the problem with an overloaded generator.
While some individuals may prefer a do-it-yourself approach, seeking professional help ensures that the issue is addressed effectively and efficiently. Professional technicians possess the necessary expertise and tools to diagnose and resolve complex problems that may arise with an overloaded generator.
To better understand the signs of generator overload and determine if professional help is required, refer to the table below:
| Signs of Generator Overload | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Frequent tripping | Excessive power demand |
| Dimming or flickering lights | Insufficient fuel supply or faulty wiring |
| Strange noises | Overheating due to heavy load |
By observing these signs, individuals can gauge whether they require professional intervention. Seeking expert assistance not only saves time but also prevents further damage or potential safety hazards. Additionally, professionals can provide valuable advice on maintenance practices and recommend suitable upgrades for future power needs.
In conclusion, when faced with persistent issues related to an overloaded generator, it is advisable to engage qualified professionals who possess the technical knowledge and experience necessary for resolving such problems efficiently.
What Happens when a Generator Gets Overloaded?
When a generator is pushed beyond its capacity, various consequences can arise. Let’s delve into the specifics of what happens when a generator gets overloaded:
- Decreased Efficiency:
- An overloaded generator struggles to produce power efficiently.
- Energy wastage increases, leading to higher operational costs.
- Overheating:
- Excessive load causes the generator’s components to heat up.
- Overheating can result in damage to the generator and pose safety risks.
- Voltage Fluctuations:
- Overloading can lead to voltage fluctuations.
- This instability can harm connected devices and disrupt their functionality.
- Breakdown and Damage:
- Prolonged overloading may lead to a generator breakdown.
- Critical components may suffer irreversible damage, necessitating costly repairs.
- Shortened Lifespan:
- Overloading accelerates wear and tear on the generator.
- The lifespan of the generator is significantly reduced with consistent overloading.
How to Restart an Overloaded Generator?
Dealing with an overloaded generator can be a challenging situation, but with the right steps, you can safely restart it. Follow these guidelines to ensure a smooth and efficient process:
- Assess the Load: Before taking any action, evaluate the current load on the generator. Identify the appliances or equipment causing the overload.
- Turn Off Non-Essential Appliances: To reduce the load on the generator, switch off any non-essential appliances or devices. This step helps prevent a recurrence of the overload.
- Allow Cooling Time: An overloaded generator can overheat. Give it sufficient time to cool down before attempting a restart. This could involve waiting for 10-15 minutes, depending on the generator type.
- Reset the Circuit Breaker: Most generators have a built-in circuit breaker. Locate the breaker and reset it, ensuring it’s in the “off” position before attempting a restart.
- Start the Generator: Once the circuit breaker is reset, start the generator following the manufacturer’s instructions. Be gradual in applying the load to avoid another overload.
- Monitor Load Conditions: After restarting, keep a close eye on the load. Gradually reconnect essential appliances, ensuring you don’t exceed the generator’s capacity.
By following these steps, you can effectively address an overloaded generator situation and resume power supply safely.
How to Prevent a Generator from Overloading?
Follow these essential tips to prevent a generator from overloading:
- Calculate Power Requirements:
- Determine the wattage of all connected devices.
- Use a reliable online tool to estimate the total power needed.
- Ensure the generator’s capacity exceeds the calculated wattage.
- Understand Generator Capacity:
- Identify the rated and maximum capacity of your generator.
- Operate within the rated capacity to avoid overheating and wear.
- Avoid consistently running the generator at maximum capacity.
- Prioritize Essential Devices:
- Prioritize critical appliances during power outages.
- Connect high-priority devices first to avoid exceeding limits.
- Consider using a separate circuit for non-essential items.
- Monitor Load Balance:
- Regularly check the load balance on the generator.
- Avoid uneven distribution to prevent certain outlets from overloading.
- Use extension cords of appropriate size and capacity.
- Invest in a Load Management System:
- Consider a load management device to distribute power intelligently.
- Automatically control power to different circuits based on demand.
- Ideal for scenarios where fluctuating power needs are common.
- Use Inrush Current Limiters:
- Install inrush current limiters to control the initial surge.
- Prevent spikes in power demand when devices start up.
- Commonly used for refrigerators, air conditioners, and other high-power appliances.
- Regular Maintenance Checks:
- Schedule routine maintenance to ensure the generator operates efficiently.
- Clean air filters, inspect wiring, and check fuel levels regularly.
- Replace worn-out parts promptly to avoid strain on the generator.
- Emergency Shut-Off Procedures:
- Familiarize yourself with the emergency shut-off feature.
- Activate it in case of a potential overload or malfunction.
- Ensure everyone using the generator understands the shut-off procedure.
