In a world where unforeseen events can disrupt our daily lives, safeguarding essential equipment becomes paramount. As we increasingly rely on generators to power our homes and businesses, the looming threat of electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) adds a layer of concern.
Picture this: you’ve invested in a reliable generator, a beacon of power in times of need. Now, imagine having the know-how to cocoon it from potential EMP havoc. Discovering how to protect a generator from EMP isn’t just about securing a machine; it’s about shielding the lifeline that connects us to light, warmth, and connectivity in the face of uncertainty.
Jump to a Specific Section
- 1 Main Highlights
- 2 What is EMP?
- 3 How Does EMP Affect a Generator?
- 4 How to Protect a Generator from EMP?
- 5 Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
- 6 Generator Maintenance Tips
- 7 Generator Safety Tips
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 References
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
- 10.1 Can a Faraday cage protect my generator from an EMP?
- 10.2 How do I choose the right grounding method for my generator?
- 10.3 What are the most effective shielding materials to use for generator protection?
- 10.4 Are surge protectors necessary for protecting my generator from an EMP?
- 10.5 Should I disconnect my generator from power sources during an EMP event?
- 10.6 How do I protect my generator from an EMP attack?
- 10.7 Can a generator endure an EMP?
- 10.8 Will aluminum foil provide protection for electronics against an EMP?
Main Highlights
- Implement a disconnection strategy from power sources during an EMP event, such as using manual transfer switches and dedicated circuit breakers for the generator’s power supply.
- Regularly test and maintain the generator, including load tests, testing protective devices, inspecting and tightening wiring connections, and monitoring the fuel system.
- Stay informed and aware of EMP threats by monitoring government reports and publications, joining online communities or forums dedicated to emergency preparedness, and sharing knowledge and experiences related to protecting generators from EMP.
- Implement robust shielding mechanisms like Faraday cages or enclosures to protect generators and sensitive components from EMP damage, ensuring continued functionality during disruptive events.
What is EMP?
An Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP) is a burst of electromagnetic radiation, typically resulting from high-energy explosions, solar flares, or certain human-made devices. The impact of EMP on electronics lies in its ability to induce a surge of electric current in conductive systems, leading to potential damage or disruption. EMP protection is crucial for sensitive electronic equipment, as it helps safeguard against the destructive effects of these pulses.
In practical terms, this involves employing shielding materials and grounding techniques to minimize the risk of damage. Understanding the intricacies of EMP in electronics is pivotal for designing resilient systems that can withstand potential threats.
How Does EMP Affect a Generator?
EMP events, whether natural or man-made, can pose a significant threat to the functionality of these essential power sources. Generators, designed to provide reliable electricity, are susceptible to the disruptive influence of EMP. EMP, characterized by a sudden surge of electromagnetic radiation, has the potential to interfere with the delicate electronic components within a generator. The vulnerability lies in the sensitive circuitry and control systems that modern generators heavily rely on. When subjected to an EMP, these electronic components can experience damage or malfunction, jeopardizing the overall performance of the generator.
To comprehend how EMP affects a generator, it’s essential to delve into the intricate workings of its electronic systems. Generators commonly incorporate microprocessors, voltage regulators, and electronic control units to ensure seamless power output. The intense electromagnetic fields generated during an EMP event induce voltage and current surges in the electronic components, leading to a cascade of potential issues.
The delicate semiconductors within the generator’s circuitry may become overwhelmed, resulting in the breakdown of critical functions. This susceptibility underscores the importance of implementing protective measures, such as EMP shielding, to mitigate the risk of damage.
Thus, the impact of EMP on a generator is a critical consideration for those relying on uninterrupted power sources. Recognizing the vulnerabilities in electronic components and investing in robust protective measures are pivotal steps to safeguard the reliability of generators in the face of potential electromagnetic disturbances.

How to Protect a Generator from EMP?
