In the hustle of modern living, power outages can throw a wrench into our daily routines. The lingering question on many minds is, Can you run a portable generator in the garage? Safety concerns and the desire for convenience collide in the quest for a reliable power source.
Picture a scenario where you seamlessly bridge the gap between comfort and preparedness. As the hum of uncertainty surrounds you, this question becomes a beacon of practicality. Let’s delve into the realm of possibilities, exploring the delicate balance between necessity and precaution. The answer may lie in finding harmony within the heartbeat of your home.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Key Points
- 2 What is a Portable Generator and How it Works?
- 3 Can You Run a Portable Generator in the Garage?
- 4 Dangers of Running a Portable Generator in the Garage
- 5 How to Run a Generator Safely in Garage?
- 6 How to Properly Place a Generator?
- 7 How to Properly Store a Generator when Not in Use?
- 8 Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
- 9 Generator Maintenance Tips
- 10 Generator Safety Tips
- 11 Conclusion
- 12 References
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions
- 13.1 Can I Use a Portable Generator in My Garage if It’s Well-Ventilated?
- 13.2 How Far Should I Place the Generator From the Walls in My Garage?
- 13.3 Is It Safe to Run a Generator in My Attached Garage?
- 13.4 Can I Use a Portable Generator in My Garage if I Have a Carbon Monoxide Detector?
- 13.5 Are There Any Specific Safety Precautions I Need to Take When Running a Generator in the Garage During Winter?
- 13.6 Can you run a portable generator in the garage with the door open?
- 13.7 What happens if you put a generator in a garage?
- 13.8 How much ventilation does a portable generator need?
Key Points
- Running a portable generator in an enclosed space poses serious risks, primarily due to the release of colorless and odorless Carbon Monoxide (CO) gas from the exhaust.
- CO exposure can lead to poisoning, with symptoms ranging from headaches and dizziness to more severe complications, including nausea and confusion.
- Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of CO can be fatal, as it competes with oxygen in the bloodstream, reducing vital organ oxygenation.
- To mitigate risks, always operate generators in well-ventilated areas, preferably outdoors, to prevent the rapid accumulation of CO and ensure the safety of individuals.
What is a Portable Generator and How it Works?
A portable generator is a compact and movable power solution that converts fuel, such as gasoline or propane, into electricity. Unlike stationary generators, which are typically installed permanently, portable generators are mobile and can be easily transported to different locations. This flexibility makes them ideal for camping trips, outdoor events, or as a backup power source during emergencies.
Portable generators typically come equipped with essential features such as multiple power outlets, circuit breakers, and fuel gauges. Some advanced models may include inverter technology for stable and clean power output, ensuring the safe operation of sensitive electronics like laptops and smartphones.
At the core of a portable generator is an internal combustion engine that drives an alternator to generate electricity. The process begins with the combustion of fuel within the engine, creating mechanical energy. This energy is then converted into electrical energy through the alternator, which produces an electric current. The generated electricity is channeled through outlets on the generator, allowing users to connect their devices or appliances.

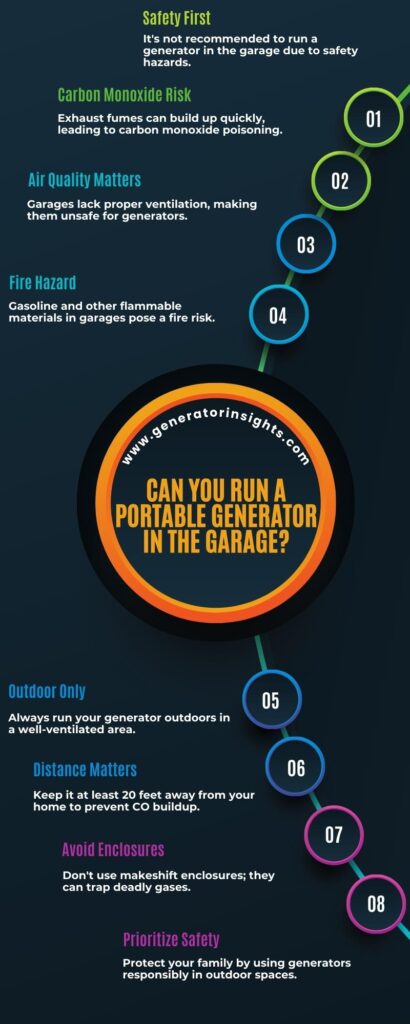
Can You Run a Portable Generator in the Garage?