Remember, preventing generator overload is not just about maintaining the machine but also about ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply during crucial times.
Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
Generators are indispensable during power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply. However, users may encounter issues that hinder their optimal performance. Below is a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot common generator issues and restore seamless operation.
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Engine Fails to Start | – Silent operation | – Check fuel levels and ensure there’s an adequate supply. |
| – Starter motor cranks but fails to ignite | – Inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or wear. Replace if necessary. | |
| – Strong smell of gasoline | – Examine the carburetor for blockages and clean or replace if needed. | |
| 2. Low Power Output | – Dimming lights and fluctuating power output | – Verify the load capacity and ensure it doesn’t exceed the generator’s limit. |
| – Appliances not running at full capacity | – Inspect the voltage regulator for malfunctions and replace if necessary. | |
| 3. Generator Overheating | – Unusual heat emanating from the generator | – Check the cooling system, including the radiator and coolant levels. Clean or replace components as required. |
| – Frequent shutdowns due to overheating | – Ensure proper ventilation around the generator and clean any debris obstructing airflow. | |
| 4. Excessive Noise Levels | – Unusual or loud sounds during operation | – Inspect the muffler for damage and replace if needed. Adjust engine RPM to recommended levels. |
| – Vibrations and rattling noises | – Tighten any loose bolts and secure all components properly. | |
| 5. Electric Shock from Generator | – Users experiencing electric shocks | – Immediately disconnect the generator from the power source. Inspect and repair any damaged wiring or outlets. |
| – Tingling sensation when touching the generator | – Check for grounding issues and ensure the generator is properly grounded. | |
| 6. Smoke Emission | – Visible smoke during operation | – Examine the oil level and quality. Change oil if it appears dirty or insufficient. |
| – Unpleasant burning smell | – Inspect the air filter for clogs and replace if necessary. | |
| 7. Fuel Leaks | – Noticeable fuel odors or wet spots around the generator | – Check the fuel lines and connections for leaks. Replace any damaged components. |
| – Decreased fuel efficiency | – Tighten loose fuel fittings and ensure the fuel tank is securely sealed. | |
| 8. Battery Issues | – Difficulty starting the generator | – Inspect the battery for corrosion or loose connections. Replace if necessary. |
| – Weak or dead battery | – Charge or replace the battery as needed. | |
| 9. Generator Running Rough | – Uneven or shaky operation – Check the air-fuel mixture; adjust the carburetor to ensure the correct ratio. Inspect for clogged fuel injectors. | – Fluctuating RPMs – Inspect the ignition system for issues. Replace faulty spark plugs or ignition coils as necessary. |
Addressing these common generator issues promptly will help maintain the reliability of your power source. If problems persist, consider seeking professional assistance for more complex diagnostics and repairs.
Generator Maintenance Tips
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, making a well-maintained generator crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply. Regular maintenance not only enhances longevity but also guarantees optimal performance. Here are some key tips to keep your generator in top shape:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct routine checks on your generator to identify any signs of wear, loose connections, or potential issues before they escalate.
- Fluid Levels: Regularly check and replenish the oil and fuel levels to guarantee efficient operation. Proper lubrication is essential for preventing friction-related damage.
- Battery Health: Ensure the generator’s battery is charged and in good condition. A healthy battery is vital for a swift start when power is needed.
- Air Filter Checks: Keep the generator’s air filter clean and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer. A clogged filter can compromise performance and fuel efficiency.
- Coolant System Inspection: Verify the coolant levels and inspect the system for leaks. Overheating can lead to severe damage, so maintaining the right coolant levels is crucial.
- Capacitor Maintenance: Check and test the generator’s capacitors regularly. Faulty capacitors can lead to electrical issues, affecting the generator’s ability to produce a consistent power output.
- Run the Generator Regularly: Regularly starting the generator, even if it’s not in use, helps keep the engine components lubricated and prevents fuel system issues.
- Storage Considerations: If the generator is stored for an extended period, use a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel deterioration. Empty the fuel tank or run the generator dry before storage to avoid gumming.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, you’ll ensure that your generator is ready to provide reliable power when you need it the most.
Generator Safety Tips
Generators are indispensable for providing power during outages, but ensuring their safe operation is paramount. Here are essential Generator Safety Tips to keep in mind:
- Proper Ventilation: Always operate generators in well-ventilated areas to prevent the buildup of harmful gases like carbon monoxide.
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific generator model to understand its unique safety requirements.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks on the generator, including fuel lines, filters, and oil levels, to guarantee optimal performance and identify potential issues early.
- Keep Flammable Materials Away: Position the generator away from flammable materials to reduce the risk of fire hazards.