When safeguarding your generator from electromagnetic pulses (EMPs), it’s crucial to implement measures that shield your equipment from potential damage. EMPs, whether natural or man-made, can disrupt electronic devices, making protection essential for ensuring your generator’s functionality. Here’s how to protect a generator from EMP:
- Enclosure with Faraday Cage:
- Build or Purchase: Construct an enclosure around your generator using conductive materials like copper or aluminum.
- Grounding: Ensure the enclosure is grounded effectively to dissipate EMP energy.
- Mesh Openings: Keep mesh openings smaller than the wavelength of the EMP for enhanced protection.
- EMP Filters:
- Installation: Integrate EMP filters or surge protectors into the generator’s electrical system.
- Rated Protection: Opt for filters with high EMP protection ratings to effectively block unwanted surges.
- Metallic Conduits for Wiring:
- Replace Standard Wiring: Swap out regular wiring with metallic conduits to create a shielded pathway.
- Minimize Gaps: Seal any gaps in conduits to prevent EMP penetration.
- Disconnect Antennas and Cables:
- Preemptive Measures: Before an expected EMP event, disconnect antennas and cables from the generator.
- Store Safely: Store disconnected parts in a protected location to avoid damage.
- EMP Hardened Electronics:
- Invest in Resilient Components: Purchase generator models with electronics specifically designed to withstand EMPs.
- Military-Grade Options: Explore military-grade generators known for their robust EMP resistance.
- Testing and Maintenance:
- Regular Checks: Conduct routine checks on your generator’s EMP protection measures.
- Simulation Tests: Consider simulated EMP tests to ensure the effectiveness of your protection setup.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of EMP damage to your generator and ensure it remains operational in the event of an electromagnetic pulse.
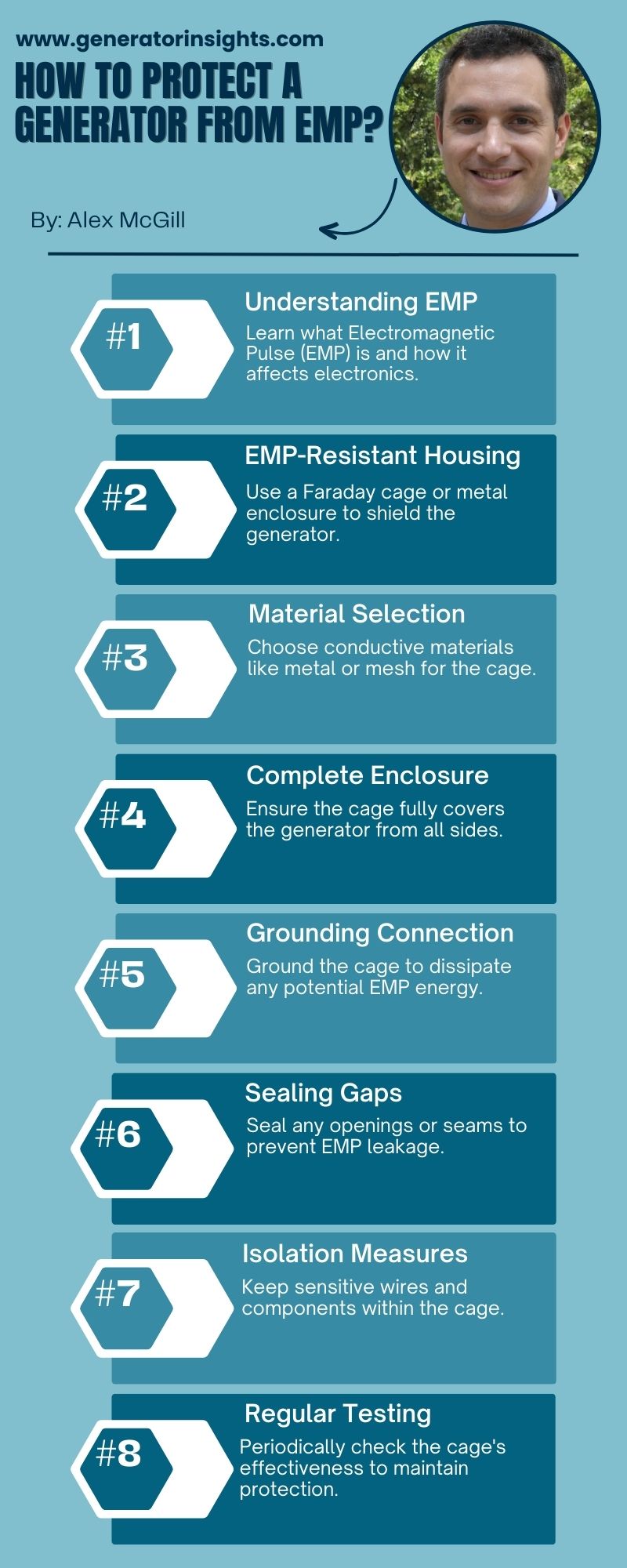
Now let’s discuss how to protect your generator from EMP in more detail.