Running a portable generator in an enclosed space like a garage poses serious risks due to the release of Carbon Monoxide (CO), a colorless and odorless gas produced by the generator’s exhaust. When a generator operates in a confined area, the ventilation is limited, allowing CO to accumulate rapidly.
Exposure to elevated levels of CO can result in poisoning, and the symptoms can vary in severity. Initially, individuals may experience mild symptoms such as headaches and dizziness. However, with prolonged exposure or high concentrations of CO, the effects can escalate to more severe complications, including nausea, confusion, and even loss of consciousness.
The danger lies in the fact that CO competes with oxygen in the bloodstream, reducing the amount of oxygen that reaches vital organs. In extreme cases, where exposure is prolonged or concentrations are exceptionally high, CO poisoning can be fatal.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to operate a portable generator in well-ventilated areas, preferably outdoors. Avoiding the use of generators in enclosed spaces such as garages or basements is a fundamental safety measure. Proper ventilation allows the dispersal of CO, reducing the concentration to levels that are not harmful to human health.
Dangers of Running a Portable Generator in the Garage
Portable generators can be lifesavers during power outages, providing a quick and convenient source of electricity. However, it’s crucial to exercise caution when using them.
Risks of Carbon Monoxide Exposure
One of the most significant dangers of running a portable generator in the garage is the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Generators emit this colorless, odorless gas, which can quickly accumulate in confined spaces. Even short exposure to high levels of carbon monoxide can lead to serious health issues or, in extreme cases, prove fatal.
Proper Ventilation is Key
To mitigate the risks, ensure proper ventilation when operating a generator. Garages typically lack the ventilation needed to disperse carbon monoxide effectively. Always position the generator in an open area, away from doors and windows, to allow for adequate air circulation.
Fire Hazards
Another peril associated with running generators in the garage is the heightened risk of fire hazards. Generators produce heat during operation, and if placed on flammable surfaces or near combustible materials, the potential for a fire outbreak increases substantially.
Electrical Safety
Improper use of extension cords or overloading the generator poses an additional threat. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding electrical connections and never exceed the generator’s capacity to prevent overheating and potential electrical fires.
Fuel Storage Risks
Improper storage of generator fuel in the garage introduces another layer of risk. Spills and leaks can occur, leading to flammable liquid pooling in the vicinity of the generator. This significantly increases the chances of a fire outbreak and underscores the importance of storing fuel in a separate, well-ventilated location away from potential ignition sources.
Noise Pollution Concerns
While not directly harmful, the noise generated by portable generators can be a concern, especially in residential areas. Operating a generator in the garage may disturb neighbors and violate local noise regulations. Consideration of noise levels and adhering to any community guidelines is essential to maintain a harmonious living environment.
Generator Theft
Running a generator in the garage can attract unwanted attention, increasing the risk of theft. Generators are valuable assets, and leaving them in plain sight may make them a target for opportunistic thieves. Secure your generator when not in use, either by storing it in a locked area or using anti-theft devices to deter potential theft.
Long-Term Engine Damage
Continuous operation of a generator in an enclosed space can lead to overheating and long-term damage to the engine. Lack of proper airflow and ventilation may cause the generator to work harder than necessary, reducing its lifespan and efficiency. Regular maintenance checks and adherence to usage guidelines are crucial to ensuring the generator’s longevity.
Adverse Effects on Health
Extended exposure to the noise and vibration of a running generator in a confined space may have adverse effects on your health. These can include increased stress, sleep disturbances, and even hearing damage. Consider using noise-reducing measures and taking breaks away from the generator to minimize these potential health risks.
While portable generators offer a reliable power source, it’s vital to be aware of the diverse risks associated with their operation in the garage. Prioritize safety measures, follow guidelines meticulously, and remain vigilant to mitigate potential dangers. Understanding these risks equips you to make informed decisions, ensuring the safe and effective use of portable generators.
How to Run a Generator Safely in Garage?
When it comes to powering your home during an outage, a generator can be a lifesaver. However, safety is paramount, especially when running a generator in confined spaces like a garage. Here’s a guide on how to ensure a safe operation.
1. Ventilation is Key:
- Open the Garage Door: Before starting the generator, ensure the garage door is fully open to allow for proper ventilation.
- Use a Fan: If possible, place a fan near the entrance to enhance airflow and prevent the buildup of exhaust gases.
2. Location Matters:
- Position the Generator Outside: If feasible, run the generator outside the garage to minimize the risk of carbon monoxide buildup.
