In times of power outages or when you need an additional power source, a portable generator can be a lifesaver. But how do you hookup a portable generator to your house? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to safely and effectively connect your portable generator to your home’s electrical system.
From selecting the right transfer switch to ensuring proper grounding and following safety protocols, we’ll cover it all. Get ready to gain the knowledge and confidence to harness the power of your portable generator and keep your home running smoothly during unexpected outages.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Critical Findings
- 2 What is a Portable Generator and How it Works?
- 3 How Do You Hookup A Portable Generator To Your House?
- 4 How Should I Connect My Generator?
- 5 Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
- 6 Generator Maintenance Tips
- 7 Generator Safety Tips
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 References
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
- 10.1 How much power can a portable generator provide?
- 10.2 Is it safe to use a portable generator indoors?
- 10.3 How long does a portable generator typically run?
- 10.4 What type of fuel does a portable generator use?
- 10.5 Does a portable generator require regular maintenance?
- 10.6 What is the best way to hook up a portable generator to your house?
- 10.7 Do I need an electrician to hook up a portable generator?
- 10.8 How to hook up a generator to your house without a transfer switch?
Critical Findings
- Safety First: Prioritize safety measures when connecting a portable generator to your house. Use a transfer switch to prevent backfeeding and ensure the generator is properly grounded.
- Select the Right Generator Size: Determine the wattage requirements of essential appliances and systems in your home to choose a generator with an adequate capacity. A generator that’s too small may not power all necessary devices.
- Proper Connection Points: Identify the appropriate connection points, typically an exterior power inlet box and a transfer switch. Install them according to local codes and guidelines to ensure a secure connection.
- Fuel Source and Storage: Determine the type of fuel your generator uses (e.g., gasoline, propane, natural gas) and ensure you have a sufficient and safe storage solution in place.
- Regular Maintenance and Testing: Conduct routine maintenance checks on your generator, including oil changes, fuel level monitoring, and starter battery checks. Periodically run the generator to ensure it’s in good working condition.
What is a Portable Generator and How it Works?
A portable generator is a compact and movable power solution that converts fuel, such as gasoline or propane, into electricity. Unlike stationary generators, which are typically installed permanently, portable generators are mobile and can be easily transported to different locations. This flexibility makes them ideal for camping trips, outdoor events, or as a backup power source during emergencies.
Portable generators typically come equipped with essential features such as multiple power outlets, circuit breakers, and fuel gauges. Some advanced models may include inverter technology for stable and clean power output, ensuring the safe operation of sensitive electronics like laptops and smartphones.
At the core of a portable generator is an internal combustion engine that drives an alternator to generate electricity. The process begins with the combustion of fuel within the engine, creating mechanical energy. This energy is then converted into electrical energy through the alternator, which produces an electric current. The generated electricity is channeled through outlets on the generator, allowing users to connect their devices or appliances.