Building an Enclosure with Faraday Cage
When it comes to safeguarding your generator from electromagnetic pulses (EMPs), constructing an enclosure with a Faraday cage is a highly effective measure. The Faraday cage acts as a protective shield by preventing EMP penetration and safeguarding the electronic components within. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how to implement this crucial step:
- Choosing the Right Materials: Select conductive materials such as copper or aluminum for building the enclosure. These materials are effective in creating a barrier that redirects and absorbs electromagnetic energy.
- Grounding for Enhanced Protection: Grounding the Faraday cage is essential for dissipating the absorbed EMP energy safely into the ground. Ensure a robust grounding system to maximize the protective capabilities of the cage.
- Mesh Openings and Size Considerations: The effectiveness of the Faraday cage relies on the size of the mesh openings. Keep the openings smaller than the wavelength of the EMP to ensure optimal protection. The smaller the openings, the better the cage can block electromagnetic waves.
- Sealing Gaps and Joints: To create a seamless shield against EMPs, it’s crucial to seal any gaps or joints in the enclosure. This prevents electromagnetic waves from finding their way into the protected space and compromising the generator.
By implementing these measures in building a Faraday cage around your generator, you create a robust defense against the potential damage caused by EMPs. This proactive approach ensures that your generator remains functional and reliable, even in the face of electromagnetic disturbances.
Integrating EMP Filters
To fortify your generator against the detrimental effects of electromagnetic pulses (EMPs), the integration of EMP filters is a crucial step. These filters act as a line of defense within the generator’s electrical system, mitigating the impact of EMP-induced surges. Here’s a comprehensive look at incorporating EMP filters into your generator setup:
- Strategic Installation: Install EMP filters strategically within the generator’s electrical circuit. Focus on key points, such as the input and output connections, where EMP surges are likely to enter or exit.
- Selection of High EMP Protection Ratings: Opt for EMP filters with high protection ratings. Look for filters specifically designed to withstand and divert the intense energy associated with EMPs. Higher protection ratings ensure a more resilient defense against electromagnetic interference.
- Compatibility with Generator Specifications: Ensure that the EMP filters chosen are compatible with the specifications of your generator. Consider factors such as voltage, current, and frequency to guarantee seamless integration without compromising the generator’s performance.
- Regular Maintenance and Testing: Incorporate regular maintenance checks for the EMP filters. Periodically inspect and test the filters to confirm their functionality. This proactive approach helps identify any potential issues and ensures the ongoing effectiveness of the EMP protection system.
By integrating EMP filters into your generator, you add an additional layer of defense against EMP-induced disturbances. These filters act as gatekeepers, preventing harmful surges from compromising the integrity of your generator’s electrical components. This strategic measure enhances the overall resilience of your generator in the face of electromagnetic threats.