- Keep a Safe Distance: Place the generator at least 20 feet away from the garage to reduce the likelihood of harmful fumes entering the space.
3. Carbon Monoxide Detectors:
- Install Detectors: Have a working carbon monoxide detector installed in the garage to provide an early warning if gas levels become unsafe.
- Regular Checks: Test the detector regularly and replace batteries as needed to ensure continuous functionality.
4. Generator Maintenance:
- Regular Inspections: Perform routine checks on the generator to ensure it’s in good working condition.
- Exhaust System Inspection: Regularly inspect the exhaust system for leaks or damage, addressing any issues promptly.
5. Avoid Overloading:
- Check Wattage Limits: Be aware of the generator’s wattage capacity and avoid overloading it with too many appliances.
- Prioritize Essentials: Only connect essential appliances to the generator to prevent strain on the system.
While it is not recommended to run a generator in a garage due to the potential hazards associated with carbon monoxide, following these safety tips can help mitigate risks if you find yourself in a situation where it’s necessary. Always prioritize safety and explore alternative options when possible.
How to Properly Place a Generator?
When it comes to ensuring the efficiency and safety of a generator, proper placement plays a pivotal role. Incorrectly positioning a generator can lead to performance issues and even safety hazards.
1. Outdoor Placement
Generators designed for outdoor use should be installed in a location shielded from direct sunlight and harsh weather conditions. This safeguards the equipment from potential damage and extends its operational life.
Remember to elevate the generator slightly above ground level to prevent water ingress during heavy rains. Adequate drainage around the area is essential to avoid water pooling, minimizing the risk of electrical malfunctions.
2. Choose a Stable Ground
Begin by selecting a location with stable ground. A level surface is crucial to prevent any potential issues with the generator’s operation and stability.
2. Provide Adequate Ventilation
Ensure that the generator has sufficient ventilation. Generators emit exhaust fumes, and proper airflow is essential to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
3. Keep it Sheltered
While generators are designed to withstand various weather conditions, it’s advisable to provide some form of shelter or cover. This protects the equipment from direct exposure to rain, snow, or excessive sunlight, prolonging its lifespan.
4. Maintain Accessibility
Consider the accessibility of the generator. It’s vital for maintenance purposes and in case of emergencies. Ensure there’s enough space around the generator for technicians to perform routine checks or repairs.
Remember, the right placement not only ensures the generator operates at its best but also contributes to the safety of your property and those around it.
How to Properly Store a Generator when Not in Use?
When your generator isn’t in use, proper storage is crucial for maintaining its longevity and ensuring it’s ready when needed. Follow these guidelines to store your generator effectively:
- Clean Before Storage:
- Remove dirt and debris to prevent corrosion.
- Wipe down the generator with a clean, dry cloth.
- Fuel Considerations:
- Add a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel deterioration during storage.
- Run the generator until it’s out of fuel or drain the tank if storing for an extended period.
- Oil Maintenance:
- Change the oil before storage to prevent contaminants.
- Use high-quality oil with the recommended viscosity.
- Battery Care:
- Disconnect the battery to prevent discharge.
- Store it in a cool, dry place, periodically checking its charge level.
- Ventilation:
- Store the generator in a well-ventilated area to prevent fumes buildup.
- Consider using a generator storage cover to protect it from dust and moisture.
- Secure Location:
- Choose a location that is dry and sheltered from the elements.
- Elevate the generator to avoid contact with the ground and potential moisture.
- Regular Inspection:
- Conduct periodic checks during storage to ensure everything remains in optimal condition.
- Address any issues promptly to prevent long-term damage.
Remember, proper storage not only ensures your generator’s reliability but also contributes to its overall safety and performance when you need it most.
Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
Generators are indispensable during power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply. However, users may encounter issues that hinder their optimal performance. Below is a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot common generator issues and restore seamless operation.