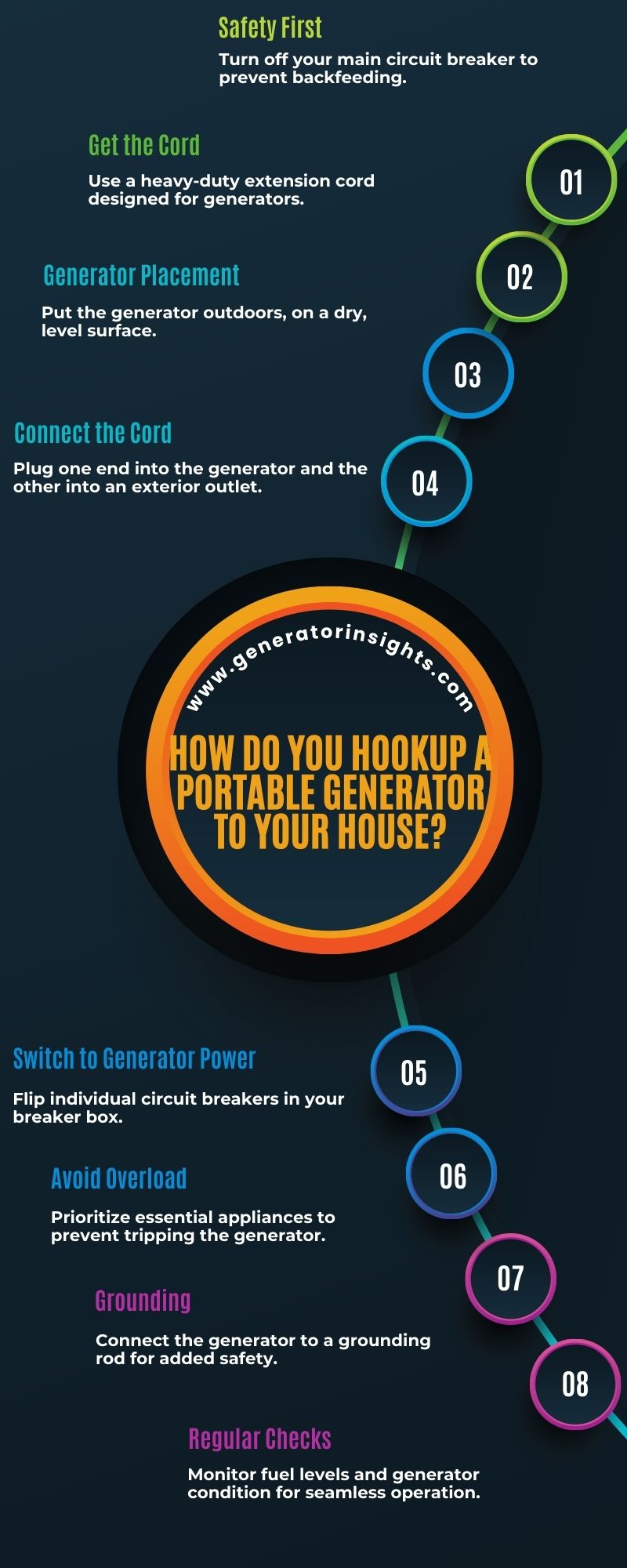
How Do You Hookup A Portable Generator To Your House?
When it comes to ensuring a seamless power supply during outages or emergencies, connecting a portable generator to your house is a valuable skill. Follow these steps for a safe and effective hookup.
- Safety First:
- Before anything else, prioritize safety. Turn off the main circuit breaker to avoid backfeeding electricity into the grid.
- Ensure the generator is placed in a well-ventilated area to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
- Select the Right Generator:
- Determine your power needs. Choose a generator with the appropriate wattage for your household requirements.
- Ensure the generator has the right outlets, including 120V and 240V options.
- Use a Transfer Switch:
- Invest in a transfer switch for a secure connection. This prevents electricity from flowing back into the grid and protects utility workers.
- Connect the generator to the transfer switch using the provided cables.
- Connection Process:
- Start by turning off all circuits in the main electrical panel. This prevents overload when the generator is powering your home.
- Connect the generator to the transfer switch using a dedicated power cord.
- Grounding:
- Proper grounding is crucial. Connect the generator to a grounding rod with a grounding wire.
- This reduces the risk of electrical shock and ensures the safe dissipation of excess electricity.
- Testing:
- Before an actual outage, test your setup. Start the generator and check if power is successfully transferred to your home.
- Identify any issues during testing and address them promptly.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Perform routine maintenance on your generator. This includes oil changes, air filter checks, and ensuring all connections are secure.
- A well-maintained generator is more reliable during emergencies.
Remember, safety and adherence to local codes are paramount when setting up a generator. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines and consider seeking professional advice if needed.
Now let’s discuss this whole process in detail.
Choose the Right Generator
Choosing the right generator is essential for successfully connecting a portable generator to one’s house. When deciding which generator to purchase, there are several factors to consider. Size is an important factor as it must be able to accommodate the amount of wattage needed for powering your home.
Fuel selection is another factor, as some generators use gasoline while others run on diesel or propane. Additionally, buying tips such as researching reviews and warranties should be taken into account prior to purchasing a portable generator. It is also beneficial to select a model that has low noise output and long running times, so that it does not disturb neighbors or require frequent refueling.
With these considerations in mind, one can make an informed decision when selecting the best portable generator for their home’s needs. After selecting the appropriate model, one can then move onto the next step: preparing their house for installation.
Prepare Your Home
Begin by identifying a suitable location for the generator, preferably outdoors in a well-ventilated area. Make sure it’s placed on a stable, level surface to prevent any accidents. Before connecting the generator, inspect its power cord for any damages and use a heavy-duty extension cord if necessary.