Implementing Metallic Conduits for Wiring
When safeguarding your generator from electromagnetic pulses (EMPs), a key protective measure involves the implementation of metallic conduits for wiring. This step enhances the generator’s resilience by providing a shielded pathway for electrical currents. Here’s a detailed exploration of how to effectively implement metallic conduits for wiring:
- Replacement of Standard Wiring: Begin by replacing standard wiring with metallic conduits. The use of materials like copper or aluminum in conduits offers superior conductivity and acts as a barrier against EMP-induced interference.
- Sealing Gaps to Prevent Penetration: To maximize the effectiveness of the conduits, it’s crucial to seal any gaps along the wiring path. This prevents electromagnetic waves from penetrating the conduit and reaching the generator’s sensitive electronic components.
- Minimizing the Risk of EMP Penetration: Metallic conduits serve as a protective shield, minimizing the risk of EMP penetration. By creating a conductive pathway, these conduits help channel electrical currents while deflecting and grounding electromagnetic interference.
- Integration with Faraday Cage: For a comprehensive defense strategy, integrate the metallic conduits with the previously discussed Faraday cage. This ensures a holistic approach to protecting the generator, combining the shielding capabilities of both the cage and conduits.
By implementing metallic conduits for wiring, you establish a fortified pathway that shields the generator’s electrical system from EMP-induced disturbances. This integrated approach contributes to the overall resilience of your generator, enhancing its ability to withstand electromagnetic threats and ensuring reliable functionality when needed.
Disconnecting Antennas and Cables
An essential precautionary step in protecting your generator from electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) involves disconnecting antennas and cables. This proactive measure helps minimize the risk of EMP-induced damage to the generator’s electronic components. Here’s a detailed guide on implementing this safeguard:
- Timely Disconnection Before Expected EMP Events: In anticipation of anticipated EMP events, such as solar flares or potential geopolitical scenarios, proactively disconnect antennas and cables from the generator. This minimizes the chances of EMP-induced surges affecting the connected components.
- Strategic Storage of Disconnected Parts: Once antennas and cables are disconnected, store them in a protected location. This ensures that these components remain unexposed to potential EMP impacts and can be easily reconnected when needed.
- Reducing Conductive Paths: By disconnecting antennas and cables, you effectively reduce conductive paths that could act as channels for EMP energy to reach the generator. This interruption disrupts the potential flow of electromagnetic interference into the generator.
- Consideration for Portable Generators: For portable generators, emphasize the importance of disconnecting antennas and cables before storage or transport. This precautionary measure is especially relevant for generators that might be moved to different locations where environmental conditions can vary.
By conscientiously disconnecting antennas and cables, you add an extra layer of defense against EMP-induced risks. This precautionary step, when combined with other protective measures, contributes to a comprehensive strategy for safeguarding your generator and ensuring its reliability in the face of electromagnetic threats.
Opting for EMP-Hardened Electronics
Opting for EMP-hardened components ensures a higher level of resilience. Here’s an in-depth look at this key protective measure:
- Investing in Resilient Components: When purchasing a generator, prioritize models equipped with EMP-hardened electronics. These components are designed and tested to endure the intense energy and rapid changes associated with EMP events.
- Exploring Military-Grade Options: Military-grade generators are often engineered with a focus on EMP resistance. These generators undergo rigorous testing to meet stringent standards for electromagnetic resilience, making them a reliable choice for situations where EMP protection is paramount.
- Integrated Hardening Technologies: EMP-hardened electronics incorporate technologies that mitigate the impact of electromagnetic interference. This may include specialized coatings, shielding materials, and circuit designs optimized for EMP resilience.
- Application of EMP-Resistant Materials: Generators featuring EMP-hardened electronics are constructed with materials specifically chosen for their resistance to electromagnetic interference. These materials contribute to the overall robustness of the generator in the face of EMP events.