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Engine Fails to Start | – Silent operation | – Check fuel levels and ensure there’s an adequate supply. |
| – Starter motor cranks but fails to ignite | – Inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or wear. Replace if necessary. | |
| – Strong smell of gasoline | – Examine the carburetor for blockages and clean or replace if needed. | |
| 2. Low Power Output | – Dimming lights and fluctuating power output | – Verify the load capacity and ensure it doesn’t exceed the generator’s limit. |
| – Appliances not running at full capacity | – Inspect the voltage regulator for malfunctions and replace if necessary. | |
| 3. Generator Overheating | – Unusual heat emanating from the generator | – Check the cooling system, including the radiator and coolant levels. Clean or replace components as required. |
| – Frequent shutdowns due to overheating | – Ensure proper ventilation around the generator and clean any debris obstructing airflow. | |
| 4. Excessive Noise Levels | – Unusual or loud sounds during operation | – Inspect the muffler for damage and replace if needed. Adjust engine RPM to recommended levels. |
| – Vibrations and rattling noises | – Tighten any loose bolts and secure all components properly. | |
| 5. Electric Shock from Generator | – Users experiencing electric shocks | – Immediately disconnect the generator from the power source. Inspect and repair any damaged wiring or outlets. |
| – Tingling sensation when touching the generator | – Check for grounding issues and ensure the generator is properly grounded. | |
| 6. Smoke Emission | – Visible smoke during operation | – Examine the oil level and quality. Change oil if it appears dirty or insufficient. |
| – Unpleasant burning smell | – Inspect the air filter for clogs and replace if necessary. | |
| 7. Fuel Leaks | – Noticeable fuel odors or wet spots around the generator | – Check the fuel lines and connections for leaks. Replace any damaged components. |
| – Decreased fuel efficiency | – Tighten loose fuel fittings and ensure the fuel tank is securely sealed. | |
| 8. Battery Issues | – Difficulty starting the generator | – Inspect the battery for corrosion or loose connections. Replace if necessary. |
| – Weak or dead battery | – Charge or replace the battery as needed. | |
| 9. Generator Running Rough | – Uneven or shaky operation – Check the air-fuel mixture; adjust the carburetor to ensure the correct ratio. Inspect for clogged fuel injectors. | – Fluctuating RPMs – Inspect the ignition system for issues. Replace faulty spark plugs or ignition coils as necessary. |
Addressing these common generator issues promptly will help maintain the reliability of your power source. If problems persist, consider seeking professional assistance for more complex diagnostics and repairs.
Generator Maintenance Tips
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, making a well-maintained generator crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply. Regular maintenance not only enhances longevity but also guarantees optimal performance. Here are some key tips to keep your generator in top shape:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct routine checks on your generator to identify any signs of wear, loose connections, or potential issues before they escalate.
- Fluid Levels: Regularly check and replenish the oil and fuel levels to guarantee efficient operation. Proper lubrication is essential for preventing friction-related damage.
- Battery Health: Ensure the generator’s battery is charged and in good condition. A healthy battery is vital for a swift start when power is needed.
- Air Filter Checks: Keep the generator’s air filter clean and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer. A clogged filter can compromise performance and fuel efficiency.
- Coolant System Inspection: Verify the coolant levels and inspect the system for leaks. Overheating can lead to severe damage, so maintaining the right coolant levels is crucial.
- Capacitor Maintenance: Check and test the generator’s capacitors regularly. Faulty capacitors can lead to electrical issues, affecting the generator’s ability to produce a consistent power output.
- Run the Generator Regularly: Regularly starting the generator, even if it’s not in use, helps keep the engine components lubricated and prevents fuel system issues.
- Storage Considerations: If the generator is stored for an extended period, use a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel deterioration. Empty the fuel tank or run the generator dry before storage to avoid gumming.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, you’ll ensure that your generator is ready to provide reliable power when you need it the most.
Generator Safety Tips
Generators are indispensable for providing power during outages, but ensuring their safe operation is paramount. Here are essential Generator Safety Tips to keep in mind:
- Proper Ventilation: Always operate generators in well-ventilated areas to prevent the buildup of harmful gases like carbon monoxide.
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific generator model to understand its unique safety requirements.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks on the generator, including fuel lines, filters, and oil levels, to guarantee optimal performance and identify potential issues early.
- Keep Flammable Materials Away: Position the generator away from flammable materials to reduce the risk of fire hazards.
- Carbon Monoxide Alarms: Install and regularly test carbon monoxide detectors near the generator area to provide an early warning of any dangerous gas levels.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of the generator to prevent electrical shocks and protect both the equipment and users.
- Fuel Safety: Store fuel in approved containers, away from heat sources, and follow guidelines for proper storage to avoid spills and contamination.
- Emergency Shutdown: Understand and practice the emergency shutdown procedures to swiftly respond to potential dangers.
- Children and Pets: Keep children and pets away from the generator during operation to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Avoid Overloading: Respect the generator’s rated capacity and avoid overloading it to maintain efficient and safe operation.