Safety measures should be a top priority. Install a carbon monoxide detector near the generator to monitor gas levels. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the generator’s manual to understand its features and specifications. It’s essential to have a clear understanding of the wattage requirements of your appliances to avoid overloading the generator. Labeling your circuit breakers and turning off the main breaker before connecting the generator can prevent backfeeding, safeguarding both your home and the utility lines.
Use a Transfer Switch
Investing in a transfer switch is a critical aspect of setting up a portable generator to power your house safely and effectively. The transfer switch serves as a vital intermediary between your home’s electrical panel and the generator, ensuring a secure connection during power outages. This device is indispensable for preventing electricity from flowing back into the grid, a situation known as backfeeding, which not only jeopardizes the safety of your household but can also pose a significant risk to utility workers trying to restore power.
To initiate this connection, carefully follow these steps:
- Purchase a Quality Transfer Switch: When investing in a transfer switch, prioritize quality and reliability. Choose a switch that matches the power requirements of your generator and has the appropriate features for seamless operation.
- Proper Installation: Mount the transfer switch in close proximity to your main electrical panel. This facilitates a straightforward connection between the generator and the switch. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions meticulously to ensure correct installation.
- Connect the Generator: Use the cables provided by the generator manufacturer to establish a secure connection between the generator and the transfer switch. The transfer switch essentially acts as a bridge, allowing you to selectively power essential circuits in your home.
Complete the Connection Process
Before delving into the connection process, prioritize safety measures. Turn off all circuits in the main electrical panel to prevent any potential overload. This step is crucial to avoid damage to the generator and ensure a smooth transition to backup power.
- Main Power Disconnect: If your generator doesn’t have an electric start, ensure that the main power is disconnected before starting the generator. This prevents any potential issues and ensures a safe startup.
- Dedicated Power Cord: Connect the generator to the transfer switch using a dedicated power cord. This cord is specifically designed for this purpose, and its use is paramount in maintaining a secure and stable electrical connection.
- Automatic or Manual Transfer: Depending on the type of transfer switch, it might offer automatic or manual transfer options. Automatic transfer switches can sense a power outage and switch to generator power seamlessly, while manual switches require you to initiate the transfer.
Install Grounding Rod and Wire
- Select a Suitable Grounding Rod:
- Choose a corrosion-resistant grounding rod, preferably copper or copper-plated.
- Ensure the rod’s length is sufficient to reach a depth that provides effective grounding.
- Connect the Grounding Wire:
- Use a grounding wire suitable for the generator’s power capacity.
- Attach one end of the wire securely to the grounding terminal on the generator.
- Attach the Wire to the Grounding Rod:
- Connect the other end of the grounding wire securely to the grounding rod.
- Ensure a tight and reliable connection to facilitate efficient grounding.
- Location Consideration:
- Place the grounding rod in a location where it can establish good contact with moist soil.
- Avoid areas with poor soil conductivity, such as rocky or sandy terrain.
- Regular Inspection:
- Periodically inspect the grounding system to ensure all connections are tight and free from corrosion.
- Promptly address any signs of wear or damage to maintain the effectiveness of the grounding.
By following these steps, you establish a proper grounding system for your generator, contributing to a safer and more reliable setup.
Test the Generator Setup
After completing the grounding and making the necessary connections, it’s crucial to test your generator setup to ensure it functions as intended. Here are the steps for testing:
- Turn Off Main Circuits:
- Before testing, turn off all circuits in the main electrical panel to prevent overloading when the generator powers your home.
- Start the Generator:
- Start the generator according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Allow it to run for a few minutes to stabilize.
- Transfer Switch Activation:
- If you have a transfer switch installed, ensure it is in the proper position for generator use.
- Activate the transfer switch to allow the generator to supply power to your home.
- Monitor Power Supply:
- Inside your home, monitor the power supply. Check specific appliances and lights to confirm they are receiving power from the generator.
- Identify Issues:
- During the test, identify any issues or anomalies. This could include flickering lights, appliances not functioning, or unusual noises from the generator.
- If any problems arise, immediately shut down the generator and address the issues before further use.
- Check Voltage Output:
- Use a voltage meter to check the generator’s voltage output. Ensure it matches the required voltage for your appliances and electrical systems.
- Repeat Periodically:
- Perform these tests periodically, especially if the generator hasn’t been used for an extended period.
- Regular testing ensures the system is ready to provide power when needed during an outage.