By opting for a generator with EMP-hardened electronics, you proactively elevate your defense against potential EMP-induced disruptions. This strategic investment ensures that your generator is equipped with components engineered to endure and maintain functionality even in the presence of electromagnetic pulses.
Testing and Maintenance for EMP Protection:
Ensuring the continued effectiveness of your generator’s protection against electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) requires a commitment to regular testing and maintenance. This proactive approach is essential for identifying vulnerabilities and maintaining the overall integrity of your EMP protection system. Here’s a comprehensive guide to incorporating testing and maintenance into your protective strategy:
- Regular Checks for Protection Measures: Conduct routine inspections of the EMP protection measures implemented for your generator. This includes verifying the integrity of the Faraday cage, inspecting EMP filters, and ensuring the proper functioning of metallic conduits.
- Simulation Tests for Effectiveness: Consider simulated EMP tests to gauge the effectiveness of your protection setup. Simulations can help identify potential weaknesses and areas for improvement in a controlled environment before facing a real EMP event.
- Addressing Wear and Tear: Over time, components of the EMP protection system may experience wear and tear. Regular maintenance involves addressing any signs of deterioration promptly, such as repairing damaged conduits, replacing worn-out filters, or reinforcing the Faraday cage as needed.
- Documentation of Maintenance Activities: Maintain comprehensive documentation of all maintenance activities performed on your generator’s EMP protection system. This documentation serves as a valuable reference and helps track the history of modifications, replacements, or upgrades.
By incorporating regular testing and maintenance into your routine, you ensure that your generator’s EMP protection measures remain robust and reliable. This commitment to proactive care contributes significantly to the overall resilience of your generator, offering peace of mind in the face of potential electromagnetic disturbances.
Troubleshooting Common Generator Issues
Generators are indispensable during power outages, ensuring a continuous power supply. However, users may encounter issues that hinder their optimal performance. Below is a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot common generator issues and restore seamless operation.
| Issue | Symptoms | Troubleshooting Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Engine Fails to Start | – Silent operation | – Check fuel levels and ensure there’s an adequate supply. |
| – Starter motor cranks but fails to ignite | – Inspect the spark plug for signs of damage or wear. Replace if necessary. | |
| – Strong smell of gasoline | – Examine the carburetor for blockages and clean or replace if needed. | |
| 2. Low Power Output | – Dimming lights and fluctuating power output | – Verify the load capacity and ensure it doesn’t exceed the generator’s limit. |
| – Appliances not running at full capacity | – Inspect the voltage regulator for malfunctions and replace if necessary. | |
| 3. Generator Overheating | – Unusual heat emanating from the generator | – Check the cooling system, including the radiator and coolant levels. Clean or replace components as required. |
| – Frequent shutdowns due to overheating | – Ensure proper ventilation around the generator and clean any debris obstructing airflow. | |
| 4. Excessive Noise Levels | – Unusual or loud sounds during operation | – Inspect the muffler for damage and replace if needed. Adjust engine RPM to recommended levels. |
| – Vibrations and rattling noises | – Tighten any loose bolts and secure all components properly. | |
| 5. Electric Shock from Generator | – Users experiencing electric shocks | – Immediately disconnect the generator from the power source. Inspect and repair any damaged wiring or outlets. |
| – Tingling sensation when touching the generator | – Check for grounding issues and ensure the generator is properly grounded. | |
| 6. Smoke Emission | – Visible smoke during operation | – Examine the oil level and quality. Change oil if it appears dirty or insufficient. |
| – Unpleasant burning smell | – Inspect the air filter for clogs and replace if necessary. | |
| 7. Fuel Leaks | – Noticeable fuel odors or wet spots around the generator | – Check the fuel lines and connections for leaks. Replace any damaged components. |
| – Decreased fuel efficiency | – Tighten loose fuel fittings and ensure the fuel tank is securely sealed. | |
| 8. Battery Issues | – Difficulty starting the generator | – Inspect the battery for corrosion or loose connections. Replace if necessary. |
| – Weak or dead battery | – Charge or replace the battery as needed. | |
| 9. Generator Running Rough | – Uneven or shaky operation – Check the air-fuel mixture; adjust the carburetor to ensure the correct ratio. Inspect for clogged fuel injectors. | – Fluctuating RPMs – Inspect the ignition system for issues. Replace faulty spark plugs or ignition coils as necessary. |
Addressing these common generator issues promptly will help maintain the reliability of your power source. If problems persist, consider seeking professional assistance for more complex diagnostics and repairs.