- Cooling Time: Allow the generator to cool down before refueling to prevent accidental fires or burns. Follow the recommended cooldown period specified in the manual.
- Secure Placement: Place the generator on a stable, flat surface to prevent tipping and ensure safe operation. Avoid placing it on uneven or sloped terrain.
- Regular Testing: Periodically run the generator to ensure it starts easily and operates smoothly. This practice helps identify potential issues before they become major problems during an emergency.
- Extension Cord Safety: If using extension cords, ensure they are of sufficient gauge for the load and in good condition. Overloading cords can lead to overheating and pose a fire risk.
- Weather Considerations: Shelter the generator from the elements to protect it from rain and snow. Use appropriate covers or enclosures designed for your specific generator model.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule regular professional inspections to check for hidden issues and ensure all components are in good working order. This is especially important for standby generators.
- Emergency Services Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency shut-off switches and how to quickly contact relevant services in case of a malfunction or emergency.
- Storage Precautions: If the generator is not in use for an extended period, follow proper storage procedures. This includes draining the fuel, disconnecting the battery, and storing it in a dry, cool place.
- Educate Users: Ensure that anyone who may need to operate the generator is familiar with its safety features and operation. Provide clear instructions to prevent accidents caused by misuse.
- Legal Compliance: Be aware of and adhere to local regulations regarding generator usage, emissions, and noise levels. Non-compliance may result in fines or other penalties.
Remember, adhering to these Generator Safety Tips is crucial to ensure the reliable and secure use of your generator.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Can You Run a Portable Generator in the Garage underscores the vital importance of safety when operating generators. While the convenience of garage placement may seem appealing, it’s crucial to understand the potential dangers of carbon monoxide accumulation. Proper ventilation and the use of carbon monoxide detectors are non-negotiable safeguards.
As you consider generator placement, let this guide be your trusted resource, emphasizing the significance of safe operation. With careful planning and adherence to safety guidelines, you can harness the full potential of your portable generator without compromising the well-being of your household.
References
- Development of micro power generators–a review
- Renewable energy systems with photovoltaic power generators: Operation and modeling
- High-power generators for offshore wind turbines
- Nationwide assessment of potential output from wind-powered generators
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Use a Portable Generator in My Garage if It’s Well-Ventilated?
Generator placement in the garage necessitates careful consideration of ventilation. Adequate airflow is crucial to prevent dangerous accumulation of exhaust fumes. Consult local building codes and manufacturer guidelines to ensure safe operation and protect against carbon monoxide poisoning.
How Far Should I Place the Generator From the Walls in My Garage?
When considering the placement of a generator in a garage, it is important to ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the accumulation of dangerous fumes. Additionally, generators should be positioned at a safe distance from walls to reduce fire hazards and allow for proper airflow.
Is It Safe to Run a Generator in My Attached Garage?
The safety of running a generator in a garage depends on proper placement and ventilation. Careful consideration must be given to the potential risks associated with carbon monoxide buildup and fire hazards.
Can I Use a Portable Generator in My Garage if I Have a Carbon Monoxide Detector?
Using a portable generator in a garage, even if winterized, poses significant risks due to the potential accumulation of carbon monoxide. The use of a carbon monoxide detector is not sufficient to guarantee safety during power outages.
Are There Any Specific Safety Precautions I Need to Take When Running a Generator in the Garage During Winter?
Safety precautions must be taken when running a generator in the garage during winter. These include ensuring proper ventilation to prevent carbon monoxide buildup, keeping flammable materials away, and following manufacturer guidelines for safe operation.
Can you run a portable generator in the garage with the door open?
It is not advisable to run a portable generator in an enclosed space. However, if placed in an open area within a garage to protect it from the elements, ensure the garage door is fully open for proper ventilation. To prevent backfeed, it’s crucial to have a licensed electrician connect a building’s electrical system to the generator.
What happens if you put a generator in a garage?
Running a portable generator in an enclosed area, like a garage, is highly unsafe. The risk of excessive carbon monoxide fumes entering your home is significant. Even with the garage door open, the dangers persist, making it essential to avoid placing generators in enclosed spaces.
How much ventilation does a portable generator need?
To guarantee sufficient ventilation, maintain 3 to 4 feet of clear space around and above the generator. Avoid placing the generator outdoors if its proximity to doors, windows, and vents could allow carbon monoxide to enter and accumulate in occupied spaces.