By systematically testing your generator setup, you verify its reliability and address any issues before an actual power outage occurs. Always adhere to safety guidelines and consult the generator’s manual for specific testing procedures.
If interested you can read our guide on how to use a generator with a transfer switch. Moreover, if you do not have a transfer switch, you can read how to connect a portable generator to your house without a transfer switch here.
Install Smoke Detectors
Installing smoke detectors in areas with combustible engine-powered generators is an important safety measure to prevent the potential risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Smoke detectors provide an early warning system for elevated levels of carbon monoxide, which can be fatal. Properly installing and maintaining smoke detectors can save lives.
When installing smoke detectors near a generator, it is important to ensure proper ventilation by keeping windows and doors open or using a fan to keep air circulating.
The detector should be placed on the ceiling in accordance with local building codes and not too close to the generator exhaust vent. Carbon monoxide alarms should also be installed in all rooms that are connected to the generator exhaust system, even if they are located far from the generator itself.
In addition, it is important that all wiring connections are secure and grounded properly. It is also necessary to check for any gas leaks before operating a generator inside a building or near any living space.
Taking these precautions will help reduce the risk of fire or explosion due to improper installation or maintenance of smoke detectors near combustible engine-powered generators. By following these steps, one can ensure their safety while using a portable generator at home or elsewhere.
Monitor the Generator
Monitoring the generator is essential to ensure safe and optimal performance, using a visual metaphor to emphasize the importance of such an action. Paying close attention to power monitoring, fuel consumption, and temperature of the generator are all critical components in keeping it functioning correctly.
- Power Monitoring: Regularly checking the wattage being supplied by the generator is key for ensuring that it does not exceed its maximum output capacity. This can be done with a multimeter or an inverter/charger system that has built-in metering capabilities.
- Fuel Consumption: Keeping track of how much fuel is being consumed is important for both safety and efficiency reasons. This can be accomplished by measuring the level of fuel in storage tanks with a dipstick or gauging system, as well as monitoring any changes in engine speed and idle time associated with fuel consumption.
- Temperature: Heat buildup inside a generator can cause irreparable damage if left unchecked, so it’s important to monitor engine temperatures on a regular basis. This can be done either manually or via an automated system that monitors temperature levels through sensors placed throughout the engine compartment.
Adhering to these guidelines will help maximize the lifespan of your portable generator while avoiding costly repairs due to preventable damages caused by inadequate maintenance.
It’s also important to follow safety measures when handling any type of equipment powered by combustion engines; always read and adhere to manufacturer instructions before attempting any repair work yourself.
How Should I Connect My Generator?
When it comes to powering your home during outages, connecting your generator properly is crucial. Let’s delve into various methods, highlighting the pros and cons of each:
| Method | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer Switch | A transfer switch is a dedicated electrical device that connects your generator to the main electrical panel. | – Seamless transition during power outages | – Professional installation required |
| – Allows selective powering of essential circuits | – Higher upfront cost | ||
| – Enhances safety by preventing backfeeding | |||
| Interlock Kit | An alternative to the transfer switch, an interlock kit modifies the existing panel to allow safe generator use. | – Cost-effective solution | – Limited to specific panel models |
| – Avoids risk of backfeeding | – Requires professional installation | ||
| Generator Cord | Using a heavy-duty generator cord to connect appliances directly to the generator. | – Simple and cost-effective | – Limited to powering specific appliances |
| – No installation required | – Manual switching of appliances necessary | ||
| Extension Cords | For temporary connections, outdoor-rated extension cords can be used to power individual devices. | – Easy setup and flexibility | – Limited range and capacity |
| – Budget-friendly option | – Not suitable for whole-house power |
Remember, the right choice depends on your specific needs, budget, and the level of convenience you’re looking for in powering your home with a generator. Always prioritize safety and follow manufacturer guidelines.
Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
Generators are indispensable during power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply. However, users may encounter issues that hinder their optimal performance. Below is a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot common generator issues and restore seamless operation.