Generator Maintenance Tips
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, making a well-maintained generator crucial for ensuring a continuous power supply. Regular maintenance not only enhances longevity but also guarantees optimal performance. Here are some key tips to keep your generator in top shape:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct routine checks on your generator to identify any signs of wear, loose connections, or potential issues before they escalate.
- Fluid Levels: Regularly check and replenish the oil and fuel levels to guarantee efficient operation. Proper lubrication is essential for preventing friction-related damage.
- Battery Health: Ensure the generator’s battery is charged and in good condition. A healthy battery is vital for a swift start when power is needed.
- Air Filter Checks: Keep the generator’s air filter clean and replace it as recommended by the manufacturer. A clogged filter can compromise performance and fuel efficiency.
- Coolant System Inspection: Verify the coolant levels and inspect the system for leaks. Overheating can lead to severe damage, so maintaining the right coolant levels is crucial.
- Capacitor Maintenance: Check and test the generator’s capacitors regularly. Faulty capacitors can lead to electrical issues, affecting the generator’s ability to produce a consistent power output.
- Run the Generator Regularly: Regularly starting the generator, even if it’s not in use, helps keep the engine components lubricated and prevents fuel system issues.
- Storage Considerations: If the generator is stored for an extended period, use a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel deterioration. Empty the fuel tank or run the generator dry before storage to avoid gumming.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, you’ll ensure that your generator is ready to provide reliable power when you need it the most.
Generator Safety Tips
Generators are indispensable for providing power during outages, but ensuring their safe operation is paramount. Here are essential Generator Safety Tips to keep in mind:
- Proper Ventilation: Always operate generators in well-ventilated areas to prevent the buildup of harmful gases like carbon monoxide.
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific generator model to understand its unique safety requirements.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks on the generator, including fuel lines, filters, and oil levels, to guarantee optimal performance and identify potential issues early.
- Keep Flammable Materials Away: Position the generator away from flammable materials to reduce the risk of fire hazards.
- Carbon Monoxide Alarms: Install and regularly test carbon monoxide detectors near the generator area to provide an early warning of any dangerous gas levels.
- Grounding: Ensure proper grounding of the generator to prevent electrical shocks and protect both the equipment and users.
- Fuel Safety: Store fuel in approved containers, away from heat sources, and follow guidelines for proper storage to avoid spills and contamination.
- Emergency Shutdown: Understand and practice the emergency shutdown procedures to swiftly respond to potential dangers.
- Children and Pets: Keep children and pets away from the generator during operation to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Avoid Overloading: Respect the generator’s rated capacity and avoid overloading it to maintain efficient and safe operation.
- Cooling Time: Allow the generator to cool down before refueling to prevent accidental fires or burns. Follow the recommended cooldown period specified in the manual.
- Secure Placement: Place the generator on a stable, flat surface to prevent tipping and ensure safe operation. Avoid placing it on uneven or sloped terrain.
- Regular Testing: Periodically run the generator to ensure it starts easily and operates smoothly. This practice helps identify potential issues before they become major problems during an emergency.
- Extension Cord Safety: If using extension cords, ensure they are of sufficient gauge for the load and in good condition. Overloading cords can lead to overheating and pose a fire risk.