- Carbon Monoxide Alarms: Install and regularly test carbon monoxide detectors near the generator area to provide an early warning of any dangerous gas levels.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of the generator to prevent electrical shocks and protect both the equipment and users.
- Fuel Safety: Store fuel in approved containers, away from heat sources, and follow guidelines for proper storage to avoid spills and contamination.
- Emergency Shutdown: Understand and practice the emergency shutdown procedures to swiftly respond to potential dangers.
- Children and Pets: Keep children and pets away from the generator during operation to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Avoid Overloading: Respect the generator’s rated capacity and avoid overloading it to maintain efficient and safe operation.
- Cooling Time: Allow the generator to cool down before refueling to prevent accidental fires or burns. Follow the recommended cooldown period specified in the manual.
- Secure Placement: Place the generator on a stable, flat surface to prevent tipping and ensure safe operation. Avoid placing it on uneven or sloped terrain.
- Regular Testing: Periodically run the generator to ensure it starts easily and operates smoothly. This practice helps identify potential issues before they become major problems during an emergency.
- Extension Cord Safety: If using extension cords, ensure they are of sufficient gauge for the load and in good condition. Overloading cords can lead to overheating and pose a fire risk.
- Weather Considerations: Shelter the generator from the elements to protect it from rain and snow. Use appropriate covers or enclosures designed for your specific generator model.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule regular professional inspections to check for hidden issues and ensure all components are in good working order. This is especially important for standby generators.
- Emergency Services Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency shut-off switches and how to quickly contact relevant services in case of a malfunction or emergency.
- Storage Precautions: If the generator is not in use for an extended period, follow proper storage procedures. This includes draining the fuel, disconnecting the battery, and storing it in a dry, cool place.
- Educate Users: Ensure that anyone who may need to operate the generator is familiar with its safety features and operation. Provide clear instructions to prevent accidents caused by misuse.
- Legal Compliance: Be aware of and adhere to local regulations regarding generator usage, emissions, and noise levels. Non-compliance may result in fines or other penalties.
Remember, adhering to these Generator Safety Tips is crucial to ensure the reliable and secure use of your generator.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing how to fix an overloaded generator is essential for maintaining its efficiency and longevity. The tips provided in this guide enable you to identify the signs of an overloaded generator and take prompt action. From reducing the load and redistributing power to upgrading your generator’s capacity, addressing an overload ensures uninterrupted power supply and prevents potential damage.
As you navigate the challenges of power management, let this guide be your resource, guiding you through the process of resolving an overloaded generator and ensuring its reliable performance in times of need.
References
- Biomechanical energy‐driven hybridized generator as a universal portable power source for smart/wearable electronics
- Portable fuel cell power generator
- A thermophotovoltaic micro-generator for portable power applications
- Fuel cells-the clean and efficient power generators
Frequently Asked Questions
Can an overloaded generator cause damage to my electrical appliances?
An overloaded generator can potentially cause damage to electrical appliances. Preventing generator overload and troubleshooting an overloaded generator are essential in order to protect your appliances from potential harm.
How often should I perform regular maintenance on my generator?
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity of a generator. Determining the optimal maintenance schedule depends on factors such as usage, manufacturer recommendations, and environmental conditions. Following these guidelines will help maintain peak performance and prevent costly breakdowns.
Can I use an extension cord to reduce the load on the generator?
Using a power strip or extension cord to reduce the load on a generator can be risky. It may lead to overheating and damage. Proper grounding is essential for safety and preventing electrical hazards.
What are the common signs of an overloaded generator?
Common signs of an overloaded generator include flickering lights, appliances not running at full power, unusual noises or smells, and the generator’s engine overheating. Preventing generator overload involves proper load management and regular maintenance to avoid overheating.
Are there any specific safety precautions I should take while allowing the generator to cool down?
When allowing a generator to cool down, it is important to follow specific safety precautions. These include ensuring proper ventilation, avoiding contact with hot surfaces, and refraining from refueling until the generator has completely cooled down to prevent accidents or injuries.
What happens if you put too much load on a generator?
In the event of an overload, the generator’s circuit breaker will trip, disconnecting the unit from the load. To resolve the overload, one should correct the issue causing it and then reset the generator’s breaker.
What causes overload on a generator?
Generator overload is often triggered by damaged or worn components within the generator. An indication of this is observing the generator’s exhaust pipe. While dark smoke is normal, the presence of black soot residue after use suggests a potential issue with the components.
Will overloading a generator damage it?
Overloading a generator not only reduces its lifespan but also risks damaging vital components. Operating the generator beyond its capacity or allowing it to become excessively hot can lead to the burning out of the alternator and other crucial parts, ultimately shortening the equipment’s overall life.