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Engine Fails to Start | – Silent operation | – Check fuel levels and ensure there’s an adequate supply. |
| – Starter motor cranks but fails to ignite | – Inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or wear. Replace if necessary. | |
| – Strong smell of gasoline | – Examine the carburetor for blockages and clean or replace if needed. | |
| 2. Low Power Output | – Dimming lights and fluctuating power output | – Verify the load capacity and ensure it doesn’t exceed the generator’s limit. |
| – Appliances not running at full capacity | – Inspect the voltage regulator for malfunctions and replace if necessary. | |
| 3. Generator Overheating | – Unusual heat emanating from the generator | – Check the cooling system, including the radiator and coolant levels. Clean or replace components as required. |
| – Frequent shutdowns due to overheating | – Ensure proper ventilation around the generator and clean any debris obstructing airflow. | |
| 4. Excessive Noise Levels | – Unusual or loud sounds during operation | – Inspect the muffler for damage and replace if needed. Adjust engine RPM to recommended levels. |
| – Vibrations and rattling noises | – Tighten any loose bolts and secure all components properly. | |
| 5. Electric Shock from Generator | – Users experiencing electric shocks | – Immediately disconnect the generator from the power source. Inspect and repair any damaged wiring or outlets. |
| – Tingling sensation when touching the generator | – Check for grounding issues and ensure the generator is properly grounded. | |
| 6. Smoke Emission | – Visible smoke during operation | – Examine the oil level and quality. Change oil if it appears dirty or insufficient. |
| – Unpleasant burning smell | – Inspect the air filter for clogs and replace if necessary. | |
| 7. Fuel Leaks | – Noticeable fuel odors or wet spots around the generator | – Check the fuel lines and connections for leaks. Replace any damaged components. |
| – Decreased fuel efficiency | – Tighten loose fuel fittings and ensure the fuel tank is securely sealed. | |
| 8. Battery Issues | – Difficulty starting the generator | – Inspect the battery for corrosion or loose connections. Replace if necessary. |
| – Weak or dead battery | – Charge or replace the battery as needed. | |
| 9. Generator Running Rough | – Uneven or shaky operation – Check the air-fuel mixture; adjust the carburetor to ensure the correct ratio. Inspect for clogged fuel injectors. | – Fluctuating RPMs – Inspect the ignition system for issues. Replace faulty spark plugs or ignition coils as necessary. |
Addressing these common generator issues promptly will help maintain the reliability of your power source. If problems persist, consider seeking professional assistance for more complex diagnostics and repairs.
Generator Maintenance Tips
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, making a well-maintained generator crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply. Regular maintenance not only enhances longevity but also guarantees optimal performance. Here are some key tips to keep your generator in top shape:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct routine checks on your generator to identify any signs of wear, loose connections, or potential issues before they escalate.
- Fluid Levels: Regularly check and replenish the oil and fuel levels to guarantee efficient operation. Proper lubrication is essential for preventing friction-related damage.
- Battery Health: Ensure the generator’s battery is charged and in good condition. A healthy battery is vital for a swift start when power is needed.
- Air Filter Checks: Keep the generator’s air filter clean and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer. A clogged filter can compromise performance and fuel efficiency.
- Coolant System Inspection: Verify the coolant levels and inspect the system for leaks. Overheating can lead to severe damage, so maintaining the right coolant levels is crucial.
- Capacitor Maintenance: Check and test the generator’s capacitors regularly. Faulty capacitors can lead to electrical issues, affecting the generator’s ability to produce a consistent power output.
- Run the Generator Regularly: Regularly starting the generator, even if it’s not in use, helps keep the engine components lubricated and prevents fuel system issues.
- Storage Considerations: If the generator is stored for an extended period, use a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel deterioration. Empty the fuel tank or run the generator dry before storage to avoid gumming.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, you’ll ensure that your generator is ready to provide reliable power when you need it the most.
Generator Safety Tips
Generators are indispensable for providing power during outages, but ensuring their safe operation is paramount. Here are essential Generator Safety Tips to keep in mind:
- Proper Ventilation: Always operate generators in well-ventilated areas to prevent the buildup of harmful gases like carbon monoxide.
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific generator model to understand its unique safety requirements.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks on the generator, including fuel lines, filters, and oil levels, to guarantee optimal performance and identify potential issues early.
- Keep Flammable Materials Away: Position the generator away from flammable materials to reduce the risk of fire hazards.
- Carbon Monoxide Alarms: Install and regularly test carbon monoxide detectors near the generator area to provide an early warning of any dangerous gas levels.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of the generator to prevent electrical shocks and protect both the equipment and users.
- Fuel Safety: Store fuel in approved containers, away from heat sources, and follow guidelines for proper storage to avoid spills and contamination.
- Emergency Shutdown: Understand and practice the emergency shutdown procedures to swiftly respond to potential dangers.