- Weather Considerations: Shelter the generator from the elements to protect it from rain and snow. Use appropriate covers or enclosures designed for your specific generator model.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule regular professional inspections to check for hidden issues and ensure all components are in good working order. This is especially important for standby generators.
- Emergency Services Awareness: Familiarize yourself with the location of emergency shut-off switches and how to quickly contact relevant services in case of a malfunction or emergency.
- Storage Precautions: If the generator is not in use for an extended period, follow proper storage procedures. This includes draining the fuel, disconnecting the battery, and storing it in a dry, cool place.
- Educate Users: Ensure that anyone who may need to operate the generator is familiar with its safety features and operation. Provide clear instructions to prevent accidents caused by misuse.
- Legal Compliance: Be aware of and adhere to local regulations regarding generator usage, emissions, and noise levels. Non-compliance may result in fines or other penalties.
Remember, adhering to these Generator Safety Tips is crucial to ensure the reliable and secure use of your generator.
Conclusion
In conclusion, How to Protect a Generator from EMP is your shield against the disruptive forces of electromagnetic pulses. By embracing a range of protective measures and fortifying vulnerable components, you ensure that your generator remains operational even in the face of EMP threats. The importance of safeguarding your power source cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts your ability to weather unforeseen challenges.
As you delve into the world of EMP protection, let this guide be your trusted ally, offering invaluable insights and empowering you to take proactive steps in securing your generator. With preparedness and knowledge, you can face the uncertainties of the future with confidence, knowing that your generator is well-guarded against potential EMP disruptions.
References
- Development of 500 W PEM fuel cell stack for portable power generators
- Modeling low-bandgap thermophotovoltaic diodes for high-efficiency portable power generators
- Biomechanical energy‐driven hybridized generator as a universal portable power source for smart/wearable electronics
- Portable fuel cell power generator
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Faraday cage protect my generator from an EMP?
The effectiveness of a Faraday cage in protecting a generator from EMP is a subject of debate. Generator maintenance and EMP preparedness are crucial considerations, but further research is needed to determine the viability of using a Faraday cage for protection.
How do I choose the right grounding method for my generator?
Grounding techniques for generator protection are crucial for EMP protection. Proper grounding ensures the dissipation of electrical charges and reduces the risk of damage. The choice of grounding method depends on factors such as soil resistivity, equipment specifications, and local regulations.
What are the most effective shielding materials to use for generator protection?
The shielding effectiveness of materials for generator protection varies depending on their composition and thickness. Best practices for generator grounding involve using conductive materials, such as copper or aluminum, to create a low-resistance path to dissipate electrical energy.
Are surge protectors necessary for protecting my generator from an EMP?
The importance of regular maintenance for generator protection against EMP cannot be overstated. While surge protectors are commonly believed to provide sufficient protection, they are not effective in shielding against the high-intensity electromagnetic pulses caused by an EMP event.
Should I disconnect my generator from power sources during an EMP event?
Running a generator during an EMP event can pose potential dangers. By leaving the generator connected to power sources, it may become vulnerable to damage due to electromagnetic pulses. Disconnecting the generator from power sources is advisable to protect it from EMP effects.
How do I protect my generator from an EMP attack?
Two primary methods exist for shielding inverters and portable generators. First, enclosing the inverter or generator in a conductive material proves effective, and EMP bags or EMP cloth are recommended for this purpose. Second, utilizing transient protection devices adds an extra layer of defense against EMP threats.
Can a generator endure an EMP?
Appliances like fireplaces, solar ovens, power tools, or generators remain unaffected by an EMP, provided that safety precautions are taken. These non-electric devices, operating without solid-state electronic controls, are likely to continue functioning even after an EMP event has occurred.
Will aluminum foil provide protection for electronics against an EMP?
A practical approach involves crafting a homemade Faraday cage using aluminum foil. By wrapping electronic devices in tin foil, individuals can enhance their defense against EMPs. This method serves as an effective means to shield against electromagnetic pulsed attacks.