- Children and Pets: Keep children and pets away from the generator during operation to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Avoid Overloading: Respect the generator’s rated capacity and avoid overloading it to maintain efficient and safe operation.
- Cooling Time: Allow the generator to cool down before refueling to prevent accidental fires or burns. Follow the recommended cooldown period specified in the manual.
- Secure Placement: Place the generator on a stable, flat surface to prevent tipping and ensure safe operation. Avoid placing it on uneven or sloped terrain.
- Regular Testing: Periodically run the generator to ensure it starts easily and operates smoothly. This practice helps identify potential issues before they become major problems during an emergency.
- Extension Cord Safety: If using extension cords, ensure they are of sufficient gauge for the load and in good condition. Overloading cords can lead to overheating and pose a fire risk.
- Weather Considerations: Shelter the generator from the elements to protect it from rain and snow. Use appropriate covers or enclosures designed for your specific generator model.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule regular professional inspections to check for hidden issues and ensure all components are in good working order. This is especially important for standby generators.
- Emergency Services Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency shut-off switches and how to quickly contact relevant services in case of a malfunction or emergency.
- Storage Precautions: If the generator is not in use for an extended period, follow proper storage procedures. This includes draining the fuel, disconnecting the battery, and storing it in a dry, cool place.
- Educate Users: Ensure that anyone who may need to operate the generator is familiar with its safety features and operation. Provide clear instructions to prevent accidents caused by misuse.
- Legal Compliance: Be aware of and adhere to local regulations regarding generator usage, emissions, and noise levels. Non-compliance may result in fines or other penalties.
Remember, adhering to these Generator Safety Tips is crucial to ensure the reliable and secure use of your generator.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knowing how do you hookup a portable generator to your house can provide peace of mind and ensure uninterrupted power supply during emergencies. By following the proper steps, such as selecting the appropriate transfer switch, ensuring proper grounding, and adhering to safety guidelines, you can safely connect your portable generator to your home’s electrical system.
Remember to consult a professional electrician if you are unsure or need assistance with the installation process. With the ability to seamlessly hookup a portable generator to your house, you can confidently navigate power outages and keep your essential appliances and devices running, providing comfort and convenience for you and your family.
References
- High-power generators for offshore wind turbines
- Nationwide assessment of potential output from wind-powered generators
- An electromagnetic, vibration-powered generator for intelligent sensor systems
- Electric generators and motors: An overview
Frequently Asked Questions
How much power can a portable generator provide?
Comparing generator models is important when reviewing wattage. Technical details such as size, power output, and fuel consumption should be considered for the best fit. Establishing a connection to the home requires knowledge that goes beyond general specs in order to create an inviting atmosphere of belonging.
Is it safe to use a portable generator indoors?
It is not recommended to use a portable generator indoors due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning and potential cordless connections causing electrical safety hazards. Portable generators should be used in well-ventilated areas outdoors, for optimal safety.
How long does a portable generator typically run?
A portable generator typically runs for a few hours, depending on the size and fuel type. It must be connected to the house with connecting cables and have sufficient fuel stored in order to provide long-term power. It is important to maintain proper connections and fuel levels for optimal running time.
What type of fuel does a portable generator use?
Despite the convenience of installing fuel for a portable generator, it is important to choose the right type of fuel. Popular options include gas, propane, and diesel; however, each have their own advantages and disadvantages when it comes to cost, availability, and environmental impact. Knowing which one best suits your needs is essential for long-term use.
Does a portable generator require regular maintenance?
Yes, maintaining a portable generator requires regular upkeep in order to ensure safe operation. This includes checking fuel levels, inspecting for signs of wear and tear, and making sure the generator is properly ventilated when in use. Additionally, using extension cords can help protect the generator against overloading.
What is the best way to hook up a portable generator to your house?
Two methods are commonly used for connecting a portable gas generator to a home. The first involves plugging individual appliances using separate cords, while the second method powers a circuit panel through a transfer switch.
Do I need an electrician to hook up a portable generator?
During a power outage, individuals can connect their portable generator to an outdoor outlet linked, through the house, to a transfer switch. Typically, an electrician installs the transfer switch, usually positioned beside the main circuit breaker panel.
How to hook up a generator to your house without a transfer switch?
An uncomplicated approach to powering appliances from a generator without a transfer switch is to use extension cords. Users can connect one end to the generator and plug their appliances into the other end.

